Merchants
- More like traders.
- Mudbrick house.
- Trades through barter.
- Goods included:
- vegetables, fish, sycamore figs, drinking cups, drink, and cloths.
- on special days: giraffes, baboons, or lions.
- Goods were set up in baskets.
- Crouched with their baskets.
- Trade beyond local trades were done by wholesale merchants who act for the Pharaoh or for large temples.
What did craftspeople and merchants do in ancient Egypt?
Who were the two most important Egyptian gods goddesses?
- AMUN-RA: The Hidden One.
- MUT: The Mother Goddess.
- OSIRIS: The King of the Living.
- ANUBIS: The Divine Embalmer.
- RA: God of the Sun and Radiance.
- HORUS: God of Vengeance.
- THOTH: God of Knowledge and Wisdom.
- HATHOR: Goddess of Motherhood.
What are facts about ancient Egyptian merchants?
Merchants
- More like traders.
- Mudbrick house.
- Trades through barter.
- Goods included:
- vegetables, fish, sycamore figs, drinking cups, drink, and cloths.
- on special days: giraffes, baboons, or lions.
- Goods were set up in baskets.
- Crouched with their baskets.
- Trade beyond local trades were done by wholesale merchants who act for the Pharaoh or for large temples.
What were the noblemen tools of trade in ancient Egypt?
What were noblemen jobs and responsibilities in ancient Egypt? Nobles in Egyptian society were related to the pharaoh, priests, scribes, doctors, lawyers, or important military personnel. Many of the nobles were overseers of the lands worked by peasants. Taxes from these lands were paid to the government in the form of crops or cattle.
What did the craftsmen do in ancient Egypt?
What did craftsmen do in their free time in ancient Egypt? The Craftsmen and workers lived in a simple house in a neighborhood of many other Workers. On their free time they played a board game called senit. Their jobs were to build new temples for the Pharaoh and go to meetings. The Craftsmen had a day full of hard work and building.
Why were merchants important in ancient Egypt?
For social ranking, merchants were right under scribes in importance. They were respected. The ancient Egyptians bought goods from merchants. They traded goods through their shops and in the public marketplaces.
What class were merchants in ancient Egypt?
The middle classThe middle class was made up chiefly of merchants, manufacturers, and artisans.
What did merchants do in ancient civilizations?
The merchant is an agent dedicated to the procurement, movement, and exchange of goods. The more vital resource movement is in meeting provisioning needs, the more important the role of merchant traders becomes within society.
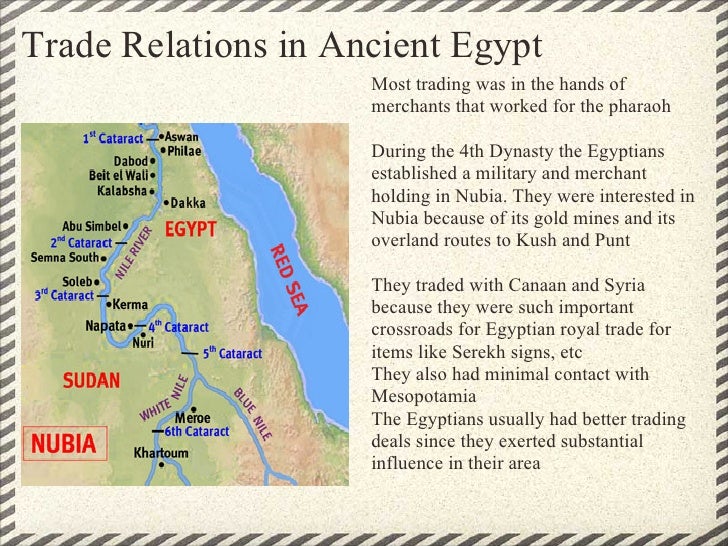
Who did Egyptian merchants trade with?
Egypt also traded with Anatolia for tin and copper in order to make bronze. Mediterranean trading partners provided olive oil and other fine goods. Egypt commonly exported grain, gold, linen, papyrus, and finished goods, such as glass and stone objects. Depiction of Queen Hatshepsut's Expedition to Punt.
What do merchants do?
A merchant is a person who trades in commodities produced by other people, especially one who trades with foreign countries. Historically, a merchant is anyone who is involved in business or trade. Merchants have operated for as long as industry, commerce, and trade have existed.
What was the importance of merchants?
Merchants specifically, played a vital role in the building of extensive networks of exchange of not only goods but of knowledge, ideas, cultures and beliefs.
What is a meaning of merchant?
Definition of merchant (Entry 1 of 3) 1 : a buyer and seller of commodities for profit : trader. 2 : the operator of a retail business : storekeeper. 3 : one that is noted for a particular quality or activity : specialist a speed merchant on the base paths.
Where did merchants live in ancient Egypt?
Egypt had a trading colony in Canaan, a number in Syria, and even more in Nubia. The Egyptians had already graduated from building papyrus reed boats to ships of wood and these were sent regularly to Lebanon for cedar.
What did craftsmen and merchants do in ancient Egypt?
Most craftsman would work as sculptures, metal workers, painters and stone cutters. These were the most important jobs that craftsmen would have, and architecture played a huge role in this as well. Most craftsmen would work together in workshops that were considered official.
Who were the peasants and servants?
The majority of peasants worked in the fields producing crops, while some worked as servants in the homes of wealthy nobles. During the flooding season, which lasted up to three months, peasants often worked on large building projects for the government. Slaves were most commonly prisoners of war.
What did Egyptian merchants trade?
Some merchants would exchange native products like gold, papyrus, linen cloth, and jewelry for cedar, ebony wood, and panther skins.
Why did merchants return to Egypt?
The merchants would return to Egypt to trade these items to the high class in exchange for grains and other goods. Farmers and fisherman could double as a merchant and sell their fish and other produce at the local market.
What did merchants wear in ancient Egypt?
Merchants spent most of their time in the sun and were required to wear human hair wigs, and protective makeup. Good craftsmen were appreciated in ancient Egypt. They usually lived comfortable lives. They were used to build or craft objects from jewlery to tables and even boats.
What were craftsmen paid for?
Craftsmen were not paid with money but with goods such as grain, vegetables, fish, milk and firewood.
What were the jobs of servants in ancient Egypt?
Jobs for servants in ancient Egyptcould include cooking, cleaning, running errands, babysitting children. Though being a servant was definitely one of the ancient Egypt jobs done by peasants, it was relatively comfortable.
What was the economy of Ancient Egypt?
Just like in any other civilization, the economy of Ancient Egypt relied on a variety of skilled and unskilled labor. There were many different careers available in Egypt, ranging from breaking rocks in mines to making scientific discoveries in a university. Over the course of 3,000 years, the ancient Egyptian empire remained remarkably stable. The same basic jobs were an essential part of ancient Egyptian civilization throughout the centuries.
What were the craftsmen responsible for?
Craftsmen were responsible for most of the beautiful goodsthat Egypt is known for in modern times. They made the sculptures and beautiful gold jewelry that was found in Egyptian tombs. A craftsman who made fine goods for the nobility was very well off, but even more common craftsmen who made cooking pots or wove clothing lived a comfortable life. Most craftsmen resided in cities and sold their items in family shops or at markets.
How did the Egyptian bureaucracy work?
The vast Egyptian bureaucracyneeded a lot of workers to run efficiently. A vizier collected taxes and reported directly to the king. Most villages were run by a governor or overseer who reported to the vizier. Huge armies of scribes worked underneath overseers to keep records of taxes and laws.
What was the middle class in Egypt?
Unlike many other countries where everyone was either a peasant or a nobleman, Egypt had a very large middle class. These people tended to live in cities or on small country estates. They made a decent amount of money from skilled labor, so they could afford to buy food and other items instead of making it themselves.
What crops did the Nile floods produce?
After each yearly flood of the Nile, farmers waited until the waters receded to plant their crops. The most common crops were wheat, corn, and barley. Farmers also planted vegetables, melons, pomegranates, figs, and flax.
Who took over the family business in Egypt?
Most Egyptians followed in their parents footsteps and took over the family business.