| Name of Muscle | Action |
|---|---|
| Iliocostalis | Extends and flexes laterally vertebral column |
| Longissimus | Extends and flexes laterally vertebral column |
| Spinalis | Extends vertebral column |
| Semispinalis | Extends neck and vertebral column |
Which muscle is responsible for flexion of the vertebral column?
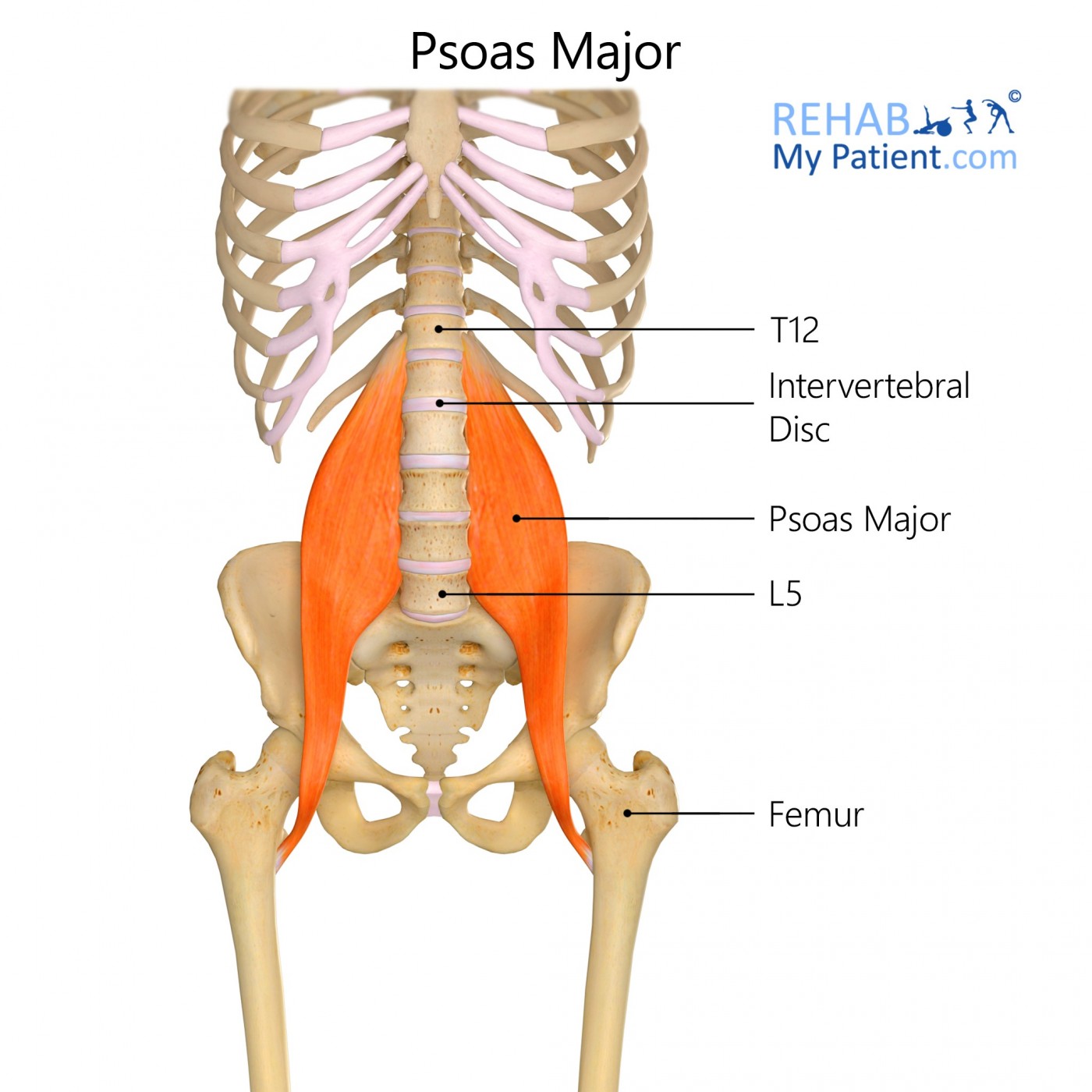
Psoas major is innervated by the L1-L3 spinal nerve. The second muscle in this group is psoas minor which originates on the vertebrae and intervertebral discs of T12-L1 and inserts on the iliopectineal arch. This muscle causes flexion, lateral flexion of the spine and upward rotation of the pelvis.
Which of the following muscles flexes the vertebral column quizlet?
Rectus abdominis. Arises from the superior surface of the pubis and inserts into the costal cartilages of ribs 5-7/ It depresses the ribs, flexes the vertebral column and compresses the abdomen. It is supplied by nerves deriving from the anterior rami of the spinal nerves.
What muscle moves the vertebral column?
The erector spinae groupThe erector spinae group forms the majority of the muscle mass of the back and it is the primary extensor of the vertebral column. It controls flexion, lateral flexion, and rotation of the vertebral column, and maintains the lumbar curve.
What is flexion of the vertebral column?
The principal movements permitted by the vertebral column are: flexion (bending forward), extension (bending backwards), lateral flexion (bending right/left), and rotation (torsion/twisting).
Which muscle flexes the vertebral column and compresses the abdomen?
beside the rectus abdominis. Flexes vertebral column, compresses the abdomen and laterally flexes and rotates vertebral column when only one contracts.
What are the erector muscles?
The erector spinae muscles include: iliocostalis, longissimus, and spinalis. Each of these muscles can be divided into three sections. We have iliocostalis cervicis, iliocostalis thoracis, and iliocostalis lumborum.
Which is the strongest flexor of the vertebral column?
As one of the primary movers in spine flexion, the rectus abdominis also helps to flex the vertebral column and bring the pelvis forward. The internal and external obliques are the other primary movers in spine flexion.
What does the latissimus dorsi do?
Latissimus dorsi works collaboratively with the teres major and pectoralis major to perform actions of the upper extremity. Together, these muscles will work to adduct, medially rotate, and extend the arm at the glenohumeral joint.
What muscles flex the cervical spine?
The scalene muscles help with neck flexion and side bending. The deep cervical flexors are a muscle group consisting of the longus capitus and longus colli muscles, which run down the front of the cervical spine. The deep cervical flexor muscles help flex the neck forward as well as stabilize the cervical spine.
What is the multifidus muscle?
The Multifidus muscle is a series of small, triangular muscular and tendinous bundles located on either side of the spinal column, where they fill the groove between the transverse and spinous processes of the vertebrae.
Is erector spinae a muscle?
The erector spinae muscles comprise the intermediate layer of the deep (intrinsic) muscles of the back. They extend on either side of the vertebral column, between the base of the cranium superiorly and pelvis inferiorly. The erector spinae are divided into three groups, from medial to lateral: Spinalis muscles.
What motion is the erector spinae responsible for?
Definition. Erector spinae muscles or paraspinal muscles run vertically along the spinal vertebrae and work to stabilize the back from the lower sacral to the cervical vertebrae and enable spinal flexion, extension, and rotation.
What is the term for the extension of the vertebral column?
Iliocostalis Lumborum. Extension, lateral flexion of vertebral column, rib rotation. Dorsal primary divisions of spinal nerves. Muscle Fascia. Fascia is thickened connective tissue that envelops a muscle or a group of muscles. Superficial fascia is found directly under the skin.
Which connective tissue divides muscle fibers into fascia?
Superficial fascia is found directly under the skin. Epimysium is the fascia closest to the muscle. Perimysium divides the muscle into facicles – muscle fibers.
What are the functions of muscles?
Muscles are named according to their shape, location, or a combination. They are further categorized according function such as flexion, extension, or rotation. Muscles and ligaments work together to support the spine, hold it upright, and control movement during rest and activity. Skeletal muscle is striated (striped) in appearance.
Which muscle has the fastest contraction rate?
Skeletal muscle is striated (striped) in appearance. It is innervated, under voluntary control, and has the fastest contraction rate of all muscle. Prior to a muscle contracting, a nerve impulse originates in the brain and travels through the spinal cord to the muscle.
What is the energy needed for muscle contraction?
Energy is needed for the muscle to contract (work). Mitochondria (cellular level) produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate), a chemical cells need for energy. ATP is produced as the mitochondria burn glucose (sugar). Blood vessels deliver the oxygen and nutrients the mitochondria needs to provide a steady supply of ATP. 1.
What are the muscles of the lumbar spine?
The muscles of the lumbar spine/trunk can be divided into posterior and anterior groups. Although this division is not perfect (e.g., the external and internal abdominal oblique muscles of the anterior abdominal wall attach all the way around to the posterior abdominal wall), it is a good beginning framework.
Which muscle has a horizontal fiber?
Muscles that perform right or left rotation must have a horizontal component to their fiber direction; in fact, it can be helpful to view them as partially “wrapping” horizontally around the trunk. Thus, considering the fiber direction of a trunk muscle is important when determining its rotational ability.
What are the three groups of transversospinalis?
The transversospinalis is composed of three groups: semispinalis, multifidus, and rotatores (the semispinalis does not attach into the lumbar spine). The multifidus and semispinalis are shown on the left side, and the rotatores are shown on the right side. Note: The multifidus is the largest muscle of the lumbar spine.
What does a lumbar therapist need to know?
Furthermore, the therapist needs to know the mover actions of the muscles of the lumbar spine. Knowing the mover actions allows the therapist to ask the client to contract and engage the target muscle so that it palpably hardens.
Which spinae extends, laterally flexes, and ipsilaterally rotates the trunk
As a group, the erector spinae extends, laterally flexes, and ipsilaterally rotates the trunk at the spinal joints. It also anteriorly tilts and contralaterally rotates the pelvis and elevates the same-side pelvis at the lumbosacral joint. Figure 20. Posterior view of the transversospinalis musculature.
Where are the multifidus and rotatores located?
The multifidus and rotatores of the transversospinalis group in the trunk lie within the laminar groove of the lumbar and thoracic spine. The multifidus attaches from the sacrum and PSIS and the mammillary processes of the lumbar spine and transverse processes of the thoracic spine to the spinous processes of vertebral segments three to four levels superior to the inferior attachment. The rotatores attach from transverse processes of the lumbar and thoracic spine to vertebral segments one to two levels superior to the inferior attachment.
Where is the erector spinae located?
The erector spinae in the trunk and pelvis attaches from the sacrum, medial iliac crest, vertebral transverse and spinous processes, and angles of ribs to angles of ribs and transverse and spinous processes of vertebrae above.