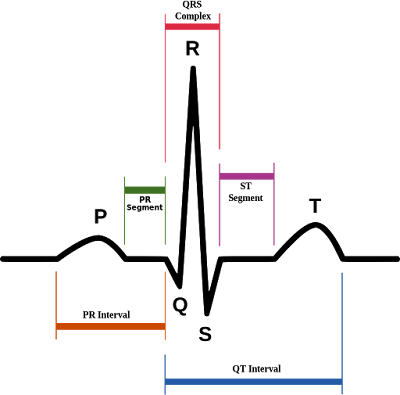
A term used to describe a straight line on the ECG strip with illustrates the resting state of the myocardial cells. The isoelectric line represents the beginning and ending point of the five major waves of the cardiac cycle. Begins with the firing of the SA node, which is represented by a P wave on the ECG.
How do you find isoelectric line?
To find the J point, follow these steps:
- Identify the point where the QRS complex and the ST segment meet. ...
- Move one small box (0.04 second) to the right; this is the J point.
- Find the isoelectric line (baseline) of the cardiac cycle by looking at the T-P segment. ...
What does the isoelectric line represents?
- Overview of the normal electrocardiogram (ECG) ECG interpretation includes an assessment of the morphology (appearance) of the waves and intervals on the ECG curve.
- The P-wave. ...
- PR interval and PR segment. ...
- The QRS complex (ventricular complex) A complete QRS complex consists of a Q-, R- and S-wave. ...
- Implications and causes of wide (broad) QRS complex. ...
What is an isoelectric line?
The isoelectric line represents the beginning and ending point of the five major waves of the cardiac cycle. Begins with the firing of the SA node, which is represented by a P wave on the ECG.
What component is measured along the isoelectric line?
What component is measured along the isoelectric line? The component of the ecg that is normally measured along the isoelectric line is the ST segment. The ST segment is found on the isoelectric section of the electrocardiogram, located at the beginning of the T wave and also at the end of the S wave.
What does the isoelectric line of the ECG represent?
The baseline of an ECG tracing is called the isoelectric line and denotes resting membrane potentials. Deflections from this point are lettered in alphabetical order, and following each, the tracing normally returns to the isoelectric point.
What is the isoelectric line of the ECG quizlet?
The isoelectric line represents the beginning and ending point of the five major waves of the cardiac cycle. Begins with the firing of the SA node, which is represented by a P wave on the ECG.
How do you find the isoelectric line on an ECG?
Find the isoelectric line (baseline) of the cardiac cycle by looking at the T-P segment. (Some references suggest finding the isoelectric line by looking at the PR segment.2) Measure the height (amplitude) of the ST segment from the isoelectric line at the J point in mm (each small box is 1 mm) (see J point elevation).
Which segment is isoelectric on the ECG trace?
The isoelectric period (ST segment) following the QRS and ending at the beginning of the T wave is the time at which both ventricles are completely depolarized. This segment roughly corresponds to the plateau phase of the ventricular action potentials.
Which components of the ECG are normally measured along the isoelectric line?
Which components of the ECG are normally measured along the isoelectric line? Recorded as a pattern of a baseline broken by a P wave, a QRS complex, and T wave.
Which part of the cardiac cycle is represented as a flat line on the ECG strip?
a. Slows conduction of the impulse 0.08 seconds to allow time for the atria to contract and empty into the ventricles (atrial kick) before the ventricles contract. This delay is represented on the ECG as the flat line portion of the PR interval.
What does an isoelectric ST segment mean?
The ST segment is the flat, isoelectric section of the ECG between the end of the S wave (the J point) and the beginning of the T wave. The ST Segment represents the interval between ventricular depolarization and repolarization.Mar 16, 2022
What ECG leads reflect the heart's normal axis?
The normal cardiac axis is expected to lie between -30º and 90º, which means the overall direction of electrical activity is toward leads I, II, and III. Electrocardiographic axis.Mar 11, 2019
What is the isoelectric line?
The isoelectric line represents the beginning and ending point of the five major waves of the cardiac cycle. Begins with the firing of the SA node, which is represented by a P wave on the ECG.
What are the components of an ECG?
Components of the ECG The electrical events of the heart (ECG) are usually recorded as a pattern of a baseline (isoelectric line), broken by a P wave, a QRS complex, and a T wave.
What does the isoelectric line of the ECG strip represent?
Similarly, what does the isoelectric line of the ECG represent? A term used to describe a straight line on the ECG strip with illustrates the resting state of the myocardial cells. The isoelectric line represents the beginning and ending point of the five major waves of the cardiac cycle.
What is an EKG tracing?
An EKG tracing is a series of boxes upon which positive and negative deflections or waves that represent the electrical impulses of the heart are recorded. Each EKG has a baseline or isoelectric line, which represents the absence of electrical activity. Besides, what is the isoelectric line?
What is the isoelectric line?
What Is an Isoelectric Line? The isoelectric line of an electrocardiogram designates the flat part of the diagram in between P waves and T waves, according to lecturer Chris Schwirian of Ohio University. The isoelectric line is completely flat, while positive waves are above the line and negative waves are below it.
What is the base line on an EKG?
The isoelectric line, also known as the base line, is in the middle of the ECG reading. This part of the ECG is most prominent after the last T wave until the next P wave.
Which node initiates the ECG?
The ECG Tracing. The electrical sequence of a cardiac cycle is initiated by the sinoatrial node, the so-called pacemaker of the heart. This is because the SA node has a faster rate of spontaneous firing than the remaining specialized tissues (see Figure 1).
What is ECG monitoring?
The use of dynamic electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring is regarded as a standard of care during general anesthesia and is strongly encouraged when providing deep sedation. Although significant cardiovascular changes rarely if ever can be attributed to mild or moderate sedation techniques, the American Dental Association recommends ECG monitoring ...
What happens during the PR interval?
Because the PR interval commences with atrial muscle depolarization and ends with the start of ventricular depolarization, one can assume that the electrical impulse passes through the AV node into the ventricle during this interval. If the PR interval is prolonged, one may deduce that AV block is present.
Which cells initiate and conduct electrical impulses throughout the myocardium?
Specialized cells include the sinuatrial (SA) node, the atrioventricular (AV) node, the bundle of His, and the Purkinje fibers (Figure 1). These cells initiate and conduct electrical impulses throughout the myocardium, and this regulates the rhythm of a cardiac cycle.
What is the abbreviation for EEG?
Many prefer EKG to ECG because it is less likely to be confused verbally with EEG, the abbreviation for electroencephalogram. However, we will arbitrarily adopt ECG for this presentation.
What are the two main cells of the heart?
The heart is composed of 2 principal cell types: working cells and specialized neural-like conductive cells. The working cells are the muscle or myocardium of the atria and ventricles.
Does a complex represent ventricular contraction?
In any case, the complex does not represent ventricular contraction. One assumes that contraction will commence at the peak of the R portion of the complex. Unlike contraction of the atria, ventricular contraction can be confirmed clinically by palpating a pulse or by monitoring a pulse oximeter wave form.