What does it mean to have an echogenic focus?
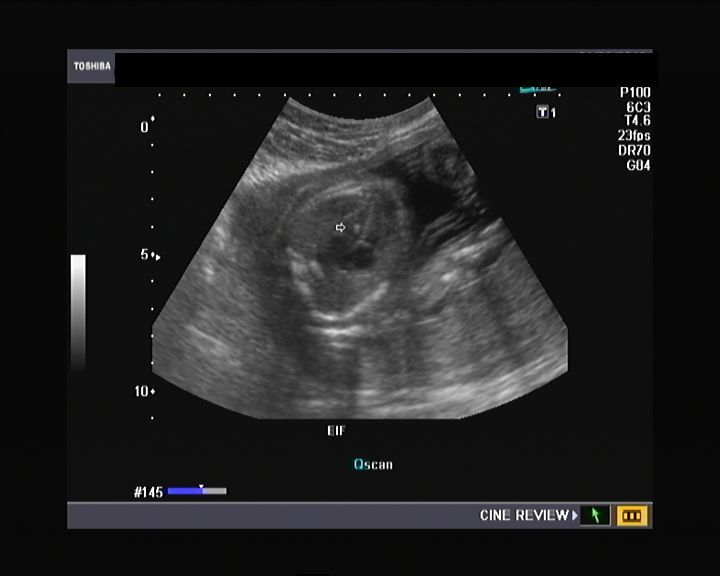
An echogenic intracardiac focus is a hyperechogenic spot (aka bright spot) that is seen on a baby’s ultrasound in utero; the most common location of this “bright spot” is the left ventricle of the heart. Like many topics about pregnancy, echogenic intracardiac focus is surrounded by myths that scare the pregnant couple and that lack any ...
What is echogenic cardiac focus?
Echogenic Cardiac Focus. Echogenic cardiac foci refer to a high number of. echoes inside an area (see next section) of an unborn. child’s heart. The high number of echoes shows up as. bright spots (that resemble a small white pea or pearl) in the heart on an echocardiography. Echocardiography. is an imaging technique that uses types of sound.
What is an Echogenic intracardiac focus?
- Offer screening options NIPS or quad screen (if NIPS not available or too expensive)
- If aneuploidy screening is negative No further aneuploidy evaluation, follow up ultrasound or postnatal evaluation is recommended
- If aneuploidy screen result is positive Refer for genetic counseling and consideration of diagnostic testing options
How serious is an echogenic focus found in heart?
How serious is an echogenic focus found in heart? An echogenic intracardiac focus is linked to a suspected cardiac malformation or may lead to a congenital heart defect at birth. However, the most worrisome effect that it may have is that it signals the presence of Down’s syndrome .
What is the reason of echogenic focus in left ventricle?
Echogenic foci within the left ventricle of the fetal heart represent papillary muscle mineralization. Until more data are available to investigate any possible association with aneuploidy, an echogenic focus in the left ventricle should still be considered a normal variant.
How serious is an echogenic focus found in heart?
An echogenic intracardiac focus (or EIF) is a small bright spot seen on a developing baby's heart during an ultrasound. The cause of EIF is unknown, but the condition is generally harmless. EIF is considered a normal pregnancy variation, but prenatal screening tests may be desirable to test for any abnormalities.
Is echogenic focus common?
This common ultrasound finding is seen in about 1 out of every 20 or 30 pregnancies (~3-5%). An echogenic intracardiac focus (EIF) does not affect health of the baby or how the baby's heart works. This finding is generally considered a normal variation.
How do you treat echogenic focus?
No treatment is required for this condition. The echogenic focus may go away on its own or it may not, but it doesn't affect a child's cardiac function so there is no need for treatment or even follow-up testing to see if it is still there.
Can echogenic focus go away?
An echogenic intracardiac focus is found in 1 out of every 20 to 30 pregnancies. It does not affect the health of your baby or how his or her heart develops. The spots usually do not go away before your baby is born.
Should I be worried about EIF?
But echogenic intracardiac focus (EIF) is almost never something to worry about. It shows up as a bright spot on the heart in imaging, and it's thought to be a microcalcification on the heart muscle. EIF occurs in as many as 5 percent of all pregnancies.
How many babies with EIF have Down syndrome?
The results showed existence of EIF in 3.8% of all fetuses. The prevalence of down syndrome among the population studied was 0.4% with all having EIF.
What does it mean when a baby has calcium in the heart?
Echogenic intracardiac focus (EIF) is a small bright spot seen in the baby's heart on an ultrasound exam. This is thought to represent mineralization, or small deposits of calcium, in the muscle of the heart. EIFs are found in about 3–5% of normal pregnancies and cause no health problems.
What causes white spots on fetal heart?
An echogenic intracardiac focus (EIF) is a bright white spot in the fetal heart that looks like a tiny golf ball. This bright spot is due to a bit of calcium in one of the muscles that attaches to the heart valve. It is NOT an abnormality and is NOT associated with heart defects.
Does EIF mean Down syndrome?
Conclusion: Fetuses with an echogenic intracardiac focus have a significantly increased risk of Down syndrome. Although most fetuses with this finding are normal, patients carrying fetuses with an echogenic intracardiac focus should be counseled about the increased risk of trisomy 21.
How common is echogenic intracardiac focus in left ventricle?
EIF are most often seen in the left ventricle (94%) and are usually single. They usually measure 1 to 4 mm in size.
What is meaning of echogenic?
Meaning of echogenic in English able to send back an echo (= a sound that reflects off a surface), and therefore showing as a light area in an ultrasound scan (= a medical examination that produces an image using sound waves): Ultrasonography revealed large, echogenic kidneys.
Where are echogenic foci found?
They are usually found in the ventricles within the papillary muscles or chordae tendinae. To be considered echogenic intracardiac foci, they must be of the same echogenicity as fetal bone and must move along with the fetal heart motion. They are seen in 4% of all pregnancies, but there is a higher incidence among Asians.
What is the course of action to be followed once an echogenic intracardiac focus is found?
A detailed ultrasound is performed to look for signs of chromosomal mutations in the developing fetus. If all parts of the fetus are not clearly visible, the radiologist will schedule another ultrasound to be performed after a week.
How many Asians have echogenic ultrasounds?
They are seen in 4% of all pregnancies, but there is a higher incidence among Asians. Echogenic intracardiac focus occurrence on ultrasound is nearly 13% of ultrasounds among Asians.
How many babies have echogenic intracardiac focus?
One in five babies seem to have at least one echogenic intracardiac focus. Some may even have more than one such focus and they may be distributed in different areas of the infant heart. They are never attached to the walls of the chambers of the heart. They are usually found in the ventricles within the papillary muscles or chordae tendinae.
What is the procedure to test for amniotic fluid?
Should any abnormality be seen in the ultrasound, the doctor will suggest performing a test of the amniotic fluid. An amniocentesis is a procedure in which a thin needle is inserted into the sac of the pregnant woman to collect some of the amniotic fluid within. This fluid is tested for skin cells shed by the fetus during development.
Can an infant have an echogenic foci?
In most cases, infants with intracardiac foci will be born healthy with no issues. However, in some cases things could take a turn for the worse as it may be associated with the chance of a chromosome change in the infant. An echogenic intracardiac focus is linked to a suspected cardiac malformation or may lead to a congenital heart defect at birth.
What are echogenic foci in fetal heart?
We identified three fetuses with this sonographic finding in whom pathologic correlation was available. The only consistent histologic finding present in all three fetuses was mineralization within a papillary muscle; the chordae tendineae were normal. One of the three fetuses had trisomy 21. Echogenic foci within the left ventricle of the fetal heart represent papillary muscle mineralization. Until more data are available to investigate any possible association with aneuploidy, an echogenic focus in the left ventricle should still be considered a normal variant.
What is the only consistent histologic finding present in all three fetuses?
The only consistent histologic finding present in all three fetuses was mineralization within a papillary muscle; the chordae tendineae were normal. One of the three fetuses had trisomy 21. Echogenic foci within the left ventricle of the fetal heart represent papillary muscle mineralization.
Symptoms
- EIF causes no symptoms for the fetus or pregnant person. As noted above, this condition doesn't affect the health or function of the baby's heart.
Causes
- The exact cause of an EIF is not known.3 However, it is believed that the bright spot or spots show up because there is an excess of calcium in that area of the heart muscle. On an ultrasound, areas with more calcium tend to appear brighter. For example, teeth show up brightly as well.2 An echogenic focus can occur in any pregnancy. However, the rates of EIF in pre…
Diagnosis and Further Testing
- An echogenic focus on its own poses no health risk to the fetus, and when the baby is born, there are no risks to their health or cardiac functioning as a result of an EIF. It is considered a variation of normal heart anatomy and is not associated with any short- or long-term health problems. However, EIF may be associated with a higher risk for chromosomal abnormalities, such as Dow…
Treatment
- No treatment is required for this condition. The echogenic focus may go away on its own or it may not, but it doesn’t affect a child’s cardiac function so there is no need for treatment or even follow-up testing to see if it is still there.
A Word from Verywell
- It can be frightening and confusing when you hear that something has been found on your baby’s ultrasound. Even if it’s considered normal, this can be scary. Know that in the vast majority of cases, an EIF is a benign anomaly. Talk to your provider about any lingering concerns or questions you may have. Pregnancy, for all its joys, can also bring stressors—and that’s OK. Just make sur…
Why Is An Echogenic Intracardiac Focus A Cause For Concern?
- In most cases, infants with intracardiac foci will be born healthy with no issues. However, in some cases things could take a turn for the worse as it may be associated with the chance of a chromosome change in the infant. An echogenic intracardiac focus is linked to a suspected cardiac malformation or may lead to a congenital heart defect at birth. However, the most worris…
Course of Action to Be Followed Once An Echogenic Intracardiac Focus Is Found
- A detailed ultrasound is performed to look for signs of chromosomal mutations in the developing fetus. If all parts of the fetus are not clearly visible, the radiologist will schedule another ultrasound to be performed after a week. Should any abnormality be seen in the ultrasound, the doctor will suggest performing a test of the amniotic fluid. An...
What If There Is No Chromosomal Change?
- Often the amniocentesis is negative. In this case the doctor will continue to monitor the fetus via regular ultrasounds. The echogenic intracardiac focus will also be studied and recorded. Fetal development will be observed for any possible abnormality. As long as all the examinations are normal, there is no reason why a child with an echogenic intracardiac focus may not grow up to …
Further Reading