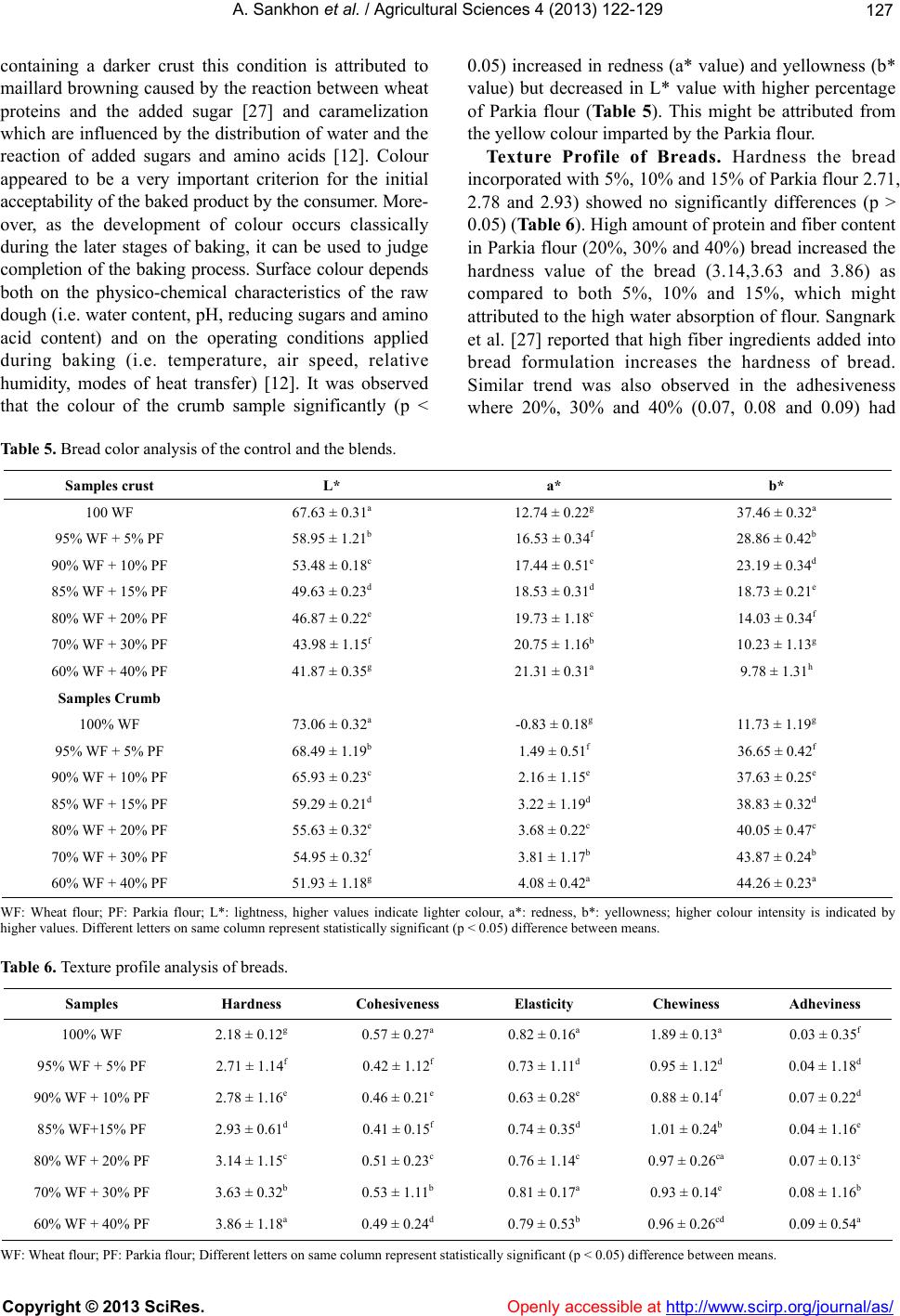
Caramelization is an entirely different process from Maillard browning, though the results of the two processes are sometimes similar to the naked eye (and taste buds). … They are both promoted by heating, but the Maillard reaction
Maillard reaction
The Maillard reaction is a chemical reaction between amino acids and reducing sugars that gives browned food its desirable flavor. Seared steaks, pan-fried dumplings, cookies (widely known in the United Kingdom as biscuits), breads, toasted marshmallows, and many other foods un…
What is the difference between caramelization and Maillard reaction?
This means, caramelization involves the thermal decomposition of materials in food (sugar), while Maillard reaction does not involve any thermal decomposition; it occurs via a chemical reaction between amino acids and reducing sugars in food. 1. “Maillard Reaction.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 3 Aug. 2018.
Is Browning the same as caramelizing?
Some of the foods that benefit from browning are grilled and roasted meats and bread. Like caramelizing, browning creates a tremendous number of flavors and colors, but they’re not the same as those created by caramelization because protein is involved.
What is Maillard browning?
It basically means food will “brown” even in the absence of enzymes. The reaction is named after the French scientist Louis-Camille Maillard for its discovery in the early 1900s.
What is caramelization?
Caramelization is a chemical reaction that takes place involving sugar in food. Therefore we can define it as browning of sugar. This process gives the food its sweet, nutty flavor and brown color while cooking. There are three polymer groups which are responsible for the brown color of the food. they are;
What is the main difference between Maillard reaction and caramelization reaction?
The key difference between Maillard reaction and caramelization is that the Maillard reaction is non-pyrolytic whereas the caramelization is pyrolytic. The Maillard reaction and caramelization are two different non-enzymatic browning processes of food.
What is the difference between the Maillard reaction and caramelization what temperature temperature range does each take place?
~330°-400°F (165-200°C) - increasing caramelization with higher temps, which uses up sugars and thus inhibits Maillard at the high end of this range. ~300-330°F (150-165°C) - Maillard progresses at a fast pace, causing browning noticeably within minutes.
Is caramelization the same as browning?
Like caramelizing, browning creates a tremendous number of flavors and colors, but they're not the same as those created by caramelization because protein is involved.
Is Maillard reaction the same as browning?
The Maillard reaction is a form of non-enzymatic browning that occurs in foods when proteins and/or amino acids chemically react with carbohydrates of reducing sugars. Applying heat during cooking accelerates and continues this intricate process, which elevates the taste, aromas, and appearance of food.
What is the difference between Maillard reaction and caramelization quizlet?
The Maillard Reaction includes reduced sugars and amino group. Caramelization includes just sugar and heat.
What causes Maillard browning?
Maillard browning is a chemical reaction that usually occurs between amino acids (the building blocks of protein) and those carbohydrates known as reducing sugars – although the reaction has been known to occur between reducing sugars and whole proteins.
What does a Maillard reaction do?
The Maillard reaction creates brown pigments in cooked meat in a very specific way: by rearranging amino acids and certain simple sugars, which then arrange themselves in rings and collections of rings that reflect light in such a way as to give the meat a brown color.
What is caramel browning?
Caramelization is a process of browning of sugar used extensively in cooking for the resulting sweet nutty flavor and brown color. The brown colors are produced by three groups of polymers: caramelans (C24H36O18), caramelens (C36H50O25), and caramelins (C125H188O80).
What are examples of Maillard reaction?
Excellent examples of the Maillard reaction are the crust of roast pork or browning of salami on pizza. The Maillard reaction also creates, besides color, countless complex flavors at the same time when, for example, salami is placed on a pizza and baked under high heat.
What is caramelization reaction?
Caramelization reaction is oxidation of carbohydrates or sugar resulting in the development of the brown colour and caramellic flavour when heated at high temperature. The temperature of reaction depends on the type of sugar present in the food.
What are the 3 steps of the Maillard reaction?
The Maillard reaction, for purposes of simplicity, can be divided into three stages: early, advanced and final ( Figure 2). All these stages are interrelated and can occur simultaneously, and they are affected by reac- tion conditions (Silv an et al., 2011). ...
Does Maillard browning require heat?
The Maillard reaction is a chemical reaction between an amino acid and a reducing sugar, usually requiring the addition of heat. Like caramelization, it is a form of non-enzymatic browning.
What is caramelization in biology?
In contrast, if there is no protein involved , the process is considered “ caramelization ”. Caramelization is a form of pyrolysis, which is a generic term to denote any irreversible chemical decomposition driven by heat, more specifically in the absence of oxygen.
Why is the Maillard reaction called the Maillard reaction?
Carnivores may have heard of the Maillard Reaction because it is often brought up in discussions of grilling, frying, and other popular aspects of meat preparation, such as searing. The Maillard reaction is named after the late 19 th century French chemist and physician Louis Camille Maillard.
What is the Maillard reaction?
The Maillard reaction is broadly defined as the chemical process that occurs between amino acids and sugars at high temperatures; it is what gives food complex flavors. This is not limited to meat.
What foods can be used to cause the Maillard reaction?
The Maillard reaction can be applied to all foods, including vegetables, breads, eggs, even vegan foods ; so long as they are prepared at high temperatures and contain amino acids. The key phrase is “amino acid”, which are the building blocks of animal and plant protein.
What does "caramelization" mean in a hedonist?
Hungry Hedonists who enjoy cooking or food likely have heard the terms “Caramelization” and “Maillard reaction” in relation to their favorite meals or desserts. Chances are, they may have even confused the two, that's OK! This is here to help you impress your friends, coworkers, or your boss the next time you sweeten their day.
Is caramelization a chemical process?
Despite using the process on a daily basis, modern chemistry does not know much more. Caramelization is a very complicated process, generating hundreds of different chemical products. It is an example of pyrolysis in a carefully controlled, culinary context.
What is the difference between Maillard reaction and caramelization?
The Maillard reaction happens when there are both sugars and proteins found in foods.
What are the reactions of Maillard?
The foods that are affected by the Maillard reaction have both protein and sugar molecules present. Here are a few examples of food that are affected by the Maillard reaction: 1 Bread - develops a darker and thicker outer crust 2 Eggs - creates a brown lining and crackled edges 3 Meat and Fish - sears on a fine, crunchy brown outer coating 4 Beer - malts are roasted to various degrees and added into the brewing process 5 Coffee - coffee beans are roasted before grinding to achieve various coffee notes 6 Chocolate - cacao beans are roasted after being fermented and dried to add specific chocolate notes 7 Soy Sauce - wheat berries are roasted before being ground and added to soybeans, water, salt, and koji
What is the chemical reaction that develops diverse flavors, enticing aromas, and beautifully browned food?
Therefore, caramelization occurs on foods like fruits, honey, maple syrup, and when making caramel sauce or caramel candies. The Maillard reaction is a complex chemical reaction that develops diverse flavors, enticing aromas, and beautifully browned food.
Why do German pretzels have lye?
That’s because traditional German pretzels are dunked in something called a lye solution (food-grade lye mixed with water) before being bak ed. Lye is an alkaline, another reactant that will increase the pH in amino acids, causing a Maillard reaction. 3. Turn up the Temp.
What temperature does a maillard reaction start?
The optimal temperature to achieve the Maillard reaction sits between 284-330 degrees Fahrenheit (140-165 degrees Celsius). When food reaches 350 degrees Fahrenheit (176 degrees Celsius), the Maillard reaction starts to burn/char the food, so keep a close eye when the Maillard reaction’s browning starts.
How to get a nice sear?
Make sure your meat and fish have their excess moisture patted dry to achieve a nice sear. If roasting coffee beans or cacao beans, they should be completely dry as well. 2. Make A Wash. A wash containing both sugars and amino acids can greatly enhance the Maillard reaction for meat, fish, and bread.
What are some examples of Maillard reactions?
Here are a few examples of food that are affected by the Maillard reaction: Bread - develops a darker and thicker outer crust. Eggs - creates a brown lining and crackled edges. Meat and Fish - sears on a fine, crunchy brown outer coating.
What is caramelization?
Caramelization is a process of liquefying sugars with the help of heat. There are no proteins and enzymes needed. What you end up with is a dark brown liquid with a nutty, sweet yet slightly bitter taste. We call it caramel. Now, caramelization and the Maillard reaction often happen together.
Why does caramelization occur in food?
You’ll find caramelization more in food with high sugar and low protein, such as bread or cookies. And because of the high level of sugar, these food items give out more aromas than flavors. In our example of searing steak, the Maillard reaction is obviously more prominent because of the high level of protein.
What is the Maillard reaction?
The Maillard reaction (or effect) is a chemical reaction between proteins and reducing sugars in food, with heat being the main enabler. The end result of this process is newly-formed pigment molecules called melanoidin, along with other enhanced flavor and aroma ones.
How long can you leave a maillard sear in the fridge?
That way, the salt will draw out the moisture through osmosis. Or you can leave it like that in the fridge overnight and up to a few days. What you end up with is a well-seasoned piece of meat with a perfectly dried out surface, ready for that Maillard browning sear.
What is the name of the reaction that gives food its golden brown color?
The melanoidins are what gives food surface its distinctive golden brown color. Similar to caramelization (we’ll get to this later), the Maillard reaction is a non-enzymatic food browning. It basically means food will “brown” even in the absence of enzymes. The reaction is named after the French scientist Louis-Camille Maillard for its discovery in ...
What temperature does the Maillard reaction start?
As more heat is supplied or the temperature is rising, more and more proteins and sugars “get the invitation to the party”. When the temperature gets past 285F ( 140C), the Maillard reaction is in full effect.
Why do pork ribs turn brown?
However, time also plays a role in this. Even in a lower heat environment, Maillard reaction still occurs if given enough time. That’s why your pork ribs develop a dark brown crust or bark after being inside the smoker for 6 hours. Keep in mind that the flavor and aroma compounds will be different in each scenario.