Carbon–carbon multiple bonds are generally stronger; the double bond of ethylene Ethylene is a hydrocarbon which has the formula C₂H₄ or H₂C=CH₂. It is a colorless flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene.Ethylene
Acetylene
Acetylene is the chemical compound with the formula C₂H₂. It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in its pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution. Pure acetylene is odorless, but commer…
Which carbon carbon bond is the strongest?
Furthermore, which carbon carbon bond is strongest? The bond is labeled as "the strongest in organic chemistry," because fluorine forms the strongest single bond to carbon. Carbon–fluorine bonds can have a bond dissociation energy (BDE) of up to 544 kJ/mol.
Which Bond is the strongest single or triple bond?
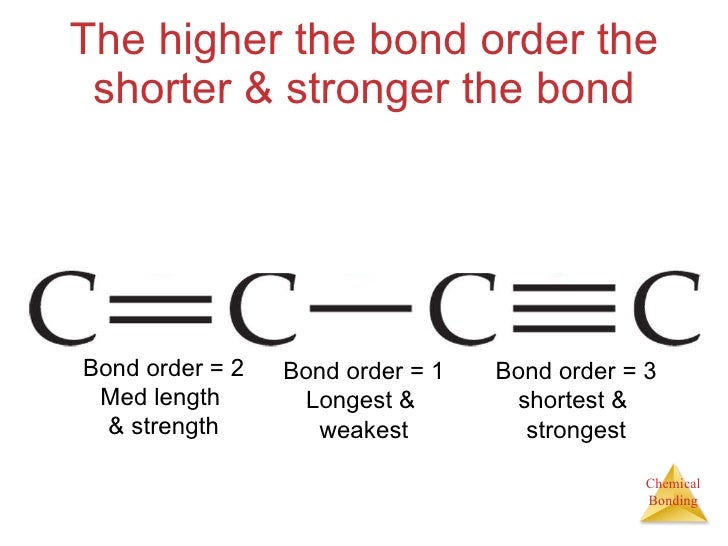
Sigma bond is strong one! But when we compare three bonds then triple bond is the strongest followed by double and then single because triple has sigma along with two pi bonds, double has one sigma with one pi and lastly single has just one sigma so interms of stability. Triple > double >single.
What is a triple bond of carbon called?
Triple bond of carbon is called Alkyne. The types of bonding can be explained in terms of orbital hybridization. In the case of acetylene each carbon atom has two sp orbitals and two p-orbitals. The two sp orbitals are linear with 180° angles and occupy the x-axis ( cartesian coordinate system ).
What are the bond energy values for carbon-carbon single double and triple bonds?
The bond energy values for the carbon-carbon single, double and triple bonds approximately are 346, 598 and 813 kJ/mole respectively. , studied at Srinivasa Vidhyalaya Matric Higher Secondary School, Udumalpet. Single bond is a sigma bond. In double bond one is sigma and another is pi bond.
Which bond is the strongest in organic chemistry?
The bond is labeled as "the strongest in organic chemistry," because fluorine forms the strongest single bond to carbon. Carbon–fluorine bonds can have a bond dissociation energy (BDE) of up to 544 kJ/mol. The BDE (strength of the bond) is higher than other carbon–halogen and carbon–hydrogen bonds. Beside above, which bond is ...
How many bonds does a carbon have?
These orbitals will overlap with each other, so each carbon forms 3 bonds with other carbons to form a hexagonal layer. The carbons form only three bonds because they are sp 2 hybridized (hence the -ene suffix).
What is triple bond?
A triple bond involves the sharing of six electrons, with a sigma bond and two [latex]pi latex] bonds. &] The simplest triple-bonded organic compound is acetylene, C2H2. Triple bonds are stronger than double bonds due to the the presence of two [latex]pi [/latex] bonds rather than one. Click to see full answer.
Which functional group has a triple bond?
The most common triple bond, that between two carbon atoms, can be found in alkynes. Other functional groups containing a triple bond are cyanides and isocyanides. Some diatomic molecules, such as dinitrogen and carbon monoxide, are also triple bonded.
What is triple bond?
A triple bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two atoms involving six bonding electrons instead of the usual two in a covalent single bond. Triple bonds are stronger than the equivalent single bonds or double bonds, with a bond order of three. The most common triple bond, that between two carbon atoms, can be found in alkynes. Other functional groups containing a triple bond are cyanides and isocyanides. Some diatomic molecules, such as dinitrogen and carbon monoxide, are also triple bonded. In skeletal formulae the triple bond is drawn as three parallel lines (≡) between the two connected atoms.
How many orbitals does acetylene have?
In the case of acetylene each carbon atom has two sp-orbitals and two p-orbitals. The two sp-orbitals are linear with 180° angles and occupy the x-axis ( cartesian coordinate system ). The p-orbitals are perpendicular on the y-axis and the z-axis.
Overview
A carbon–carbon bond is a covalent bond between two carbon atoms. The most common form is the single bond: a bond composed of two electrons, one from each of the two atoms. The carbon–carbon single bond is a sigma bond and is formed between one hybridized orbital from each of the carbon atoms. In ethane, the orbitals are sp -hybridized orbitals, but single bonds formed between carbon atoms with other hybridizations do occur (e.g. sp to sp ). In fact, the car…
Chains and branching
Carbon is one of the few elements that can form long chains of its own atoms, a property called catenation. This coupled with the strength of the carbon–carbon bond gives rise to an enormous number of molecular forms, many of which are important structural elements of life, so carbon compounds have their own field of study: organic chemistry.
Synthesis
Carbon–carbon bond-forming reactions are organic reactions in which a new carbon–carbon bond is formed. They are important in the production of many man-made chemicals such as pharmaceuticals and plastics.
Some examples of reactions which form carbon–carbon bonds are aldol reactions, Diels–Alder reactions, the addition of a Grignard reagent to a carbonyl group, a Heck reaction, a Michael reaction
Extreme cases
Various extreme cases have been identified where the C-C bond is elongated. In Gomberg's dimer, one C-C bond is rather long at 159.7 picometers. It is this bond that reversibly and readily breaks at room temperature in solution:
In the even more congested molecule hexakis(3,5-di-tert-butylphenyl)ethane, the bond dissociation energy to form the stabilized triarylmethyl radical is only 8 k…
See also
• Carbon–hydrogen bond
• Carbon–oxygen bond