What is the vascular tunic?
The vascular tunic is mesodermal in origin and is situated between the outer fibrous tunic and the inner nervous tunic. The vascular tunic is also refered to as the uvea. The iris is the anterior most portion of the vascular tunic and functions as a moveable diaphragm between the anterior and posterior chambers.
What is the anterior segment of the vascular tunic?
VASCULAR TUNIC FUNCTIONS. The choroid is also continuous with the anterior segment of the vascular tunic, which is known as the iris of the eye. From an external view of the eye, this is the colored portion. Smooth muscles which lie in a continuous, radial, but circular pattern make up the iris.
What is the tunica of the eye?
the vascular, pigmentary, or middle coat of the eye, comprising the choroid, ciliary body, and iris. Synonym(s): tunica vasculosa bulbi [TA], Haller tunica vasculosa, tunica vasculosa oculi, uvea, uveal tract, vascular tunic of eye.
What is Haller tunica vasculosa?
Haller tunica vasculosa- the vascular, pigmentary, or middle coat of the eye, comprising the choroid, ciliary body, and iris. Synonym(s): vascular tunic of eye
What is vascular tunic?
The vascular tunic is comprised of three distinct regions, (1) the iris, (2) the ciliary body, and (3) the choroid. The vascular tunic is mesodermal in origin and is situated between the outer fibrous tunic and the inner nervous tunic. The vascular tunic is also refered to as the uvea.
What is the function of nervous tunic of the eye?
Nervous tunic: The inner nervous tunic is the retina. The retina consists of an outer pigmented epithelium covered by nervous tissue (the neural layer) on the inside. The dark color of the pigmented epithelium absorbs light (as with the choroid) and stores vitamin A used by photoreceptor cells in the neural layer.
What are the three eye tunics and what is the primary function of each tunic?
The eye is made up of three layers: the outer layer called the fibrous tunic, which consists of the sclera and the cornea; the middle layer responsible for nourishment, called the vascular tunic, which consists of the iris, the choroid, and the ciliary body; and the inner layer of photoreceptors and neurons called the ...
Which of the following is a function of the vascular layer of the eye?
The vascular (major blood vessel), central layer of the eye lying between the retina and sclera. Its function is to provide nourishment to the outer layers of the retina through blood vessels. It is part of the uveal tract.
Which tunic is the pupil?
The iris constricts the pupil in response to bright light and dilates the pupil in response to dim light. The innermost layer of the eye is the neural tunic, or retina, which contains the nervous tissue responsible for photoreception.
What tunic is the lens in?
All of the above are part of the vascular tunic (uvea). The anterior portion of the uvea contains the iris and ciliary body, while the posterior portion contains the choroid. The lens is found between the anterior and posterior segments of the uvea.
What are the tunics?
The eye itself can be divided into 3 concentric tunics plus the internal components. The three tunics from the outside surface of the eye inward are, (1) the fibrous tunic (cornea and sclera), (2) the vascular tunic (iris, ciliary body, and choroid) and (3) the neuroectodermal (nervous) tunic (retina).
What are the three tunics of the eye quizlet?
What are the three layers of the eye? The sclera, the choroid layer, and the retina.
What are the 3 layers of the eyeball and give a description of each?
The wall of the eye is made up of three layers namely: The outer layer, which consists of the cornea and sclera. The middle layer, which consists of the iris, the ciliary body and the choroid. The inner layer, which consists of the retina.
Which of the following structures is part of the vascular tunic?
The vascular tunic is comprised of three distinct regions, (1) the iris, (2) the ciliary body, and (3) the choroid.
What is the vascular layer of the eye quizlet?
The choroid is part of the middle vascular layer of the eye. It is highly vascular, pigmented membrane covering the posterior five-sixths of the eye. Blood vessels of the choroid nourish the eye, and its pigments absorb light.
What does vascular mean in vascular layer?
vas·cu·lar lam·i·na of cho·roid [TA] the external or superficial portion of the choroid of the eye containing the largest blood vessels.
What is the vascular tunic of the eyeball?
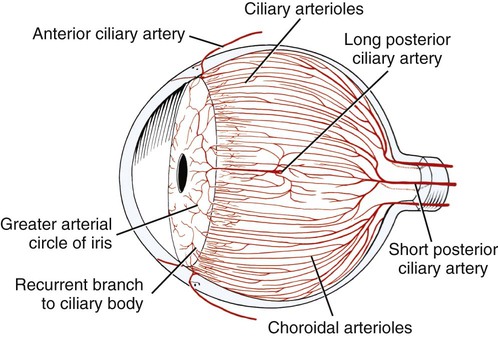
The vascular tunic of the eyeball is also referred to as the uvea. It is comprised of the iris, the choroid, and the ciliary body. The choroid, which is highly vascular, nearly immeasurably thin, and lines nearly the entire surface of the sclera, is designed to prevent the light rays from bouncing right back out of the eyeball. It achieves this through the numerous pigment producing melanocytes, which explains the brown coloring of the choroid. The choroid opens up at the rear of the eyeball, permitting the passage of the optic nerve.
What is the collection of extensions arising from the ciliary body?
There is a collection of various extensions arising from the ciliary body, which is known as ciliary processes. These attach to zonular fibers and are ultimately attached to the lens capsule through these fibers. Suspensor ligaments are actually made up of these zonular fibers.