What is the upper and lower critical temperature of steel?
May 26, 2020 · The Upper Critical Temperature for Steel below which ferrite starts to form is 1670 ºF (910 ºCelsius.) Lower critical temperature for steel's austenite-to-pearlite transformation is 1333 ºF (723 ºCelsius).
What is critical temperature in metals?
As the steel is heated above the critical temperature, about 1335°F (724°C), it undergoes a phase change, recrystallizing as austenite. There are two types of critical temperature: Lower critical temperature (Ac1). The temperature at which austenite starts to transform from ferrite. Upper critical temperature (Ac3).
What temperature is needed to harden steel?
As the steel is heated above the critical temperature, about 1335°F (724°C), it undergoes a phase change, recrystallizing as austenite. There are two types of critical temperature: Lower critical temperature (Ac1). The temperature at which austenite starts to transform from ferrite. Upper critical temperature (Ac3).
How much temperature mild steel can withstand?
Critical temperature means the highest temperature at which it is possible to separate substances into two different phases (vapour and liquid). For steel the critical temperature is slightly higher which is around 1600–2300 degree Fahrenheit. If it is heated till this temperature then it is called austenite or it is in austenitic stage.
What is meant by upper critical temperature?
What is lower and upper critical temperature of steel?
What is the lower critical temperature of steel *?
What is UCT and LCT?
What is critical temperature example?
...
| substance | critical temperature (oC) |
|---|---|
| H2O | 374 |
What are lower and upper Consolute temperature?
What happens to steel at critical temperature?
What is meant by a critical temperature of a metal?
What is the meaning of lower critical temperature?
What is critical temperature of cast iron?
What is thermal annealing?
What is the critical temperature of iron?
How does steel behave in high temperatures?
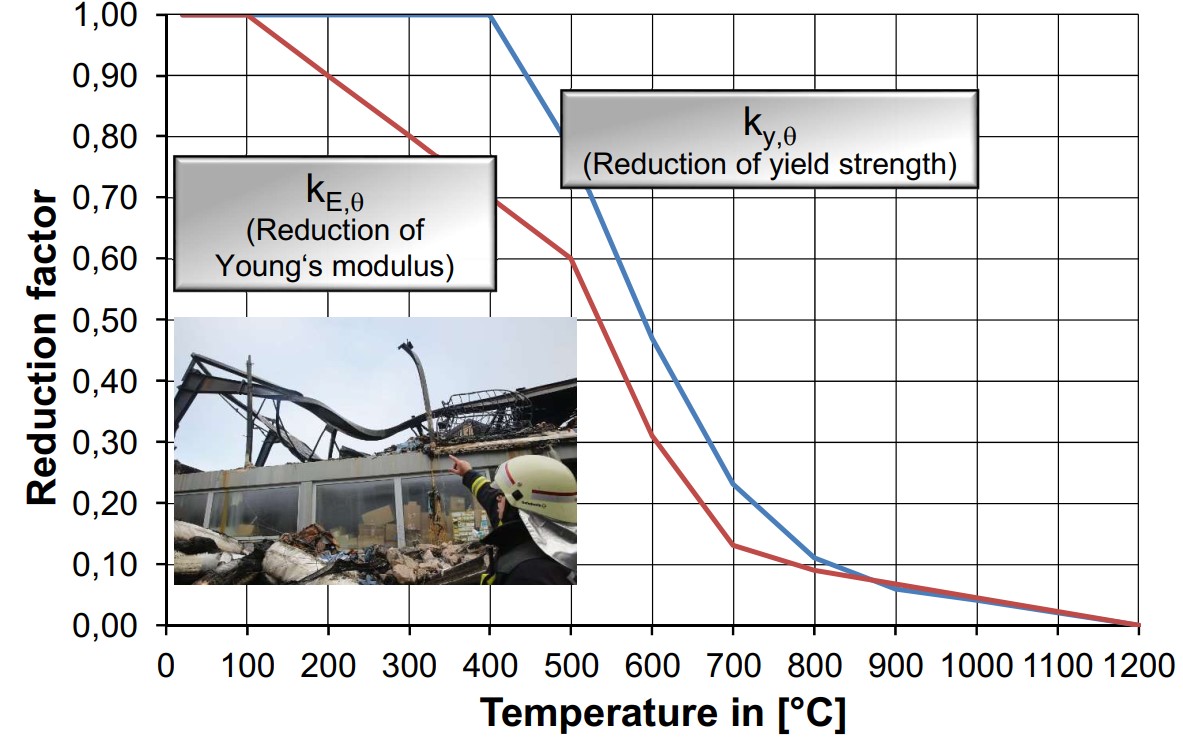
How does steel behave at high temperatures, for example when exposed to fire? Steel is non-combustible and only melts at temperatures of approx. 1400°C (with a carbon content of about 2%). Even the ISO standard fire (the relevant fire curve for determining the fire resistance in constructions) does not attain these high temperatures. Thus, steel usually does not "melt" in the event of a fire. As always, exceptions confirm the rule as there are even more unfavourable fire room curves with higher temperatures in addition to the ISO standard fire. These are for example the tunnel fire curve as well as the hydrocarbon curve for fires (e.g. for fires on oil platforms).
What is the critical temperature of steel?
As can be seen in the diagram above, this temperature refers to the reduction of the yield strength, i.e. the loss of strength of steel at high temperatures. Thus, this temperature may be regarded as critical for constructions that are not prone to stability problems, such as tension members in trusses.