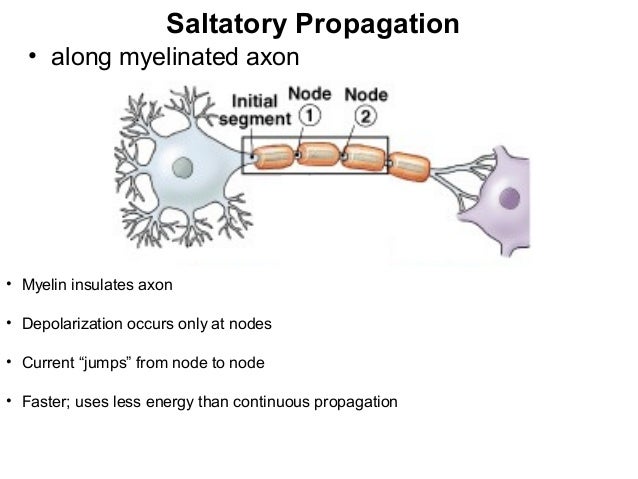
Saltatory conduction
Saltatory conduction is the propagation of action potentials along myelinated axons from one node of Ranvier to the next node, increasing the conduction velocity of action potentials. The uninsulated nodes of Ranvier are the only places along the axon where ions are exchanged across the axon membrane, regenerating the action potential between regions of the axon that are insulated b…
What is the difference between saltatory and continuous conduction?
Saltatory and continuous conduction are two types of transmission of action potentials along the nerves. Saltatory conduction occurs in myelinated axons from one node of Ranvier to the next node.
Why is salutatory conduction more efficient than continuous conduction?
Moreover, salutatory conduction uses a minimum number of voltage channels compared to the continuous conduction. Hence, it prevents the delay of nerve impulses. Furthermore, salutatory conduction is more efficient since it uses less energy to maintain the resting membrane potential.
What is saltatory conduction of action potentials?
Action potentials traveling down the axon "jump" from node to node. This is called saltatory conduction which means "to leap." Saltatory conduction is a faster way to travel down an axon than traveling in an axon without myelin. Thereof, how is Saltatory conduction different from continuous conduction?
Why is action potential conduction faster than continuous conduction?
Therefore, the action potential is only generated at the neurofibrils in myelinated axons. Hence, it is faster than continuous conduction. Continuous conduction occurs along the entire length of unmyelinated axons. Click to see full answer. Regarding this, why is Saltatory conduction much faster than continuous conduction?
Why is continuous conduction slower than saltatory conduction?
Terms in this set (8) conduction occurs in myelinated axons. Nerve signals transmit much faster than in continuous conduction because an action potential is generated only at the neurofibrils (segments of axon without myelination) of myelinated axon rather than along the entire length of unmyelinated axon.
Why is saltatory conduction faster than continuous conduction quizlet?
Saltatory conduction occurs in myelinated axons. This type of conduction is much faster than continuous conduction because action potentials occur at the exposed nodal regions of the axon.
Why is saltatory conduction along a myelinated axon faster than continuous?
Why is saltatory conduction along a myelinated axon faster than continuous conduction along an unmyelinated axon? a. Since there are many more voltage-gated channels located along a myelinated axon, the conduction rate all along the axon is more rapid than along an unmyelinated axon (which has fewer channels).
Why is saltatory conduction faster than normal conduction?
Therefore, saltatory conduction is thought as the hallmark of myelinated axons, which enables faster and more reliable propagation of signals than in unmyelinated axons of same outer diameter.Oct 13, 2014
What is the difference between continuous and saltatory conduction?
0:010:52Continuous and Saltatory Propagation Video Clip - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWhen an action potential in an axon spreads to a neighboring region of its membrane by a series ofMoreWhen an action potential in an axon spreads to a neighboring region of its membrane by a series of small steps. The process is called continuous propagation. When it propagates by jumping from one
What is the difference between saltatory and continuous propagation of nerve impulses quizlet?
What is the difference between saltatory and continuous propagation of nerve impulses? Saltatory carries impulses at a faster rate than continuous propagation. What occurs when multiple neurons feed into a single neuron?
Why is saltatory conduction along a myelinated axon faster than continuous conduction along an Unmyelinated axon quizlet?
Why is saltatory conduction along a myelinated axon faster than continuous conduction along an unmyelinated axon? The lack of myelin around unmyelinated axons causes them to be unable to conduct impulses; therefore the myelinated axons will have a faster impulse conduction rate.
Why is saltatory conduction faster than the conduction of an action potential in an Unmyelinated axon?
Electrical signals travel faster in axons that are insulated with myelin. Myelin, produced by glial support cells, wraps around axons and helps electrical current flow down the axon (just like wrapping tape around a leaky water hose would help water flow down the hose).
Why do myelinated neurons conduct impulses faster than unmyelinated ones?
Answer and Explanation: Myelinated neurons conduct impulses faster than unmyelinated neurons because nerve impulses jump over the myelin sheath rather than travel through it, making the distance to the axon terminal shorter.
How much faster is saltatory conduction?
It is by this restriction that saltatory conduction propagates an action potential along the axon of a neuron at rates significantly higher than would be possible in unmyelinated axons (150 m/s compared to 0.5 to 10 m/s).
Why does myelin make conduction faster?
Myelin can greatly increase the speed of electrical impulses in neurons because it insulates the axon and assembles voltage-gated sodium channel clusters at discrete nodes along its length.
Which is the fastest form of action potential conduction down an axon?
The fastest signals in our bodies are sent by larger, myelinated axons found in neurons that transmit the sense of touch or proprioception – 80-120 m/s (179-268 miles per hour).
Which is faster, saltatory or continuous conduction?
Saltatory conduction occurs in myelinated axons from one node of Ranvier to the next node. Therefore, the action potential is only generated at the neurofibrils in myelinated axons. Hence, it is faster than continuous conduction. Continuous conduction occurs along the entire length of unmyelinated axons.
What is the difference between saltatory and continuous conduction?
The key difference between saltatory and continuous conduction is that saltatory conduction is the propagation of action potential along myelinated axons while continuous conduction is the propagation of action potential along unmyelinated axons. Saltatory and continuous conduction are two types of transmission of action potentials along the nerves.
Why is salutatory conduction more efficient than continuous conduction?
Furthermore, salutatory conduction is more efficient since it uses less energy to maintain the resting membrane potential.
What is continuous conduction?
Continuous conduction is the second way of nerve impulse transmission. It occurs in unmyelinated axons. Action potential is generated along the entire length of the axon. Hence, it takes time to generate and transmit action potential. Compared to salutatory conduction, continuous conduction is slow.
Which method of transmission of action potential is the fastest?
Therefore, salutatory conduction is the fastest method of transmission of the action potential. In contrast, continuous conduction takes place in unmyelinated axons. The action potential is generated along the entire length of the unmyelinated axon. Hence, it transmits nerve impulses slowly.
Is continuous conduction efficient?
Compared to salutatory conduction, continuous conduction is slow. Moreover, it utilizes more energy. Hence, it is a less efficient process. Furthermore, it delays nerve impulses since it uses a higher number of ion channels to generate an action potential.
Is nerve impulse continuous or saltatory?
Moreover, the nerve impulse travels between the nodes of Ranvier in saltatory conduction, while nerve impulse travels along the entire length of the axon in continuous conduction. Therefore, we can consider this too as a significant difference between saltatory and continuous conduction. Besides, energy expenditure is low in saltatory conduction ...