Different Pipe Welding Positions
- 1G – Horizontal Rolled Position. In the 1G welding position or Horizontal rolled position, the pipe will be in the horizontal position, and it can be rotated along the horizontal ...
- 2G – Vertical Position. ...
- 5G – Horizontal Fixed Position. ...
- 6G – Inclined Position. ...
What is 6GR welding test position?
6GR Welding test Position is in accordance with AWS D1.1 Structural Welding Code – Steel. It is also called restriction welding, so the “R” in the 6GR term refers to the restriction ring, while 6G in the term 6GR is the same as in the 6G position.
What does 6GR welder stand for?
The letter G stands for Groove. The letter R stands for restriction. So, when you find a 6GR welder, know that the said individual has successfully overcome the obstacle in this test piece and welded it perfectly to have gotten that certification. The R means there’s an obstacle to overcome.
What are the factors to consider when 6G welding?
Another critical factor you need to consider in 6G welding is the level of penetration you were able to achieve. Bear in mind that a poor penetration is a recipe for disaster, and all your effort will go to waste. So, what’s the wise thing to do?
Is 6GR welding hard to get certified?
So, it’s not just a matter of obtaining 6GR certification. However, 6GR welding is somewhat more challenging to obtain.
What is 6G position and what is 6GR position?
The difference with the 6G and 6GR position is the restriction ring and the the bevel preparation. 6G is prepared as single vee at 45 degrees postion with the horizontal plane, while the 6GR bevel preparation is single bevel and the two connecting pipe has different thicknesses, one is thicker of at least 4-6mm.Jul 21, 2009
What are the 5 welding positions?
What Is a Welding Position?Flat position. Also referred to as a “downhand” position, the flat position weld is the easiest and often the first weld that new students learn. ... Horizontal Position. ... Vertical Position. ... Overhead. ... Fillet Weld (F) ... Grove Weld (G) ... Butt Joints. ... Lap Joints.More items...•Aug 13, 2020
What does 2F mean in welding?
Welding Certification Position 2F: Horizontal Fillet Weld. 2:59.Nov 28, 2012
What are the 4 AWS welding positions?
Welding PositionsHorizontal Position (2F or 2G)Vertical Position (3F or 3G)Overhead Position (4F or 4G)Jan 19, 2022
What is 5G and 6G welding?
There are mainly four types of pipe welding positions- 1G – Horizontal Rolled Position. 2G – Vertical Position. 5G – Horizontal Fixed Position. 6G – Inclined Position.
What is 8g welding position?
Perform welds using GMAW. Gas metal arc welding (GMAW) to code standard carried out using a range of materials. The person would work autonomously or in a team environment using predetermined standards of quality, safety and welding procedures.
What position is a 2F 2G?
What are the different types of welding positions?Welding symbolTypePosition2FFillet weldHorizontal2GGroove weldHorizontal3FFillet weldVertical3GGroove weldVertical4 more rows
What does 6G mean in welding?
6G Position The pipe is in a fixed position, so the welder must move around the pipe to perform the welding. This is an advanced welding position that requires a great deal of experience and technical expertise.Oct 8, 2019
What is a 5F weld?
A 5F weld joint is a tube welded to a plate where the axis of the tube is horizontal and the plate is vertical. A 5F weld joint is a bit more challenging than a 2F. ... and the thing that makes it difficult is mainly body positioning.
Why electrode is coated with flux?
The electrode is coated in a metal mixture called flux, which gives off gases as it decomposes to prevent weld contamination, introduces deoxidizers to purify the weld, causes weld-protecting slag to form, improves the arc stability, and provides alloying elements to improve the weld quality.
What is 3G and 4G welding?
Welding in a 3G position means moving the torch vertically, up and down across a surface. This is in contrast with 1G (flat surface welding), 2G (horizontal welding), and 4G (overhead ceiling welding).
What are the different welding positions?
There are four types of welding positions namely:Flat position.Horizontal position.Vertical position.Overhead position.
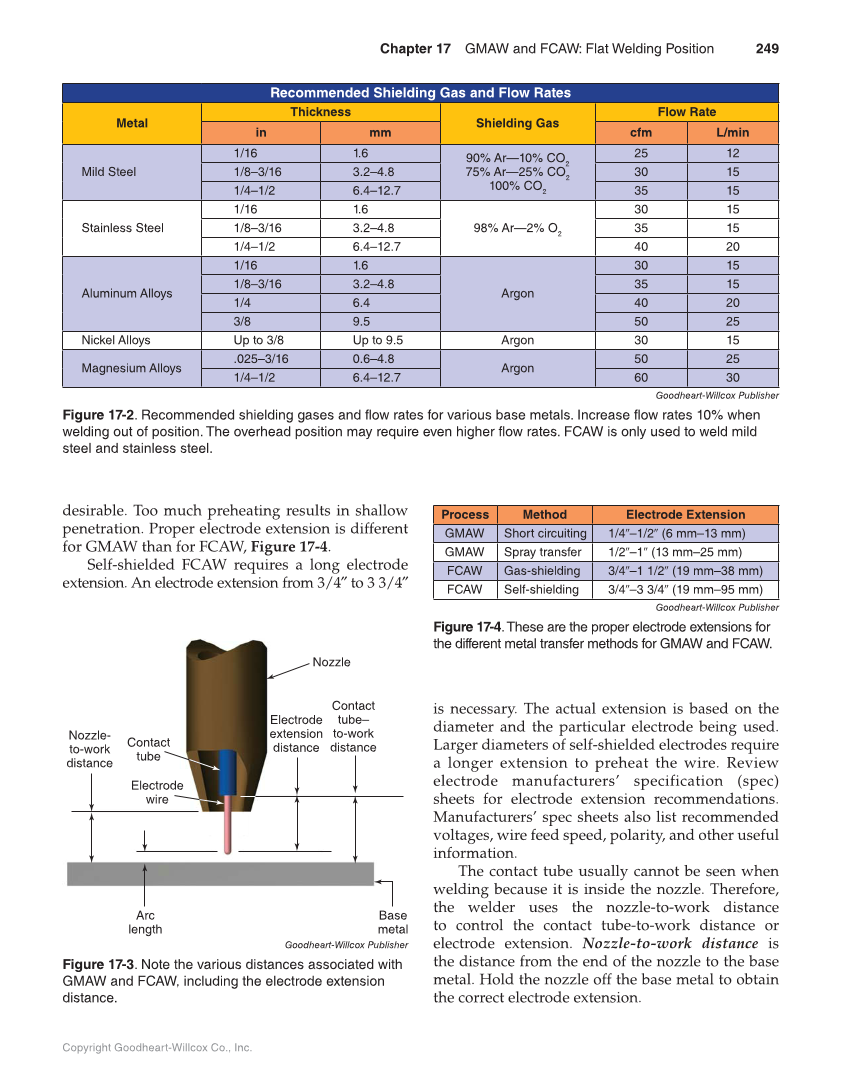
Pipe and Plate Weld Joint Positions
Normally there are six welding positions with certain numbers and letter i.e. 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, and 6G/6GR. All the positions are used in various angles and shapes while performing welding. Generally, the ways and ideas of welding are similar in different countries.
6G Welding Positions-
This is one of the hardest types of welding positions for welders to perform. The position is a pre-condition for getting certified. To some extent, this position is similar to 5G/PH/PJ but the pipe stands at 45° to the other one. Other names are 6G Uphill/H-L045 and 6G Downhill/J-L045 Position.
What does the R in 6G welding mean?
This is another 6G weld position that is also challenging. The “R” in the name stands for restricted. In this position, welding is performed in a ring mode. What this means is that a steel plate is placed under the weld site with an inch gap.
What is welding position?
A welding position means the posture you need to assume towards the workpiece you are welding. In some cases, you will need to weld the workpiece in the position you find it and not adjust it in any way.
What certification do you need to weld a pipe?
In particular, pipe welders can apply for a 5G and 6G certification . These two are used for the most complex welding positions. Therefore they require more experience. The 6G certification is seen as the gold standard of welding certification. Welders with this certification can weld all-around a stationary pipe.
What is flat welding?
In the flat position, the joint or workpiece to be welded is placed under the welding torch. In this regard, the molten metal flows downward into the joint. The result is an easy to accomplish weld. This weld position can be used to perform groove, fillet, and butt welds.
What does the 3 digit mean in welding?
These numbers refer to the characteristics of the electrode. And the third digit in an electrode’s number designation refers to the welding position it can be used in. For instance, the number “1” means an electrode can be used in all ...
What is horizontal 2G welding?
The horizontal or 2G position is a little bit more complicated than the flat position. In this position, the workpiece is placed parallel to your body when welding. Thus the workpiece remains in front of you when welding.
Do you need more hands to be a welder?
A welder’s experience will also influence their certification. Therefore, some welding positions will require more experienced hands.
What is the difference between a 6G and 6GR welder?
The welder cuts a slope at a specific angle on the metal, particularly at the edge. Furthermore, in the 6G certification test, the welder has to weld in all positions while the 6GR position is for TKY joints. That’s it on the difference between the 6G and 6GR welder. Both are used to test welders for certification purpose.
What do you need to know about 6G welding?
It has a steep learning curve and takes time to master. Therefore, if you want to pass the 6G certification with flying colors, then you need to know the ins and outs of this style of welding.
Why is 6GR so challenging?
However, the 6GR is considered to be more challenging because of the obstacles a welder needs to overcome to have a smooth weld. If you are pursuing a 6G or 6GR qualification, then we wish you the best of luck. David Huner.
What is 6G weld?
Firstly, the 6G position is the type whereby your tubular weld joint has to be included at an angle of 45 degrees. It’s a difficult test to pass, though not impossible. For a 6G welder to pass this test and obtain certification, the test piece must be welded in its original position.
Is the 6GR the hardest welding position?
The G6 test positions and welding procedures are quite demanding. But concerning difficulty levels, the 6GR tends to be the hardest compared to the 6G. Anyway, the 6GR is still more of the 6G position test position, only that it features a restriction ring.
Do 6G welders make more money?
Well, most individuals claim that the 6GR welders tend to make more money than 6G welders, and that is a reasonable point, given how difficult it is to qualify as a 6GR welder.
Can you finish a 6G welding test?
You may also not be able to finish your welding test in record time. Another critical factor you need to consider in 6G welding is the level of penetration you were able to achieve. Bear in mind that a poor penetration is a recipe for disaster, and all your effort will go to waste.
What is the most challenging welding job?
Joining curved pieces of metal is more difficult than welding flat sheets, so by far the most challenging process you’re ever likely to come across is pipe welding, where you will be required ...
What is open root welding?
If a welding joint does not use a tacked backing plate, it’s known as open root welding, which is the most common process used while pipe welding. This is particularly difficult because you’ll essentially be welding across a gap (albeit a small one) so it’s important to use the right technique so that you don’t make a mess of the whole job.
Why is 2G welding flat?
This is pretty much just flat welding because the pipe will be lying on its side (on the curved edge) and can be rotated as you weld. The 2G position is fixed, which means that the pipe cannot be turned as you weld. In this case, the pipe is placed on its base, which makes it much sturdier and more stable to weld.
What is NDT welding?
These three methods are called non-destructive testing (NDT), where the welds must remain intact. However, when you’re practicing or being tested as part of your certification, it may be appropriate to actually break apart your pipe weld by separating it into sections and testing the strength and quality of each one.
Can you use a welding machine to test a weld?
You won’t just need to prove that you can use a welding machine; your welds will be tested for penetration, quality, and you may even be forced into a tight space with a restricted view to test your all-position welding technique.
Is it important to learn welding?
As a result, before you even think about tackling pipe welding, it’s important to perfect the art of plate welding first. Learning the structural welding basics will give you a much better understanding of welding in general, which is a great foundation for more complex procedures. As pipe welding is so difficult, ...
Do you need special equipment to do welding?
You will learn some of the most challenging welding techniques in the industry, but you’ll gain a highly prized skill set which is desired by employers and which will probably lead to a higher salary. You won’t need any extra special equipment, but this isn’t a welding process for the half-hearted.
What is 6G welding?
A 6G pipe welding test as shown in the picture below is where the pipe is fixed at a 45-degree angle and welded in this fixed position . A fixed position means that once welding begins, the pipe cannot be rolled or moved. The welder has to weld all around the pipe in the same position. So, it basically covers flat, horizontal, vertical welding, and overhead in a single position. Hence considered one of the tough weld tests.
What electrode diameter is used for hot pass welding?
Hot pass welding can be carried out using 1/8’’ or 5/32’’ electrode diameter. Avoiding grinding during a hot pass is recommended as many welding inspectors don’t allow grinding during hot and fill passes to judge the quality of the welders.
What is the E6010 electrode?
E6010 is a cellulose-type SMAW electrode. The arc of E6010 is very strong and there is no slag. A welding current of 60 amp to 75 amp is well suited for welding root run using 3/32’’ E6010 electrode. Watch the below video to learn about the technique for full penetration open root welding using the E6010 electrode.
What is a hot pass weld?
The hot pass is the weld pass welded as the 2nd to 3rd pass on the pipe to cover the root weld. If done correct the hot pass will turn a flat root penetration surface to a convex, good looking one. If your root weld does not have enough penetration or even some suck back a good hot pass can fix that!
What test is required to certify a welder?
To finally certify a welder, the welder test coupon must pass a volumetric NDT such as RT or UT or can be substituted by bend test as permitted into ASME Section IX or AWS D1.1.
Where are arc strikes made?
Usually, arc strikes are made inside the weld bevel or the previous weld so they become part of the weld. Clean the root from spatters for a good root profile view. The root shall be free from lack of penetration, excessive root penetration, suck back and lack of fusion, etc.
Is it better to do a 6G or 2G welding?
Before moving to pipe welding, it’s always better to first master the plate or structural welding. Once, you got confidence in structural welding, go for pipe welding in 2G, then 5G and then practice 6G. If you follow this, you will find 6G test much easier. Otherwise, you will struggle a lot.