What are the arguments against Malthusian theory?
Criticisms of the Malthusian Theory of Population
- Population Growth. The gloom and doom forecasts put forward by Malthus have not played out. ...
- Food Production. Thanks to many technological advancements, food production has dramatically increased over the past century.
- Global Trade. The limited availability of land at the time was the basis for Malthus’ theory on food production constraints.
- Calculations. ...
What is Malthusian trap theory?
The concept of the Malthusian Trap was proposed by Thomas Robert Malthus in 1798. The Malthusian Trap or Malthusian Theory argues that gains in food production lead to an increase in population, which results in food shortages as the ever growing population takes over land meant more crop production.
What is a theory that disproves Malthusian theory?
When this was being written about during the cold war, a new type of wheat that produced 4 times as much food turned India from a net importer to a net exporter in just a few years. This was called the Green Revolution and it effectively disproved Malthusian thought.
What was the Thomas Malthus theory?
Thomas Malthus was an English economist and demographer best known for his theory that population growth will always tend to outrun the food supply and that betterment of humankind is impossible without strict limits on reproduction. Thomas Malthus found that food production did not increase at an exponential rate but instead increased more slowly.
What is Malthusian theory in simple terms?
The Malthusian theory explained that the human population grows more rapidly than the food supply until famines, war or disease reduces the population. He believed that the human population has risen over the past three centuries.
What is the Malthusian theory quizlet?
Malthusian Theory (1798) While food supply increases arithmetically, population increases geometrically. Neo-Malthusians. Generally refers to people with the same basic concerns as Malthus. Advocate population control programs to ensure resources for current and future populations.
What did Malthus say about population growth quizlet?
What was Malthus conclusion on population growth? Population would eventually surpass available food resources which would cause mass starvation and create in of itself a growth barrier.
Which was Thomas Malthus argument quizlet?
Which was Thomas Malthus's argument? He argued that if there was no control over population growth, then the population would come under check because of war, disease, and starvation.
What is the Malthusian theory of population?
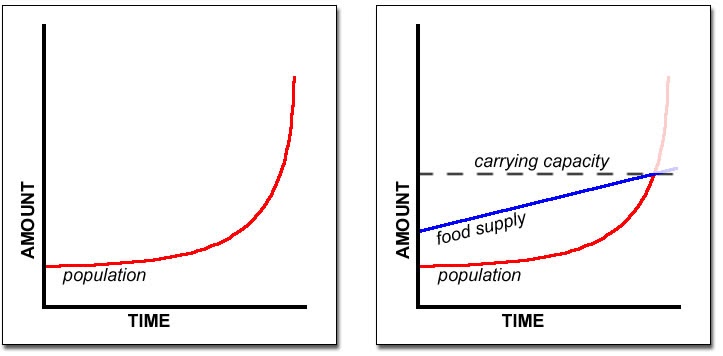
The Malthusian Theory of Population is the theory of exponential population and arithmetic food supply growth. The theory was proposed by Thomas Robert Malthus. He believed that a balance between population growth and food supply can be established through preventive and positive checks.
How does the Malthusian theory explain the growth of the population?
The Malthusian theory explained that the population grows in a geometrical fashion. The population would double in 25 years at this rate. However, the food supply grows in an arithmetic progression. Food supply increases at a slower rate than the population. That is, the food supply will be limited in a few years.
Which theory of population is based on the relationship between population growth and resources?
A.1. Malthus examined the relationship between population growth and resources in one of his works. He then proposed the Malthusian theory of population where he said that the population grows exponentially and the food supply grows arithmetically and that a balance between the two can be established through positive and preventive checks. Q.2.
Which theory explained that the human population grows more rapidly than the food supply until famines, war or disease reduce
A.2. The Malthusian theory explained that the human population grows more rapidly than the food supply until famines, war or disease reduces the population. He believed that the human population has risen over the past three centuries.
AP Human Geo Models & Theories to Know!
The models & theories for each unit are centerpieces of content and they appear alllllll over the exam. You'll be asked about them in multiple-choice and free-response questions, so it's crucial that you are familiar with each of these.
Unit 1 Models & Theories: Intro to Geography
1. Latitude, Longitude: Lat is fat! Long is Long! Latitude lines are horizontal, Longitude lines are vertical. Latitude is natural because the Earth is a globe, so half of it is 0°, also known as the equator, and each line north and south measures distance from the equator. Longitude lines are not based on a natural marker.
Unit 2 Models & Theories: Population & Migration
4. Population Pyramids: Used to analyze the demographic makeup of a population including age and gender.
Unit 3 Models & Theories: Culture
10. Diffusion S-Curve: Culture and innovation spreads for different reasons, but the S-Curve theorizes the speed at which ideas are adopted. Things start picking up slowly, then become popular quickly, then taper off. Just think about trends like the bottle flip.
Unit 4 Models & Theories: Political Geography
12. Organic Theory: Inspired by none other than Hitler, the organic theory is that states are like living organisms that have life cycles (birth and death) and need "nourishment" in the form of acquiring less powerful states to survive. Without expansion, the state will die.
Unit 5 Models & Theories: Agriculture, Food, & Rural Land Use
17. Von Thunen Agricultural Location Theory: This is super simplified map that shows where different industries are located. The inner circle is closest to the city center and is where the market is located. Outside of that is dairy or other goods that have expiration dates and therefore need to be physically close to the market.
Unit 6 Models & Theories: Industry & Development
19. Rostow’s Stages of Growth: This theory states that countries develop their industry in five stages over time. The highest stage is one of high mass consumption where there are tons of goods developed and consumed.
Malthusian Theory
- Thomas Robert Malthus (1766-1834)was a pivotal pioneer in the study of population statistics.
- His population formulation was a watershed moment in the history of population ideas. He generalized the link between demographics and social transformation.
- The rate at which human reproduction outpaced the rate at which sustenance from the land could be increased.
- Thomas Robert Malthus (1766-1834)was a pivotal pioneer in the study of population statistics.
- His population formulation was a watershed moment in the history of population ideas. He generalized the link between demographics and social transformation.
- The rate at which human reproduction outpaced the rate at which sustenance from the land could be increased.
- Malthus went on to say that if population growth is unregulated, it will rise in a geometrical ratio. Only in anarithmetic ratio does subsistence rise.'
Malthusian Theory - Major Elements
- Population and Food Supply
1. According to the Malthusian idea, population growthoccurs in a geometrical pattern. 2. At this rate, the population would double in 25 years. The food supply, on the other hand, grows in anarithmetic progression. 3. Food supply grows at a slower rate than population growth. That is… - Checks on Population
1. Disequilibrium developswhen the pace of population growth exceeds the rate of food supply. 2. As a result, people will not have enough food to survive. People will perish as a result of a shortage of food. 3. Adversities like plagues, wars, hunger, famines, and other natural disasters …
Malthusian Theory - Criticism
- The population of Western Europe was rapidly increasing. At the same time, technical advancements had expanded food supplies.
- Food production has frequently expanded faster than population growth. In the United States, for example, the agriculture industry employs 2% of the overall population. Nonetheless, the overall GDP...
- The population of Western Europe was rapidly increasing. At the same time, technical advancements had expanded food supplies.
- Food production has frequently expanded faster than population growth. In the United States, for example, the agriculture industry employs 2% of the overall population. Nonetheless, the overall GDP...
- According to the Malthusian hypothesis, one of the causes of the limited food supply is a lack of available land.
- However, as a result of greater globalization, the amount of food supply in diverse nations has expanded.
Malthusian Theory - Applicability
- Although the Malthusian philosophyis not relevant to Western Europe and England, its main instruments have been ingrained in the population of these nations.
- If these places do not suffer from overpopulation and unhappiness, it is entirely owing to the dread and pessimism of Malthusian theory.
- The fact that individuals adopt preventative measures on a large scale, such as late marriag…
- Although the Malthusian philosophyis not relevant to Western Europe and England, its main instruments have been ingrained in the population of these nations.
- If these places do not suffer from overpopulation and unhappiness, it is entirely owing to the dread and pessimism of Malthusian theory.
- The fact that individuals adopt preventative measures on a large scale, such as late marriage and different contraception and birth control procedures, demonstrates the importance ofthe Malthusian...
- TheMalthusian philosophymay no longer be appropriate in its original location, yet its effect extends over two-thirds of the universe.
Conclusion
- Malthus thought that the population could be controlled by preventative and positive checks in order to balance the food supply with the population level. These checks would result in the Malthusian disaster. Thomas Robert Malthus (1766-1834) was a pivotal pioneer in the study of population statistics. His population formulation was a watershed moment in the history of pop…
Mcqs
- Question: Consider the following statements: 1. Preventive measures will balance population growth and food supply. 2. These methods not only limit population increase. Which of the following statements above is/ are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 Question: Which of the following statements is/are correct. 1. Malthusian Theory is not relevan…