In France, cancer of the cervix affects nearly 3,000 women every year and is responsible for 1,100 deaths. This pathology is related to a persistent infection caused by viruses called “human papillomaviruses” (HPV), which are particularly transmitted during sexual intercourse. There are two simple and effective ways to prevent or overcome this cancer: HPV vaccination and Pap smears. The latter is recommended by the European Union for 70% of women. What is a Pap smear? Who should use it? Will it be reimbursed? We tell you everything you need to know about this preventive act that can save lives.
The Pap smear, what is it?
The Pap smear (or Pap smear) is a gynecological exam that can detect precancerous and cancerous lesions of the cervix. Specifically, it is a sample of cells taken from the cervix. The cells are then examined under a microscope, as part of a cytological examination. If they are abnormal, a Human Papilloma Virus-High Risk Test (HPV-HR) may be performed to look for the presence of HPV virus DNA.
The Pap smear can sometimes be unpleasant, but that’s about it painless and usually takes less than five minutes. This preventive act makes it possible to treat any precancerous lesions before they develop into cancer or to diagnose cancer at an early stage, increasing the chances of recovery. Cervical cancer screening has been part of an organized national program since 2018.
Who is affected by this screening test?
All asymptomatic women aged 25 to 65 years old and having a cervix are eligible for cervical cancer screening. This includes pregnant women, postmenopausal women and women who have been vaccinated against human papillomaviruses. In fact, the vaccine does not protect against all papillomaviruses.
Regardless of age, the absence of sexual intercourse is not exempt from regular Pap smear screening, the National Cancer Institute (INCa) recalls.
How often should a Pap smear be taken?
Cervical cancer screening is part of a national program that provides several methods depending on the age of the patients: [1]
- For women between the ages of 25 and 29 : the screening test is performed by cytological examination every 3 yearsafter two initial tests performed 1 year apart and with normal results.
- For ladies between 30 and 65 years: the High Authority of Health (HAS) recommends that the HPV test, which is more effective for these women, replace the cytological examination. Performed this test 3 years later the last cytological examination with a normal result. A new test has been done again every 5 yearsup to the age of 65, provided the test result is negative.
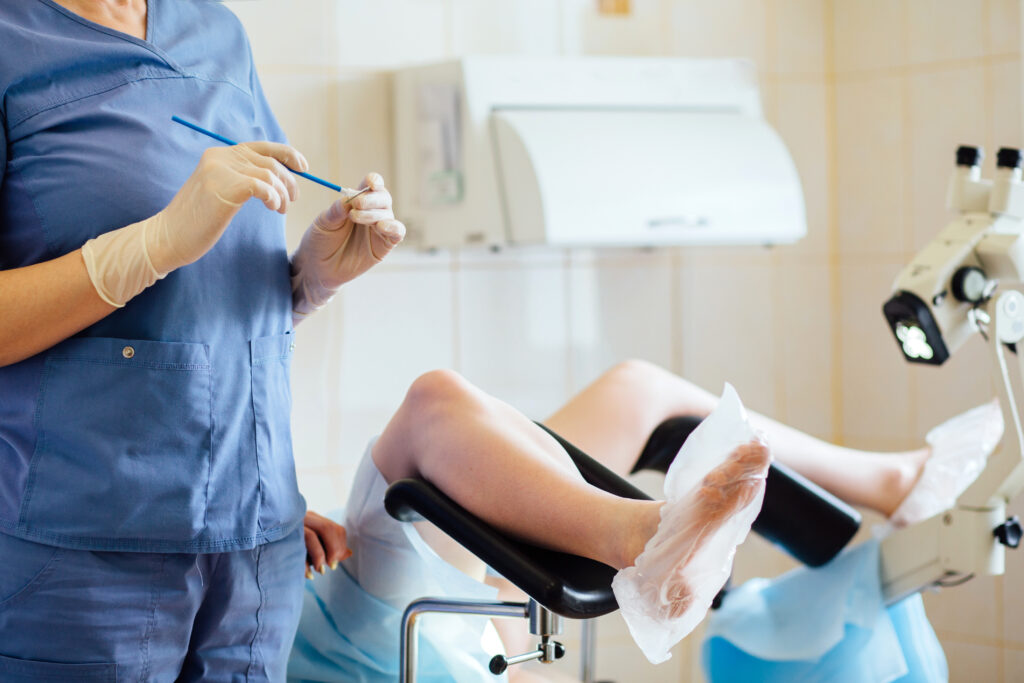
Who should I contact to get tested?
The smear can be made by a gynaecologist, general practitioner or obstetrician. Nearly 9 out of 10 Pap smears are taken by gynecologists during routine gynecological visits. This examination cannot be performed without the patient’s consent, you are free to refuse it.
It is also possible to have a smear made on medical prescription in certain medical-biological analysis laboratories or in health research centers during a health check.
Is the screening free?
As part of the national population screening for cervical cancer, the cytological examination and the HPV test for the smear are 100% reimbursed by the health insurance. Outside the national program the HPV test is reimbursed for 70%.
In France, only 59% of women aged 25-65 were screened between 2018 and 2020 (compared to 58% in 2017-2019). Now that you know all about the Pap smear, think about it!