What is the mechanism of action of biguanides Quizlet?
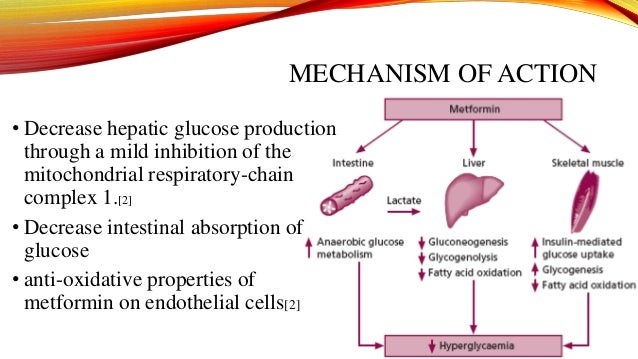
What is the mechanism of action of biguanides? Biguanides stimulate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) thereby decreasing blood glucose concentrations by several different actions. They decrease hepatic gluconeogenesis, improve tissue sensitivity to insulin, increase peripheral glucose uptake and use, and decrease intestinal absorption of glucose.
What are biguanides used for?
Biguanides. The only available biguanide medication is metformin, which is commonly used as a first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes (i.e. the first option for type 2 diabetics who are unable to control their blood sugars through diet and exercise alone). Metformin is usually prescribed as a single treatment (monotherpay),...
What are the possible adverse effects of biguanides?
Because biguanides do not increase insulin levels, they are not associated with a significant risk of hypoglycemia. The most common adverse events are gastrointestinal: nausea, abdominal pain or bloating, and diarrhea. Up to a third of patients have some gastrointestinal distress, especially early in their course of treatment.
What is the absorption profile of biguanides?
Biguanides, particularly the widely prescribed drug metformin, have been marketed for many decades and have well-established absorption profiles. They are commonly administered via the oral route and, despite variation in oral uptake, remain commonly prescribed for diabetes mellitus, typically type 2.
What is metformin mechanism of action?
The centre of metformin's mechanism of action is the alteration of the energy metabolism of the cell. Metformin exerts its prevailing, glucose-lowering effect by inhibiting hepatic gluconeogenesis and opposing the action of glucagon.
What is the mechanism of action for biguanides such as metformin?
Metformin has been shown to act via both AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-dependent and AMPK-independent mechanisms; by inhibition of mitochondrial respiration but also perhaps by inhibition of mitochondrial glycerophosphate dehydrogenase, and a mechanism involving the lysosome.
What is the mechanism of action of biguanides and thiazolidinediones?
BIGUANIDES AND THIAZOLIDINEDIONESDRUG NAMEmetformin (Glucophage, Glucophage XR, Fortamet, Glumetza, Riomet)CLASSBiguanidesMECHANISM OF ACTIONDecrease blood glucose levels by increasing insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake by muscle and fat cells inhibiting gluconeogenesis by liverINDICATIONSType 2 diabetes mellitus3 more rows
What is the use of biguanides?
Biguanides are used as an oral drug for the management of mild to moderately severe noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, or NIDDM, (Type II) in obese or overweight patients who are usually above 40 years of age. It is important that for the administration of this drug the disease should have adult onset.
How do biguanides work on diabetes?
Biguanides are a group of oral antihyperglycemic drugs that work by preventing the production of glucose in the liver, improving the body's sensitivity to insulin, and reducing the amount of sugar absorbed by the intestines.
What is the mechanism of action of metformin in type 2 diabetes?
Metformin is a potent antihyperglycemic agent widely used in the management of type 2 diabetes whose main actions are the suppression of gluconeogenesis and the improvement of glucose uptake and insulin sensitivity.
What is the mechanism of action of pioglitazone?
Mechanism of action Pioglitazone selectively stimulates the nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ) and to a lesser extent PPAR-α. It modulates the transcription of the genes involved in the control of glucose and lipid metabolism in the muscle, adipose tissue, and the liver.
What is the mechanism of action of meglitinides?
MOA (Mechanism of Action) The meglitinides are insulin secretagogues, stimulating the release of insulin from pancreatic beta cells in a manner similar to that of the sulfonylureas (Figure 14-5).
Which of the following is a biguanide hypoglycemic agents?
As already mentioned, metformin is the only biguanide available on the market. However, there are two different versions of the drug; Metformin IR (immediate release) – taken up to three times a day. Metformin SR (slow release) – usually taken once per day.
Which one is example of biguanides?
Biguanides are classed as nonsulfonylureas which act directly against insulin resistance. A notable example is metformin, which is the only biguanide for the treatment of diabetes. It works by inhibiting the quantity of glucose produced by the liver.
What is meant by biguanide?
: a strong base C2H7N5 that is soluble in water and alcohol also : any of various derivatives of this base including some (such as chlorhexidine) that are used as antiseptic and disinfecting agents and others (such as metformin) that are used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes — see proguanil.
Which drug is classified as a biguanide?
Biguanides are a class of medications used to treat type 2 diabetes and other conditions. They work by reducing the production of glucose that occurs during digestion. Metformin is the only biguanide currently available in most countries for treating diabetes.
How does Biguanide work?
Biguanides and Mechanism of Action 1 Reducing the blood sugars will reduced the need for insulin secretion from the Beta-cells of islets of pancreas. 2 Since these drugs also improve the sensitivity of muscle cells for insulin, they are used especially in individuals with insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes. 3 Continued lowering of blood glucose concentrations also result in lowering of hemoglobin A1c, which is an indicator of blood glucose control over the past 2 to 3 months. 4 Biguanides can used either alone or in combination with other oral antidiabetic medications and insulin.
How does Biguanide help with blood sugar?
Biguanides help in reducing absorption of glucose in the intestines , thus contributing towards reduced blood sugar.
Can you take Biguanides alone?
Biguanides can used either alone or in combination with other oral antidiabetic medications and insulin.
What is Biguanidine used for?
The term "biguanidine" often refers specifically to a class of drugs that function as oral antihyperglycemic drugs used for diabetes mellitus or prediabetes treatment . Examples include: Metformin - widely used in treatment of diabetes mellitus type 2.
What is the formula for Biguanide?
Biguanide ( / baɪˈɡwɒnaɪd /) is the organic compound with the formula HN (C (NH)NH 2) 2. It is a colorless solid that dissolves in water to give highly basic solution. These solutions slowly hydrolyse to ammonia and urea.
When were guanidines discovered?
In the 1920s, guanidine compounds were discovered in Galega extracts. Animal studies showed that these compounds lowered blood glucose levels. Some less toxic derivatives, synthalin A and synthalin B, were used for diabetes treatment, but after the discovery of insulin, their use declined. Biguanides were reintroduced into Type 2 diabetes treatment ...
Do biguanides affect insulin?
Biguanides do not affect the output of insulin, unlike other hypoglycemic agents such as sulfonylureas and meglitinides. Therefore, they are effective in Type 2 diabetics; and in Type 1 diabetes when used in conjunction with insulin therapy.
Can biguanides lower insulin levels?
However, in hyperinsulinemia, biguanides can lower fasting levels of insulin in plasma. Their therapeutic uses derive from their tendency to reduce gluconeogenesis in the liver, and, as a result, reduce the level of glucose in the blood.
Do biguanides release insulin?
It is not clearly understood. Biguanides do not cause insulin release, but presence of some insulin is essential for their action. Explanations offered for their hypoglycaemic action are—
Is Biguanide contraindicated in alcoholics?
In addition to general restrictions for use of oral hypoglycaemics (see below), biguanides are contraindicated in hypotensive states, cardiovascular, respiratory, hepatic and renal disease and in alcoholics because of increased risk of lactic acidosis.
Who are biguanides suitable for?
Metformin is generally suitable for most people with type 2 diabetes as a first line of medication if lifestyle changes have no sufficiently lowered blood glucose levels.
What is the name of the drug that helps the liver produce glucose?
Biguanides. The term biguanide refers to a group of oral type 2 diabetes drugs that work by preventing the production of glucose in the liver, improving the body’s sensitivity towards insulin and reducing the amount of sugar absorbed by the intestines. The only available biguanide medication is metformin, which is commonly used as ...
What is the CAS number for Biguanide?
Biguanide (CAS#56-03-01) is a parent compound that is used to synthesize drugs for controlling noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (Type II), or NIDDM. Three clinically important biguanides that were released into the market are buformin, phenformin, and metformin. Phenformin was withdrawn from the market in 1970s, ...
What is the name of the drug that acts as a transcription factor?
Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) are another type of insulin-sensitizing drug which act by binding peroxisome proliferator-activator nuclear receptor (PPAR)-γ, a transcription factor which is abundant in adipose cells.
What are the chemical structures of galegine?
Chemical structures of galegine, metformin and phenformin. Metformin and phenformin are synthetic derivatives of galegine. Chemically, (a) galegine (also known as isoprenylguanidine), is an isoprenyl derivative of guanidine, while (b) metformin (dimethylbiguanide) and (c) phenformin (phenethylbiguanide) are biguanides containing two coupled molecules of guanidine with additional substitutions
When was galegine first used?
At about the same time, two synthetic derivatives of galegine, metformin and phenformin, were first synthesised and tested, although they were not introduced to clinical use until the 1950s [3].
Who is responsible for drafting the article and revising it critically for important intellectual content?
All authors were responsible for drafting the article and revising it critically for important intellectual content. All authors approved the version to be published.