- Given : Few Distributions Mean & Standard Deviation.
- To find : normal distribution which has the greatest standard deviation.
- Solution:
- => Distribution 4 has the greatest standard deviation.
- Graph at top has more spread hence more standard deviation :
Which normal distribution curve has the greatest standard deviation?
Both the normal distribution curves have sample mean equal to 16. Normal distribution curve 1 is more wider than Curve 2, resulting in greater standard deviation. So, Curve 1 has the greatest standard deviation.
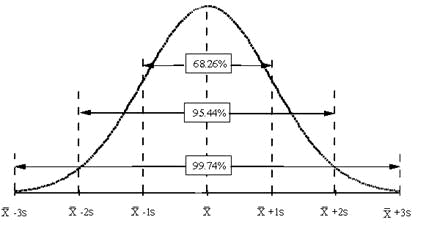
How many standard deviations is normal deviation from normal range?
likely to be within 1 standard deviation (68 out of 100 should be) very likely to be within 2 standard deviations (95 out of 100 should be) almost certainly within 3 standard deviations (997 out of 1000 should be)
How is the standard deviation connected to the distribution?
We know it’s the width of our distribution, but how is it connected to our data? The answer is σ is the standard deviation of your data, and it describes how spread out your data are: is it a wide fat distribution or a narrow skinny one. If you have a sample from some population, you calculate the standard deviation using the formula below:
What is a normal distribution in statistics?
Normal Distribution. Data can be "distributed" (spread out) in different ways. But there are many cases where the data tends to be around a central value with no bias left or right, and it gets close to a "Normal Distribution" like this: A Normal Distribution.
What is the vertical axis of probability density?
What is the central limits theorem?
About this website
How do you know which has the greatest standard deviation?
0:002:38Order Graphs of a Normal Distribution by Standard Deviation - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOrder the distributions by standard deviation from least to greatest. Where one has the smallestMoreOrder the distributions by standard deviation from least to greatest. Where one has the smallest standard deviation.
Which normal distribution has the greatest standard deviation edge?
Distribution A has the greater standard deviation because it is more spread out. In other words, the data points are farther from the mean.Jun 25, 2020
What is the standard deviation of the standard normal curve?
The standard normal distribution is a special case of the normal distribution. For the standard normal distribution, the value of the mean is equal to zero (μ=0), and the value of the standard deviation is equal to 1 (σ=1).
Normal Distribution Calculator with step by step explanation
Enter mean, standard deviation and cutoff points and this calculator will find the area under normal distribution curve. The calculator will generate a step by step explanation along with the graphic representation of the area you want to find.
What is the vertical axis of probability density?
What is meant by the vertical axis: probability density? It means that the probability of a measurement falling within a particular range is given by the area under the curve (integral in calculus language) corresponding to that range. In the figure below, the range from 50 to 60 is shaded. This region visually represents the probability of a measurement falling between 50 and 60. Now you can see why the area underneath the entire curve must be one: the probability of something happening must be 100%.
What is the central limits theorem?
The central limits theorem says that with independent random variables or independent measurements such as. the independent coins that you have in your lab. the independent pegs that the balls hit on the way down the plinko-board. if you have a lot of them, the result will tend towards a normal distribution.
How long is the mean of a standard deviation?
The Mean is 38.8 minutes, and the Standard Deviation is 11.4 minutes (you can copy and paste the values into the Standard Deviation Calculator if you want). Convert the values to z-scores ("standard scores"). To convert 26:
How to convert a standard deviation to a standard score?
So to convert a value to a Standard Score ("z-score"): first subtract the mean, then divide by the Standard Deviation. And doing that is called "Standardizing": We can take any Normal Distribution and convert it to The Standard Normal Distribution.
What is the vertical axis of probability density?
What is meant by the vertical axis: probability density? It means that the probability of a measurement falling within a particular range is given by the area under the curve (integral in calculus language) corresponding to that range. In the figure below, the range from 50 to 60 is shaded. This region visually represents the probability of a measurement falling between 50 and 60. Now you can see why the area underneath the entire curve must be one: the probability of something happening must be 100%.
What is the central limits theorem?
The central limits theorem says that with independent random variables or independent measurements such as. the independent coins that you have in your lab. the independent pegs that the balls hit on the way down the plinko-board. if you have a lot of them, the result will tend towards a normal distribution.