Why does glucose ferment faster? The control that contained no sugar produced no energy because a source of sugar is required for glycolysis
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO + H. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and N…
Why is fructose sometimes portrayed as better than sucrose?
Wherever fructose is portrayed as being better than sucrose, it's usually because fructose has a lower glycemic index. Many people mistakenly believe that the lower glycemic index makes it better for you. In actuality, fructose is worse than sucrose (half glucose, half fructose). Richard Talens covered many of the reasons in his answer.
Why is fructose considered a reducing sugar?
Fructose is a reducing sugar because it is a hemiketal. Whenever a ring forms it becomes a hemiacetal/hemiketal depending on the carbonyl carbon that is attacked. Sucrose is a non reducing sugar because the linkage is between two anomeric carbons whereas in maltose or lactose, the anomeric carbon of the second sugar is free and has a OH group ...
Does fructose have a strong effect on blood sugar?
Does fructose have a strong effect on blood sugar? Yes. Fructose has a low glycemic index and does not lead to the same spikes in blood sugar or insulin that result from glucose consumption. In addition, the excellent sweetness of fructose means that less of it is required to sweeten foods or beverages and this can translate to fewer calories ...
Why do most soft drinks contain fructose instead of glucose?
Most sodas are made with high fructose corn syrup. High fructose corn syrup is a sweetener derived from corn starch that is markedly cheaper than sugar. It has been reported to have negative effects on one’s blood sugar and may cause increased cravings for sugary foods and beverages.
Does glucose or fructose ferment faster?
Both these hexose sugars are present in unfermented wine must, mostly in equal concen- trations. As fermentation progresses, glucose is consumed at a faster rate than fructose, leading to an increase in the fructose to glucose ratio.
How does glucose affect fermentation?
Glucose concentration increases fermentation production in yeast, until the saturation gradient is reached causing a stop in carbon dioxide production (Hewitson and Hill, 2018).
Does glucose ferment faster than sucrose?
We decided that a monosaccharide's (glucose) rate of fermentation would increase more rapidly than a disaccharide's (sucrose) rate of fermentation. We organized a total of six trials, three for each solution, and compared the emission of CO₂ produced.
Is glucose easily fermented?
In order to verify this, we compared the rates of fermentation of glucose and galactose using yeast and found that in the presence of yeast glucose readily undergoes fermentation while no fermentation occurs in galactose.
Does glucose increase fermentation rate?
Glucose concentration increases fermentation production in yeast, until the saturation gradient is reached causing a stop in carbon dioxide production (Hewitson and Hill, 2018).
Why does glucose work the best with yeast?
Glucose is one of the important factors that affect the rate of respiration in yeast cells. During the process of respiration in yeast, the yeast cells use oxygen to release the energy from sugar or glucose. Therefore, more glucose affects the rate of respiration because glucose has a high rate of respiration.
Which carbohydrate ferments the fastest?
And that is the answer. The first one has the fastest fermented will be the glucose. The second is carbohydrate with the lowest gas production and slowest fermentation rate.
Does yeast prefer glucose or sucrose?
The researchers compared how both strains of yeast – free-living individuals and clumpers – fared in a weak sucrose solution. Yeast eats sucrose, but needs to break it down into glucose and fructose before it can get the food through its cell wall. To break the sucrose down, yeast produces an enzyme known as invertase.
Why does sucrose have the highest fermentation rate?
We hypothesize that sucrose and/or glucose will create a higher CO2 concentration over time in yeast fermentation because they have a simple chemical structure, making them easy to break down. Lactose is not as easily broken down in yeast fermentation due to yeast lacking the enzyme lactase which breaks lactose down.
What affects the rate of fermentation?
The rate of fermentation is influenced by several factors like temperature, type of sugar solution, concentration of yeast and concentration of glucose. In order to measure the rate of fermentation, the rate of production of carbon dioxide is measured in this experiment.
Why do monosaccharides ferment faster?
When two monosaccharides form a glycosidic bond, they become a disaccharide. By definition, monosaccharides contain fewer bonds than disaccharides, therefore, enzymes in yeast can break monosaccharides down faster.
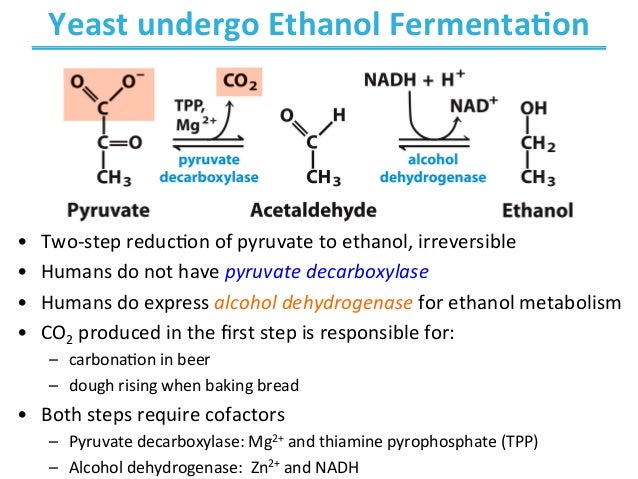
What is glucose fermentation?
fermentation, chemical process by which molecules such as glucose are broken down anaerobically. More broadly, fermentation is the foaming that occurs during the manufacture of wine and beer, a process at least 10,000 years old.
What is the process of converting sugar into alcohol?
In brewing, alcoholic fermentation is the conversion of sugar into carbon dioxide gas (CO2) and ethyl alcohol. This process is carried out by yeast cells using a range of enzymes. This is in fact a complex series of conversions that brings about the conversion of sugar to CO2 and alcohol. Yeast is a member of the fungi family which I like to think of as plants but strictly they are neither plant nor animal. To be specific yeast is a eukaryotic micro-organism. Not all yeasts are suitable for brewing. In brewing we use the sugar fungi form of yeast. These yeast cells gain energy from the conversion of the sugar into carbon dioxide and alcohol. The carbon dioxide by-product bubbles through the liquid and dissipates into the air. In confined spaces the carbon dioxide dissolve in the liquid making it fizzy. The pressure build up caused by C02 production in a confined space can be immense. Certainly enough to cause the explosion of a sealed glass bottle. Alcohol is the other by-product of fermentation. Alcohol remains in the liquid which is great for making an alcoholic beverage but not for the yeast cells, as the yeast dies when the alcohol exceeds its tolerance level. Overall chemistry of fermentation The overall process of fermentation is to convert glucose sugar (C6H12O6) to alcohol (CH3CH2OH) and carbon dioxide gas (CO2). The reactions within the yeast cell which make this happen are very complex but the overall process is as follows: C6H12O6 ====> 2 (CH3CH2OH) + 2 (CO2) + Energy (which is stored in ATP) Sugar ====> Alcohol + Carbon dioxide gas + Energy (Glucose) (Ethyl alcohol) From the above it seems nice an simple chemistry one mole of glucose is converted into two moles of ethanol and two moles of carbon dioxide but in reality it is far from this clear. There are many Continue reading >>
How does yeast work?
Yeast is most commonly used in the kitchen to make dough rise. Have you ever watched pizza crust or a loaf of bread swell in the oven? Yeast makes the dough expand. But what is yeast exactly and how does it work? Yeast strains are actually made up of living eukaryotic microbes, meaning that they contain cells with nuclei. Being classified as fungi (the same kingdom as mushrooms), yeast is more closely related to you than plants! In this experiment we will be watching yeast come to life as it breaks down sugar, also known as sucrose, through a process called fermentation. Lets explore how this happens and why! Click to find similar content by grade or subject. Fill all three dishes with about 2 inches of cold water Place your clear glasses in each dish and label them 1, 2, and 3. In glass 1, mix one teaspoon of yeast, cup of warm water, and 2 teaspoons of sugar. In glass 2, mix one teaspoon of yeast with cup of warm water. In glass 3, place one teaspoon of yeast in the glass. Observe each cups reaction. Why do you think the reactions in each glass differed from one another? Try using more of your senses to evaluate your three glasses; sight, touch, hearing and smell especially! The warm water and sugar in glass 1 caused foaming due to fermentation. Fermentation is a chemical process of breaking down a particular substance by bacteria, microorganisms, or in this case, yeast. The yeast in glass 1 was activated by adding warm water and sugar. The foaming results from the yeast eating the sucrose. Did glass 1 smell different? Typically, the sugar fermentation process gives off heat and/or gas as a waste product. In this experiment glass 1 gave off carbon dioxide as its waste. Yeast microbes react different in varying environments. Had you tried to mix yeast with sugar and c Continue reading >>
Why is glucose consumed faster in fermentation?
As fermentation progresses, glucose is consumed at a faster rate than fructose, leading to an increase in the fructose to glucose ratio. Yeast are left with the undesirable fructose at the later stages of fermentation, when the environmental stresses on the yeast can lead to stuck or sluggish fermentation.
What is the process of metabolizing sugar?
Best Answer: To metabolize sugar a process called Glycolysis will occur. Glucose is required for glycolysis , so if glucose is present there is no delay in the digestion of the sugar. In the case of fructose, which is a complex sugar, it must be broken down into Glucose before being digested.
What is the anaerobic respiration of yeast?
The anaerobic respiration of yeasts is what is used by bakers. Yeasts react at different rates to different sugars. Lactose, sucrose and maltose are disaccharides while glucose, fructose and galactose are monosaccharides. When yeast is added to sucrose, the sucrose gets broken... Different strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae are used by bakers ...
Which yeast uses glucose rather than fructose?
The glucophilic wine yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, preferentially uses glucose rather than fructose during fermentation so the glucose level declines faster than the fructose level. Residual sugar in wine is therefore made up of fructose.
What is the sugar utilization behavior of yeast?
Sugar Utilization Behavior Of Yeast (saccharomyces Cerevisae) Types And Doses On Bread Quality. The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisae is the most important ingredient of leavened products and is best known for its characteristic physiological property: the rapid fermentation of sugar to ethanol and carbon dioxide.
How does yeast use oxygen?
Yeast can use oxygen to release the energy from sugar (like you can) in the process called "respiration". So, the more sugar there is, the more active the yeast will be and the faster its growth (up to a certain point - even yeast cannot grow in very strong sugar - such as honey).
What is the process of aerobic cellular respiration?
5. Understand the process of aerobic cellular respiration The process by which cells release energy stored in carbohydrates is called cellular respiration. Although, the energy is stored in carbohydrates, the cell cannot directly use this energy.
Which sugar has the highest energy production?
Sucrose had the second-highest rate of production while fructose had the lowest rate out of the three sugars. Glucose ’s rate of energy production was more than three times that of fructose.
Which type of sugar produces the most carbon dioxide?
The different types of sugars used in fermentation had a significant impact on the amount of carbon dioxide produced. Glucose produced the most with a gas bubble of 132mm while sucrose yielded 102mm of carbon dioxide.
Why is the rate of carbon dioxide production skewed?
The data on the rate of carbon dioxide production was therefore skewed because the start of fermentation was not controlled. Glucose and sucrose appear far more efficient than fructose because of this error. If this experiment were to be repeated, extra care would be taken to ensure that fermentation began at the same time.
Does sucrose need energy?
Sucrose required an enzyme and energy input to break it down into glucose and fructose in order for it to be processed in glycolysis (Freeman, 189). Fructose also could not be used immediately in the glycolysis chain but had to be altered to enter the chain as one of the intermediates (Berg, 2002).
Is glucose the most efficient energy source?
Glucose’s rate of energy production was more than three times that of fructose. Glucose was directly used in the glycolysis cycle and did not require any extra energy to convert it into a usable form (Freeman, 154). This supported why glucose was the most efficient.
Is yeast added to fructose?
The yeast was added to the fructose solution well after the glucose and fructose yeast solutions began fermenting. Fermentation takes time to reach its maximum rate of energy production so the time gap left glucose and sucrose further ahead than fructose in the fermentation process (Berg, 2002).