What is the maximum interval for pausing CPR?
28/12/2021 · When treating people who have suffered from OHCA and do not have an advanced airway in place, it is permissible to halt compressions for about 10 seconds in order to provide two breaths. Rescuers should conduct chest compressions at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute in people suffering from OHCA.
What is the interval between compression and shock in CPR?
08/02/2022 · What is the maximum interval for pausing? For adults victims of OHCA without an advanced airway in place, it is reasonable to pause compressions for <10 seconds to deliver 2 breaths. In adults with OHCA, it is reasonable for rescuers to perform chest compressions at 100-120/minute.
What is the maximum pause in compressions to ventilate?
05/06/2020 · What is the maximum interval for pausing chest compressions ACLS? For adults victims of OHCA without an advanced airway in place, it is reasonable to pause compressions for <10 seconds to deliver 2 breaths. In adults with OHCA, it is reasonable for rescuers to perform chest compressions at 100-120/minute. Click to see full answer.
What are the guidelines for compression and shock therapy?
You should pause for no longer than 10 seconds at a time to avoid starving the body of oxygen between chest compressions. You want to supply the organs with as constant a flow of blood (and therefore oxygen) as possible, so you should only cease giving chest compressions in order to:
What is Max interval for pausing chest compressions?
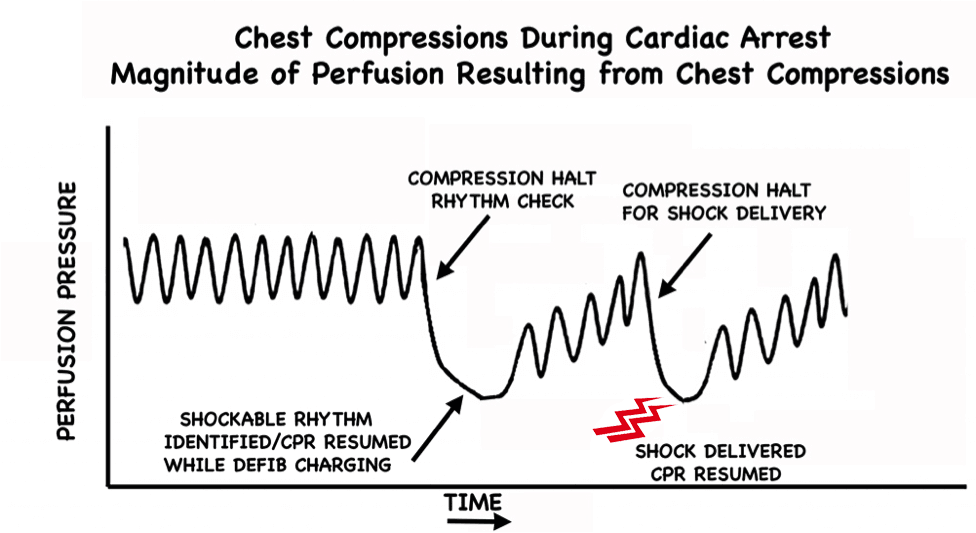
Objectives: Most guidelines recommend pausing chest compressions at 2 min intervals to analyze the cardiac rhythm.
When do you pause CPR?
Once you begin CPR, do not stop except in one of these situations: You see an obvious sign of life, such as breathing. An AED is available and ready to use. Another trained responder or EMS personnel take over.
How often should you switch chest compressions?
To combat fatigue, CPR guidelines recommend changing the person performing chest compressions every two minutes. However, the process of switching compressors introduces interruptions that have been shown to substantially increase the hands-off time (no-flow ratio), so this is better avoided if possible.
What are the current guidelines for CPR?
Giving CPRHand position: Two hands centered on the chest.Body position: Shoulders directly over hands; elbows locked.Depth: At least 2 inches.Rate: 100 to 120 per minute.Allow chest to return to normal position after each compression.
Can CPR restart a stopped heart?
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) will not restart a heart in sudden cardiac arrest. CPR is just a temporary measure used to continue a minimal supply of oxygen to the brain and other organs. When someone is in sudden cardiac arrest, defibrillation is the only way to re-establish a regular heartbeat.
How many seconds change in CPR?
Change positions about every two minutes with minimal time lost (less than 5 seconds) between changes When performing two-person CPR, the rescuer doing the compressions will quickly review compression ratio and the rescuer doing the breathing will follow that cue.19-Dec-2011
How often should you switch chest compressions to avoid fatigue ACLS?
Push hard (at least 2 inches [5 cm]) and fast (100-120/min) and allow complete chest recoil. Minimize interruptions in compressions. Avoid excessive ventilation. Change compressor every 2 minutes, or sooner if fatigued.
How often should you switch chest compressors to avoid fatigue ACLS?
If possible, in order to give consistent, high-quality CPR and prevent provider fatigue or injury, new providers should intervene every 2-3 minutes (ie, providers should swap out, giving the chest compressor a rest while another rescuer continues CPR).19-Aug-2021
How to compress a person's chest?
You place the heel of your hand on the bottom of the victim’s breastbone. Then the other hand goes over the first, you can either interlock fingers or just grasp your own wrist. You then compress to a level of no less than 2” and no more than 1/3 of the depth of the person’s chest.
How to give a child a chest compression?
Lie the child on its back. Don’t try to adjust the angle of their head or chin. Give gentle mouth-to-mouth by covering their mouth and nose with your own mouth. Then use just two fingers on the lower half of the breastbone to give chest compressions to a depth of no more than 1/3rd of the child’s chest depth.
How deep should a child's chest be for CPR?
Give chest compressions to a depth of no more than 1/3rd of the child’s chest. You use the same rhythm as you use for an adult’s CPR. As with babies, children are, until about the age of 8, a little more delicate than adults too and thus, we use a technique that is half-way between that used on babies and that on adults.
How long should you wait to do CPR?
In CPR: the maximum interval for pausing chest compressions is 10 seconds. This is an established recommendation based on the need to maintain blood flow to the heart during a cardiac arrest. Remember that CPR is a life-saving technique. Everyone should learn it as it would make the world a safer place for everyone.
Why is CPR important?
CPR is a vital step in the process of saving lives – it is meant to keep the patient’s blood flowing (and thus oxygen moving around their system) which prevents organ damage and allows trained medical staff to have a better chance of being able to revive the individual.
How many breaths should you take to ventilate?
If you are going to offer mouth-to-mouth then you want to deliver 30 compressions at the same rate (100 to 120 per minute) followed by two breaths. Remember, the maximum pause in compressions to ventilate should last no more than 10 seconds.
Can you do CPR while waiting for an ambulance?
You need to phone for an ambulance ( 911 in the US ). CPR can only help while you wait for an ambulance, they have the tools to get the victim’s heart started again. Then open up the airway. It’s fine to turn the victim onto their back if needed for this. Tilt the head back then try to open the mouth and peek inside.