Now, what happens is that when a molecule has to enter the cell it first has to interact with the polar part of the lipid membrane and then with the inner non-polar part of the membrane to pass through, hence if it is a polar molecule it will face repulsions and will not be able to pass through without the assistance of transmembrane proteins (it doesn't matter whether it is small or large, it simply won't), but, in the case of non-polar molecules, there is no repulsion from the fatty acid part of the phospholipids and hence it can pass through the membrane.
Why hydrophobic molecules can easily cross the plasma membrane?
Molecules that are hydrophobic can easily pass through the plasma membrane, if they are small enough, because they are water-hating like the interior of the membrane. The hydrophilic (polar) head group and hydrophobic tails (fatty acid chains) are depicted in the single phospholipid molecule. What can pass through the hydrophobic membrane?
Why do non polar molecules repel water molecules?
The force exerted by the van der Waals interactions is not strong enough to disrupt the hydrogen bonds between the water molecules. This means the non-polar molecules cannot insert themselves between water molecules and remain isolated, or insoluble, in water.
Can nonpolar substances cross a cell's membrane?
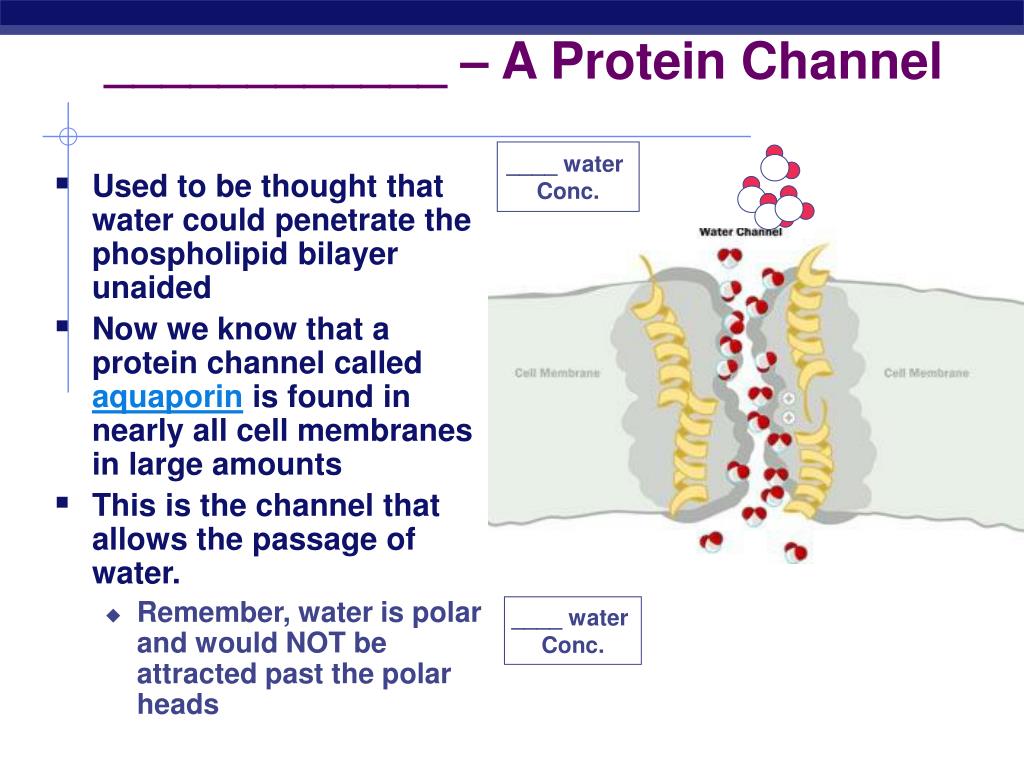
Small nonpolar molecules, such as O2 and CO2, are soluble in the lipid bilayer and therefore can readily cross cell membranes . Small uncharged polar molecules, such as H2O, also can diffuse through membranes, but larger uncharged polar molecules, such as glucose, cannot.
Why are nonpolar covalent bonds the strongest?
The strength of the covalent bond is due to the electrostatic attractive forces between the bonding electrons and the positive charges on the two nuclei, and such attractive forces outweigh the electrostatic repulsive force between the two nuclei.
Can nonpolar molecules pass through cell membrane?
Small nonpolar molecules, such as O2 and CO2, are soluble in the lipid bilayer and therefore can readily cross cell membranes. Small uncharged polar molecules, such as H2O, also can diffuse through membranes, but larger uncharged polar molecules, such as glucose, cannot.
Why do nonpolar molecules have a difficult time passing through the lipid bilayer?
Small, nonpolar molecules are hydrophobic, so they can easily cross the phospholipid bilayer of the plasma membrane. Polar molecules and ions are hydrophilic, so they cannot very easily cross the hydrophobic portion of the plasma membrane (formed by the phospholipid tails).
Is it easier for polar or nonpolar molecules to pass through the membrane?
Oxygen can pass through the cell membrane easily because of the nature of its small size! . To assist this particle across the cell membrane, the cell must expend energy. non-polar molecules can cross the cell membrane more easily than polar molecules.
Why can't polar molecules cross by simple diffusion?
Large polar or ionic molecules, which are hydrophilic, cannot easily cross the phospholipid bilayer. Charged atoms or molecules of any size cannot cross the cell membrane via simple diffusion as the charges are repelled by the hydrophobic tails in the interior of the phospholipid bilayer.
Why polar substances are impermeable through the plasma membrane?
The lipid bilayer is impermeable to entry of polar molecules Polar molecules and large ions dissolved in water cannot diffuse freely across the plasma membranedue to the hydrophobic nature of the fatty acid tails of the phospholipids that make up the lipid bilayer.
Why are membranes more permeable to nonpolar molecules?
Small, nonpolar molecules (ex: oxygen and carbon dioxide) can pass through the lipid bilayer and do so by squeezing through the phospholipid bilayers. They don't need proteins for transport and can diffuse across quickly.
How do non polar molecules get transported?
Nonpolar molecules can pass through the plasma membrane with relative ease. Even larger nonpolar molecules, such as steroid hormones, can pass through the plasma membrane easily. Passing through the membrane without the need for assisting proteins is known as passive diffusion.
How do cells transport polar and nonpolar molecules?
Small nonpolar molecules can easily diffuse across the cell membrane. However, due to the hydrophobic nature of the lipids that make up cell membranes, polar molecules (such as water) and ions cannot do so. Instead, they diffuse across the membrane through transport proteins.
How is a large, nonpolar molecule transported across the cell membrane?
A large, non-polar molecule will be transported across the cell membrane by a facilitated or simple diffusion?
What does it mean when a solute passes through a membrane?
The definition of passing through a membrane ususally means the solute starts in the aqueous phase on one side, partitions into the membrane, diffuses across and exits into the aqueous phase on the other side.
Why is the lipid bilayer impermeable?
The lipid bilayer is impermeable to entry of polar molecules Polar molecules and large ions dissolved in water cannot diffuse freely across the plasma membranedue to the hydrophobic nature of the fatty acid tails of the phospholipids that make up the lipid bilayer .
Why do proteins have nonpolar side chains?
It’s also the reason why membrane-spanning proteins have regions full of amino acids with non-polar side-chains corresponding to the part of the protein in contact with the hydrophobic lipid layer. Any part of a membrane protein that pokes out into the aqueous medium on either side is conversely rich in amino acids with charged and polar side-chains.
How are proteins associated with the membrane?
Different membrane proteins are associated with the membranes in different ways. Many extend through the lipid bilayer, with part of their mass on either side. Like their lipid neighbors, these transmembrane proteins are amphipathic, having regions that are hydrophobic and regions that are hydrophilic. Their hydrophobic regions pass through the membrane and interact with the hydrophobic tails of the lipid molecules in the interior of the bilayer, where they are sequestered away from water. Their hydrophilic regions are exposed to water on either side of the membrane. The hydrophobicity of some of these transmembrane proteins is increased by the covalent attachment of a fatty acid chain that inserts into the cytosolic monolayer of the lipid bilayer
Why does benzene diffuse across the lipid bilayer?
Substances that dissolve well in the lipid bilayer are likely to be similarly non-polar and this is why a molecule like benzene can diffuse across this barrier quite easily. It’s also the reason why membrane
What is the rule of thumb for solubility?
The simple rule of thumb for solubility is that “like dissolves like”. So polar and charged substances are more likely to dissolve in polar or charged solvents; non-polar substances are more likely to be able to dissolve in non-polar solvents.
What are the characteristics of the plasma membrane?
The plasma membrane consists of hydrophobic and hydrophillic characteristics. Towards the outsides, they are hydrophillic, so they can create bonds with water. The insides are hydrophobic, allowing no water inside and keeping them tight together due to the polar forces.
Can hydrophobic gases pass through a membrane?
So only hydrophobic (nonpolar), gases, and small particles (nonpolar) can pass through. There are exceptions of H 2 O passing through the membrane in small amounts because their electric charge is very minor.
Can polar particles move through the plasma membrane?
An non-polar particle (if small), can pass through this because it does not interfere with the hydrophobic/hydrophillic (polar) nature of the plasma membrane. However, polar particles would not have the opportunity to move in, because the insides (hydrophobic) are literally afraid of water, or charges, don't allow polar substances to pass through.
Why does a cell membrane pass through a nonpolar cell?
since it’s non polar, it passed through the cell membrane via carrier proteins. This is due to its hydrophobic exterior. Take note that cell surface membranes have a fluid mosaic model in which it has a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail.
What molecules can pass through the cell membrane?
Nonpolar and small polar molecules can pass through the cell membrane, so they diffuse across it in response to concentration gradients. Carbon dioxide and oxygen are two molecules that undergo this simple diffusion through the membrane. The simple diffusion of water is known as osmosis.
How does transport of polar and nonpolar molecules occur?
Transport of neutral and non-polar molecules occurs through phospholipid bilayer of cell membrane by simple diffusion. Transport of polar molecules occurs by facilitated diffusion and water transport occurs by osmosis. since it’s non polar, it passed through the cell membrane via carrier proteins.
Why do hydrophobic molecules diffuse through lipid bilayers?
One reason for the fact that hydrophobic molecules readily diffuse through lipid bilayers is that phospholipids, the principal components of most lipid bilayers, have relatively small hydrophilic head groups. Moreover, the associations between the individual membrane lipids are generally not very strong, giving most biomembranes a fluid-like character.
How do molecules cross the plasma membrane?
The simplest mechanism by which molecules can cross the plasma Membrane is passive Diffusion. During passive Diffusion, a molecule simply dissolves in the phospholipid Bilayer , diffuses across it, and then dissolves in the aqueous solution at the other side of the membrane.
Why is a molecule hydrophobic?
This is because it can form van der Waals interactions with the hydrocarbon tails of the phospholipids. This is the case with non-polar molecules like steroids, or water molecules, which are small enough to be able to pass through transient pores in the membrane.
How does water transport occur?
Transport of polar molecules occurs by facilitated diffusion and water transport occurs by osmosis.