Primary or Main Functions of Roots:
- Anchorage: Roots take part in fixation of the plant and supporting the aerial shoot system. ADVERTISEMENTS:
- Absorption of Water: Roots absorb water from soil.
- Absorption of Minerals: Roots absorb mineral salts from soil. ADVERTISEMENTS:
- Prevention of Soil Erosion: Roots hold the soil particles firmly to prevent soil erosion.
- Transport:
What is the main function of a root system?
What are the Main Functions of the Root System in a Plant
- Put a carrot in a glass of water containing some blue colouring agent.
- Leave the carrot in water for some days.
- Then cut it into half (lengthwise) and look inside.
What are the three types of root systems?
Types of Root System
- Taproot system. In this root system, there is a primary root that grows directly from the radicle. ...
- Fibrous root system. ...
- Adventitious root system. ...
- Prop roots. ...
- Stilt roots. ...
- Storage roots (Root tubers) These roots are meant to store reserve food material for the availability of the plant latter. ...
- Pneumatophores. ...
Does rootx really work?
RootX kills roots on contact. The dead roots decay over time and are carried out with the flow of the pipe, restoring the pipe to its full capacity. RootX also leaves a barrier on the pipe walls to prevent future root growth.
What is the definition of root system?
What does root system mean? Here are all the possible meanings and translations of the word root system. In mathematics, a root system is a configuration of vectors in a Euclidean space satisfying certain geometrical properties. The concept is fundamental in the theory of Lie groups and Lie algebras.
What are the functions of root system?
The functions of root are as follows:Anchoring of the plant to the soil.Absorption of water and nutrients from the soil.Conduction of absorbed water and nutrients to stem.Storage of food.Vegetative reproduction and competition with other plants.
What is the function of primary and secondary roots?
Roots perform two kinds of function namely primary and secondary function. The primary functions are performed by all the roots in general. In some plants the roots perform certain additional functions in order to meet some special needs. These are called secondary functions of the roots.
What are the four function of root?
It fixes the plant in the soil. Absorbs water and minerals from the soil for the entire plant. It acts as a storage part for food materials for certain plants. It binds the soil together so that it does not get washed away during rain or blown over by the wind.
What are the functions of roots and stem?
The roots of a plant take up water and nutrients from the soil. They also anchor the plant to the ground and keep it steady. The stem carries water and nutrients to different parts of the plant. It also provides support and keeps the plant standing upright.
What is the root of a flower called?
If you picked a flower for someone special, it was most likely a tap root system attached below the stem. A main root, called the tap root, grows downward. Smaller roots then grow out horizontally from the tap root and eventually turn downward into the soil.
What are the layers of the root system?
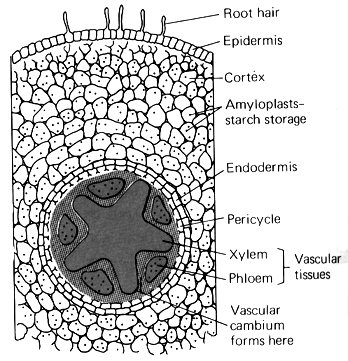
Each root is made up of three layers (epidermis, cortex and vascular cylinder) that work together to bring nutrients to and from the stem to keep each plant alive and healthy. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Create your account.
What is the outer layer of the root called?
The outside of the root is called the epidermis and is where water and nutrients are absorbed. The cortex is the middle layer. It acts like a small secret passageway that carries the water and minerals from the epidermis, inward, to the center of the root.
Where are fibrous roots found?
A fibrous root system can be found in plants such as grasses, lilies, and palm trees. The roots grow outward and downward directly from the stem. There are three main layers to a root. The outside of the root is called the epidermis and is where water and nutrients are absorbed.
Why do plants need roots?
A plant needs its roots in order to survive. The root system of a plant is typically found underground and has many different jobs. One of the main jobs of the root system is to anchor and support the plant in the soil.
What is the inner layer of a plant?
The vascular cylinder is the inner layer and is made up of small tubes that transport the water and nutrients both ways, up and down the plant. Roots Above the Ground. Watch your step! Aerial roots are roots that grow above the ground and across the land before they go down into the soil.
Who is the instructor for the plant roots lesson?
Instructor: Debra Patuto. Show bio. Debra has taught at elementary levels and has an M.ed with certification in elementary education and special education. Although they are mostly hidden underground, roots are an essential part of a plant. In this lesson, you'll learn all about plant roots and just what makes them so important.
Modifications of Roots
Roots may be modified to perform special functions like storage of food, support, and respiration apart from the normal functions. These modifications are found both in tap and adventitious roots.
Summary
The root is the non-green, underground part of the plant body. It develops from the radicle of the embryo. The roots are divided into taproot, fibrous root, and adventitious root. The different root regions are root cap, meristematic region, region of cell elongation, and region of maturation.
FAQs
Q.1. What are roots? Ans: The roots are the underground organ found in vascular plants that helps to absorb water and mineral nutrients from the soil.
Why is the root system important?
The root system is very important for the plant as it is branched and extended through the soil particles to fix the plant in the soil. The root system covers a large area of the soil to search for the water and the mineral salts that the plant needs, then absorbs them from the soil by the root hairs, and raises them to the other parts ...
How does the root system help plants survive?
The root system absorbs the water and the minerals from the environment, It anchors the plant in the ground, and it stores the food that has been made in the leaves by the photosynthesis process, So, the food can be used later by the plant to grow and survive.
What are the layers of the root system?
The root is subdivided and extended through the soil particles, it is composed of a number of the layers which are the epidermis layer, the cortex layer, the xylem (wood) layer and the pith layer.
What is the structure of a plant?
The plant structure. The plant consists of the root system and the shoot system, The root system consists of the roots, The shoot system consists of the leaves and the stems, The plant takes the raw materials from the environment to make its food by the photosynthesis process.
What is the role of mycorrhiza in plants?
Mycorrhiza: The roots of several plants are associated with fungi to form mycorrhiza. Mycorrhiza helps the plant in absorption of phosphorus and nitrogen from organic sources and protects the plants from attack of pathogenic fungi. 14. Growth Regulators: Roots synthesize certain growth regulations like cytokinins.
What are the free floating plants?
Free floating plants usually possess a cluster of adventitious roots from their nodes and bases to help in balancing the plants over the water surface, e.g., Lemna, Pistia, Eichhornia. 11. Photosynthesis: As in Trapa, Taeniophyllum, Tinospora, Podostemum.
How do roots help prevent soil erosion?
Prevention of Soil Erosion: Roots hold the soil particles firmly to prevent soil erosion. 5. Transport: They take part in transport of absorbed water and minerals to shoot system. Similarly, root has channels for the flow of organic food from aerial parts.
What are the functions of roots?
Primary or Main Functions of Roots: 1. Anchorage: Roots take part in fixation of the plant and supporting the aerial shoot system. ADVERTISEMENTS: 2. Absorption of Water: Roots absorb water from soil. 3.
Why do some plants not have roots?
Rootless Plants: Many plants growing in aquatic habitats do not possess roots because there is little requirement for absorption of water and mineral salts , e.g., Wolffia, Utricularia, Myriophyllum, Ceratophyllum.
What is the difference between a dicot root and a monocot root?
The main difference between monocot and dicot root is that the dicot root contains xylem in the middle and phloem surrounding the xylem. Whereas in monocot root, xylem and phloem are arranged circularly.
What are fibrous roots?
Fibrous roots, on the other hand, are bushy roots in which thin, moderately branching roots grow from the stem. Rice, wheat, maize, marigold, banana and all monocotyledons are some examples of the fibrous root system.
What are the primary roots of a plant?
Primary roots are the early roots in young plants that consist of taproots, basal roots, and lateral roots. Secondary roots are the side branches of the primary roots.
What is the root of a plant?
What are Roots? Roots are the important underground part of all vascular plants. This part of the plant is mainly responsible for anchoring it down into the ground and absorbing the essential mineral elements, nutrients, and water from the soil. It is also used to store food.
What are aerial roots? What are some examples?
Few examples of plants with the aerial roots are–Bonsai, Banyan Tree, Mangroves , etc.
What is the root system of plants?
Root System. The plants that we see today is the result of billions of years of evolution. Today, plants cover almost 30 per cent of the total landmass and account for the 50 per cent of the plant’s productivity (generation of biomass). Plants fulfil many roles in the ecosystem.
What are some examples of plants that are vegetative?
Storage: Plants prepare food and store in the form of starch in the leaves, shoots and roots. Prominent examples include carrots, radish, beetroot, etc. Reproduction: Even though roots are not the reproductive part of plants, they are vegetative parts.
Characteristics of The Root
Types of Roots
Regions of The Root
- A root is differentiated into four regions: 1. Root cap: 1. i. A thickened, protective cap-like structure is present at the root apex. 2. ii. The root cap cells secrete mucilage (mucus), which lubricates the passage of the root through the hard soil. 3. iii. In some aquatic plants, the root pockets are present. 2. Meristematic region: 1. i. It is situated behind the root cap. 2. ii. This region is made u…
Modifications of Roots
- Roots may be modified to perform special functions like storage of food, support, and respiration apart from the normal functions. These modifications are found both in tap and adventitious roots. (i) Taproot: (a) Conical Root:When the root is swollen at the base and gradually tapers towards the apex, it is said to be conical. Example: Carrot (Daucus carota). (b) Fusiform Root:Th…
Functions of Roots
- The Primary and Secondary functions of roots are as follows: A. Primary functions: (i) Roots help in the fixation and absorption of water and minerals from the soil. (ii) Roots help in the upward movement of the absorbed water and minerals into the stem. (iii) Roots penetrate the soil and provide support to plants. B. Secondary functions: (i) Roots...
Summary
- The root is the non-green, underground part of the plant body. It develops from the radicle of the embryo. The roots are divided into taproot, fibrous root, and adventitious root. The different root regions are root cap, meristematic region, region of cell elongation, and region of maturation. Roots help in the soil’s fixation and absorption of water and minerals. Roots may be modified to …
FAQs
- Q.1. What are roots? Ans: The roots are the underground organ found in vascular plants that helps to absorb water and mineral nutrients from the soil. Q.2. Where are root hairs present in the root? Ans:The root bears unicellular root hairs in the zone of maturation. Q.3. Mention the types of roots. Ans:The main types of roots are taproot, fibrous root, and adventitious root. Q.4. Write th…