Why was Mesopotamia also known as the land between two rivers?
Mesopotamia means “Land between Two Rivers” because it was located between Tigris and Euphrates River. Why was the Tigris and Euphrates river important to Mesopotamia? The Tigris and Euphrates rivers provided water and ameans of transportation for the people who settled in the area.
Why was Mesopotamia such good area for growing crops?
- Question 1 SURVEY 30 seconds Q. ...
- Question 2 SURVEY 30 seconds Q. ...
- Question 3 SURVEY 30 seconds Q. ...
- Question 4 SURVEY 30 seconds Q. ...
- Question 5 SURVEY 30 seconds Q. ...
- Question 6 SURVEY 30 seconds Q. ...
- Question 7 SURVEY 30 seconds Q. ...
- Question 8 SURVEY 30 seconds Q. ...
- Question 9 SURVEY 30 seconds Q. ...
- Question 10 SURVEY 30 seconds Q. ...
Why was farming so hard in Mesopotamia?
The agriculture of Northern or Upper Mesopotamia, the land that would eventually become Assyria, had enough rainfall to allow dry agriculture most of the time so that irrigation and large institutional estates were less important, but the returns were also usually lower.
Why were ziggurats so large in Mesopotamia?
why were ziggurats so large
- Interesting Facts About Ancient Mesopotamia Ziggurat
- The Ancient Sumerians: The Great Ziggurat of Ur | Ancient Architects
- The Largest Star in the Universe – Size Comparison
- WC3 – ESL Open Cup Europe #95 – Grand Final: [UD] Happy vs. Chaemiko [HU]
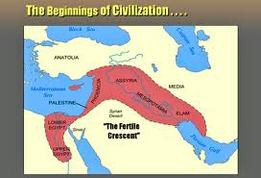
Why is Mesopotamia known as the Fertile Crescent Brainly?
The term was popularized by the American Orientalist James Henry Breasted. The Fertile Crescent includes a roughly crescent-shaped area of relatively fertile land which probably had a more moderate, agriculturally productive climate in the past than today, especially in Mesopotamia and the Nile valley.
What was known as the Fertile Crescent and why?
The Fertile Crescent is the boomerang-shaped region of the Middle East that was home to some of the earliest human civilizations. Also known as the “Cradle of Civilization,” this area was the birthplace of a number of technological innovations, including writing, the wheel, agriculture, and the use of irrigation.
Is Mesopotamia called the Fertile Crescent?
Hence we are obliged to coin a term and call it the Fertile Crescent. In current usage, the Fertile Crescent includes Israel, Palestine, Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Egypt, and Jordan, as well as the surrounding portions of Turkey and Iran.
Why was Mesopotamia known as the land between two rivers?
Mesopotamia's name comes from the ancient Greek word for “the land between the rivers.” That's a reference to the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, the twin sources of water for a region that lies mostly within the borders of modern-day Iraq, but also included parts of Syria, Turkey and Iran.
Where exactly was the Fertile Crescent?
The Fertile Crescent is a large geographic region in modern day Turkey, Iran, Iraq, Syria, Israel, Jordan, and the northern-easternmost part of Egypt, fed by the Euphrates and Tigris rivers, which have supported numerous ancient civilizations.
Why is the Fertile Crescent fertile?
Two rivers, the Tigris and the Euphrates, regularly flooded the region, and the Nile River also runs through part of it. Irrigation and agriculture developed here because of the fertile soil found near these rivers. Access to water helped with farming and trade routes.
How did Mesopotamia get its name?
The word “mesopotamia” is formed from the ancient words “meso,” meaning between or in the middle of, and “potamos,” meaning river. Situated in the fertile valleys between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, the region is now home to modern-day Iraq, Kuwait, Turkey and Syria.
When was the Fertile Crescent?
Known as the Cradle of Civilization, the Fertile Crescent is regarded as the birthplace of agriculture, urbanization, writing, trade, science, history and organized religion and was first populated c. 10,000 BCE when agriculture and the domestication of animals began in the region.
What is the fertile crescent?
Named for its rich soils, the Fertile Crescent, often called the “cradle of civilization,” is found in the Middle East. Because of this region’s relatively abundant access to water, the earliest civilizations were established in the Fertile Crescent, including the Sumerians. Its area covers what are now southern Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Palestine, Israel, Egypt, and parts of Turkey and Iran. Two rivers, the Tigris and the Euphrates, regularly flooded the region, and the Nile River also runs through part of it. Irrigation and agriculture developed here because of the fertile soil found near these rivers.
Why did agriculture and irrigation develop in the fertile Crescent?
Irrigation and agriculture developed here because of the fertile soil found near these rivers. Access to water helped with farming and trade routes. Soon, its natural riches brought travelers in and out of the Fertile Crescent.
What are the challenges of the fertile crescent?
Turkey, Syria, and Iraq all depend on the waters flowing from the region. Increased population and demands on the rivers from urbanization have depleted the once-fertile soil.
Answer
Mesopotamia is known as the Fertile Crescent for the following reasons:
Further explanation
An overview of Mesopotamia, especially Sumerian, can be found at this link brainly.com/question/1618221.
Learn more
An overview of Mesopotamia, especially Sumerian brainly.com/question/1618221.
Answer
Mesopotamia is known as the Fertile Crescent for the accompanying reasons:
New questions in History
In a paragraph, contrast the difference perspectives about the Boston Massacre. What key differences do they express? Why do you think that is?
What was the geography of the fertile crescent?
Geography of the Fertile Crescent. Due to its varied geography, Mesopotamian agriculture was highly diverse in terms of food sources, regional crop yields, and annual rainfall or irrigation variation (agricultural production could be up to 100x higher in particularly good years). There were two types of agriculture:
What type of agriculture did Mesopotamia have?
Due to its varied geography, Mesopotamian agriculture was highly diverse in terms of food sources, regional crop yields, and annual rainfall or irrigation variation (agricultural production could be up to 100x higher in particularly good years). There were two types of agriculture: 1 Dry agriculture without irrigation, where people mostly cultivated cereals and relied on rainfall, which was primarily practiced in upper Mesopotamia and Syria. 2 Irrigation agriculture, which was centered in lower Mesopotamia.
What is the birthplace of agriculture?
The ancient Near East, and the historical regions of the Fertile Crescent and Mesopotamia in particular, are generally seen as the birthplace of agriculture. In the 4th millennium BCE, this area was more temperate than it is today, and it was blessed with fertile soil, two great rivers (the Euphrates and the Tigris), as well as hills and mountains to the north.
What were the crops that were grown in Mesopotamia?
The main types of grain that were used for agriculture were barley, wheat, millet, and emmer. Rye and oats were not yet known for agricultural use.
Why did agriculture start?
Agriculture started most likely because hunter-gatherers who collected grains would have had to take them back to their camp in order to separate the grain from the chaff.
What was the soil in Babylonia?
The soil, particularly in the flood plains in the arid climate of Babylonia and Assyria, was prone to dry up, harden, and crack. In order to keep the soil arable, the plow had to be used. By 3000 BCE plows were known and in wide use – many Assyrian kings boasted to have invented a new improved type of plow.
Why did semi-nomads stay in their villages?
Over time, some of these semi-nomads decided to stay in their agricultural villages year-round to cultivate cereals, while others would continue as nomads. By 8500 BCE, the Middle East was home to many permanent villages whose inhabitants were primarily farmers. The agricultural revolution had begun.
What is the name of the fertile crescent?
In Arabic, the area was called Al-Jazirah, or "the island.". It has also been known as the fertile crescent. Mesopotamia was home to a diversity of cultures rather than a unified society like the Greeks or Egyptians. Many different empires and civilizations came from the region.
Why is Mesopotamia called the cradle of civilization?
Mesopotamia is called the cradle of civilization because the development of agriculture, including the domestication of animals , began there 8,000 years ago, before any other civilization. The advances in the region led to the development of cities, the wheel and written language by 3,000 B.C. Mesopotamia more or less occupied ...
What were the rights of women in Mesopotamia?
The rights of women to participate in society; women were able to work, own land and businesses and even file for divorce. The people shared a multi-god religion. Wine and beer are two more inventions attributed to the Mesopotamians.