What are the major regions of the body?
- the gluteal region encompassing the buttocks,
- the femoral region encompassing the thigh,
- the popliteal region encompassing the back of the knee,
- the sural region encompassing the back of the lower leg,
- the calcaneal region encompassing the heel,
- the plantar region encompassing the sole of the foot.
What is the coxal region of the body?
the coxal region encompassing the lateral (side) of hips the pubic region encompassing the area above the genitals. The pelvis and legs contain, from superior to inferior,
Is cubital and antecubital fossa the same?
The cubital fossa is the triangular area on the anterior of the elbow. It is also called the elbow pit or antecubital fossa. It signifies is an area of transition between the anatomical arm and the forearm and can be recognized as a depression on the anterior surface of the elbow joint.
How many regions are in the human body?
Regions
- the thoracic region encompassing the chest
- the mammary region encompassing each breast
- the sternal region encompassing the sternum
- the abdominal region encompassing the stomach area
- the umbilical region is located around the navel
- the coxal region (hip region) encompassing the lateral (side) of hips
Where is the cubital region of the body?
The cubital fossa is a small triangular area located on the anterior surface of the elbow, with the apex of the triangle pointing distally. It contains some important structures, on their passage from the arm to forearm. [[1] It is homologous to the popliteal fossa of the lower limb.
Does cubital mean elbow?
Cubital: 1. Pertaining to the elbow.
What is the function of the cubital fossa?
The cubital fossa contains four structures which from medial to lateral are : The median nerve- The median nerve leaves the cubital between the two heads of the pronator teres. It supplies the majority of the flexor muscles in the forearm.
What structures are in the cubital fossa?
Structures deep within the cubital fossa (lateral to medial)Radial nerve. ... Distal biceps Biceps Arm: Anatomy tendon: attaches at the radial tuberosity.Brachial artery: bifurcates into the radial and ulnar arteries. ... Median.
What is the inside elbow called?
Technically, you can refer to the area as the antecubital fossa. Antecubital is an adjective meaning "of or relating to the inner or front surface of the forearm" (in Latin ante means "before" and cubitum means "elbow"). Fossa is a Medieval Latin borrowing that is used for an anatomical pit, groove, or depression.
Can cubital tunnel cause shoulder pain?
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) has been long known to cause shoulder pain but can be easily overlooked, especially when patients report no symptoms in the hand. To our knowledge, there has been no report in the literature which describes shoulder pain as a symptom of cubital tunnel syndrome (CuTS).
What causes pain in the cubital fossa?
What causes cubital tunnel syndrome? Cubital tunnel syndrome may happen when a person bends the elbows often (when pulling, reaching, or lifting), leans on their elbow a lot, or has an injury to the area. Arthritis, bone spurs, and previous fractures or dislocations of the elbow can also cause cubital tunnel syndrome.
What nerves run through cubital fossa?
NervesBrachial Plexus.Axillary Nerve.Musculocutaneous Nerve.Median Nerve.Radial Nerve.Ulnar Nerve.
What nerve runs through the cubital tunnel?
4 At the elbow, the ulnar nerve traverses through structures that make up the cubital tunnel. The cubital tunnel's ceiling is formed by Osborne's ligament (also known as the cubital retinaculum) (Fig.
What is cubital fossa?
The cubital fossa is an area of transition between the anatomical arm and the forearm. It is located in a depression on the anterior surface of the elbow joint. It is also called the antecubital fossa because it lies anteriorly to the elbow (Latin cubitus) when in standard anatomical position.
What is the cubital fossa?
The cubital (anticubital) fossa is a triangular-shaped depression over the anterior aspect of the elbow joint. It represents an area of transition between the anatomical arm and the forearm, and conveys several important structures between these two areas. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the cubital fossa – its borders, ...
What are the three borders of the cubital fossa?
Borders. The cubital fossa is triangular in shape and consists of three borders, a roof, and a floor: Lateral border – medial border of the brachioradialis muscle. Medial border – lateral border of the pronator teres muscle. Superior border – horizontal line drawn between the epicondyles of the humerus. Roof – bicipital aponeurosis, fascia, ...
What is the medial border?
Medial border – lateral border of the pronator teres muscle.
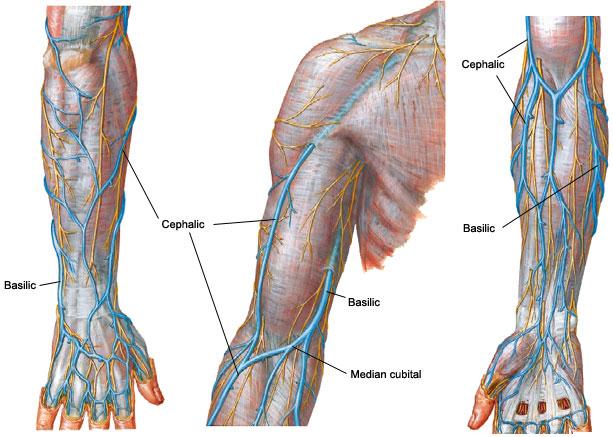
Which vein connects the basilic and cephalic veins?
Notably, the median cubital vein, which connects the basilic and cephalic veins and can be accessed easily – a common site for venepuncture. Mnemonic for contents of the cubital fossa – Really Need (radial nerve) Beer To (biceps tendon) Be At (brachial artery) My Nicest (median nerve).
Which artery travels medially through the cubital fossa?
Brachial artery – bifurcates into the radial and ulnar arteries at the apex of the cubital fossa. The brachial pulse can be felt in the cubital fossa by palpating medial to the biceps tendon. Median nerve – travels medially through the cubital fossa, exiting by passing between the two heads of the pronator teres.
Where is the brachial pulse felt?
The brachial pulse can be felt in the cubital fossa by palpating medial to the biceps tendon. Median nerve - travels medially through the cubital fossa, exiting by passing between the two heads of the pronator teres. It has a motor and sensory function in the anterior forearm and hand.
Which tendon attaches to the radial tuberosity?
Biceps tendon – passes centrally through the cubital fossa and attaches the radial tuberosity (immediately distal to the radial neck). It gives rise to the bicipital aponeurosis which contributes to the roof of the cubital fossa.
What is cubital tunnel syndrome?
Cubital tunnel syndrome happens when the ulnar nerve, which passes through the cubital tunnel (a tunnel of muscle, ligament, and bone) on the inside of the elbow, is injured and becomes inflamed, swollen, and irritated.
What is the difference between carpal tunnel and cubital tunnel?
Patients may also feel the pain radiating from their elbow down to their hand or up towards their shoulder. (light music) Carpal tunnel syndrome involve s pinching of the nerve at the level of the wrist, whereas cubital tunnel syndrome is pinching of the nerve at the level of the elbow, and typically carpal tunnel will cause numbness ...
How is cubital tunnel syndrome diagnosed?
In addition to a complete medical history and physical exam, diagnostic tests for cubital tunnel syndrome may include:
What nerve is in the elbow that causes cubital tunnel syndrome?
The "funny bone" in the elbow is actually the ulnar nerve, a nerve that crosses the elbow. The ulnar nerve begins in the side of your neck and ends in your fingers.
Can cubital tunnel syndrome cause numbness?
In many cases, the cause is not known. The most common symptom of cubital tunnel syndrome is numbness, tingling, and pain in the hand and/or ring and little finger, especially when the elbow is bent. Cubital tunnel syndrome can be treated with rest and medicines to help with pain and inflammation. Exercises may help too.
Where is the cubital fossa located?
The Cubital Fossa is a triangular-shaped depression, located between the forearm and the arm on the anterior surface of the elbow, with the apex of the triangle pointing distally. It is also known as the “antecubital” because it lies anteriorly to the elbow. It is a space filled with different structures that makes up its content. It has three boundaries/borders, and it also has a floor and a roof .
What is the antecubital?
It is also known as the “antecubital” because it lies anteriorly to the elbow. It is a space filled with different structures that makes up its content. It has three boundaries/borders, and it also has a floor and a roof . The Cubital Fossa.
What is the area of the cubital fossa used for?
Venipuncture – The area superficial to the cubital fossa is a common site used for the collection of venous blood specimens and blood transfusion. The basilic vein, median cubital vein, and cephalic vein are superficial veins that are frequently selected for venipuncture at the cubital fossa.
What is the median cubital vein?
Superficially, in the subcutaneous tissue overlying the cubital fossa are the median cubital vein, lying anterior to the brachial artery, the medial and lateral cutaneous nerves of the forearm, related to the basilic and cephalic veins.
What is bicipital aponeurosis?
The bicipital aponeurosis forms a partial protective covering to the median nerve, brachial artery, ulnar artery, and radial artery >. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device. Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations.
What causes a fracture in the cubital fossa?
The displaced fracture fragments may impinge and damage the contents of the cubital fossa such as the median and radial nerve.
How many structures are in the cubital fossa?
The cubital fossa contains four structures which from medial to lateral are :
Where is the cubital fossa located?
The lateral border of the cubital fossa is formed by the brachioradialis which originates from the lateral supra-epicondylar ridge of the humerus. This muscle is innervated by the radial nerve, as it is located in the posterior compartment of the forearm.
What are the boundaries of the cubital fossa?
Boundaries of the cubital fossa. The cubital fossa is a three-dimensional space which has a superior, lateral and medial border, as well as a roof and floor. It is bordered by two forearm muscles – brachioradialis laterally and pronator teres medially. 1.
What are the superficial veins of the cubital fossa?
Superficial veins of the cubital fossa. The superficial veins of the cubital fossa lie superior to the roof of the fossa and are separated from the brachial artery and median nerve by the bicipital aponeurosis. The superficial veins of the cubital fossa include the basilic vein located medially, the cephalic vein located laterally and ...
Where is the medial border of the cubital fossa located?
Medial border. The medial border of the cubital fossa is formed by the pronator teres muscle which origina tes from the medial epicondyle. This muscle is innervated by the median nerve and is located in the anterior compartment of the forearm.
Which veins connect the cubital fossa?
The superficial veins of the cubital fossa include the basilic vein located medially, the cephalic vein located laterally and the median cubital vein which connects these two veins together. 4
Which muscle is responsible for the cubital fossa?
The floor of the cubital fossa is formed mainly by the brachialis muscle proximally and the supinator muscle distally.
What is the area of transition between the anatomical arm and forearm?
It is an area of transition between the anatomical arm and forearm which several important structures traverse through. 1 Appreciation of its anatomy is essential to enable appropriate assessment of a patient sustaining trauma to this region and for performing procedures such as intravenous cannulation or venepuncture.