What is fixed interval schedule and variable ratio schedule?
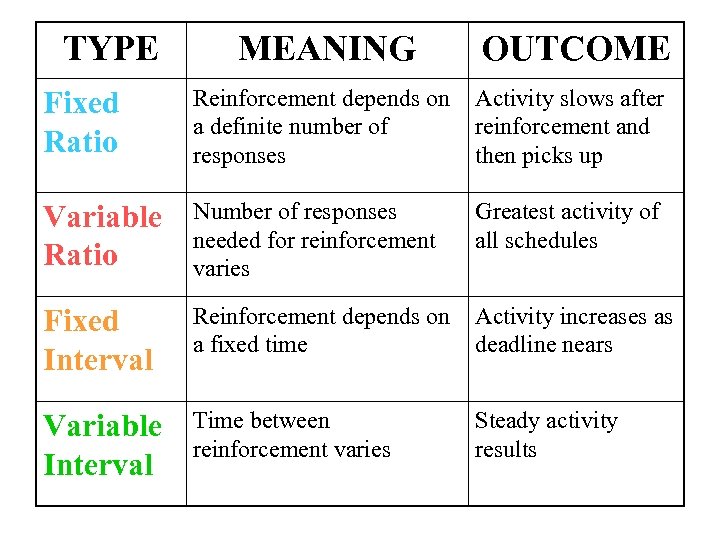
The fixed ratio schedule involves using a constant number of responses. Variable ratio schedules maintain high and steady rates of the desired behavior, and the behavior is very resistant to extinction. Fixed Interval Schedule. Interval schedules involve reinforcing a behavior after an interval of time has passed.
What are examples of interval schedule?
There are four schedules of partial reinforcement:
- Fixed-Ratio Schedules.
- Variable-Ratio Schedules.
- Fixed-Interval Schedules.
- Variable-Interval Schedules.
What is a fixed ratio schedule?
The fixed-ratio schedule can be understood by looking at the term itself. Fixed refers to the delivery of rewards on a consistent schedule. Ratio refers to the number of responses that are required in order to receive reinforcement. For example, a fixed-ratio schedule might be delivery a reward for every fifth response.
What is the definition of variable ratio schedule?
A variable ratio schedule is a schedule of reinforcement where a behavior is reinforced after a random number of responses. This kind of schedule results in high, steady rates of responding. Organisms are persistent in responding because of the hope that the next response might be one needed to receive reinforcement.
What is the difference between interval schedules and ratio schedules quizlet?
ratio schedules favor short inter-response times. interval schedules favor long inter-response times. two schedules are in effect at the same time and the subject is free to switch from one response key to another. the relative rate of responding on a key matches the relative rate of reinforcement on that key.
What are interval schedules?
In operant conditioning, a variable interval schedule is when the reinforcement is provided after a random (unpredictable) amount of time has passes and following a specific behavior being performed.Jul 2, 2020
What is ratio schedule?
Ratio schedules yield reinforcers on the basis of number of responses made. After a specified number of responses have been produced, the reinforcement isadministered. Time is not a factor. There are two major types of ratio schedules.
What are the 4 types of schedules?
There are four schedules of partial reinforcement:Fixed-Ratio Schedules.Variable-Ratio Schedules.Fixed-Interval Schedules.Variable-Interval Schedules.Jul 24, 2020
What is the difference between ratio and interval schedules of reinforcement?
Interval means the schedule is based on the time between reinforcements, and ratio means the schedule is based on the number of responses between reinforcements. Reinforcement is delivered at predictable time intervals (e.g., after 5, 10, 15, and 20 minutes).
What is the difference between variable ratio and variable interval?
Variable ratio schedules maintain high and steady rates of the desired behavior, and the behavior is very resistant to extinction. Interval schedules involve reinforcing a behavior after an interval of time has passed.
What fixed ratio schedule?
In operant conditioning, a fixed-ratio schedule is a schedule of reinforcement where a response is reinforced only after a specified number of responses. Essentially, the subject provides a set number of responses and then the trainer offers a reward.May 9, 2020
Why do ratio schedules produce higher rates of response than interval schedules?
-in a ratio schedule there are no time constraints and the faster the participant completes the ratio requirement, the faster they will receive the reinforcer. this favors not waiting long btw responses. -interval schedules favor waiting longer between responses.
What is an example of a variable-interval schedule?
Your Employer Checking Your Work: Does your boss drop by your office a few times throughout the day to check your progress? This is an example of a variable-interval schedule. These check-ins occur at unpredictable times, so you never know when they might happen.May 15, 2020
What are the two forms of ratio schedules?
Two types of ratio reinforcement schedules may be used: fixed and variable.Variable.Fixed interval.Variable Ratio.Fixed Ratio.
What is ratio strain?
Ratio strain is a term used to describe a situation in which the required amount of work, or response, no longer produces the desired behaviors that were previously produced by lower requirements.Jul 22, 2021
What does fixed ratio mean?
Fixed ratio is a schedule of reinforcement. In this schedule, reinforcement is delivered after the completion of a number of responses. The required number of responses remains constant. The schedule is denoted as FR-#, with the number specifying the number of responses that must be produced to attain reinforcement.
What are the main assumptions of statistical tests?
Statistical tests commonly assume that: the data are normally distributed the groups that are being compared have similar variance the data are i...
What is a test statistic?
A test statistic is a number calculated by a statistical test . It describes how far your observed data is from the null hypothesis of no rela...
What is statistical significance?
Statistical significance is a term used by researchers to state that it is unlikely their observations could have occurred under the null hypothe...
What is a t-test?
A t-test is a statistical test that compares the means of two samples . It is used in hypothesis testing , with a null hypothesis that the di...
Which t-test should I use?
Your choice of t-test depends on whether you are studying one group or two groups, and whether you care about the direction of the difference in...
What does a t-test measure?
A t-test measures the difference in group means divided by the pooled standard error of the two group means. In this way, it calculates a numbe...
What is the difference between a one-sample t-test and a paired t-test?
A one-sample t-test is used to compare a single population to a standard value (for example, to determine whether the average lifespan of a speci...
Can I use a t-test to measure the difference among several groups?
A t-test should not be used to measure differences among more than two groups, because the error structure for a t-test will underestimate the ac...
What is a regression model?
A regression model is a statistical model that estimates the relationship between one dependent variable and one or more independent variables us...
What is interval scale?
Interval scale and ratio scale are two of the levels of measurement or scales of measurement where they describe the attributes in quantitative scales. The concept was first introduced by the psychologist Stanley Smith Stevens in 1946. In his article titled “on the theory of the scales of the measurements” published in the nature magazine, he categorized all the measurements into four categories; namely nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. The first two explains the categorical or qualitative measurements, and the latter explain the quantitative measurements.
What is a zero point in an interval scale?
The zero point in the interval scale is arbitrary , and also negative values are also defined. The variables measured on an interval scale are known as ‘interval variables’ or ‘scaled variables’. It is common for these measurements to carry units. As pointed out earlier the ratios between measurements on interval scales are not meaningful.
Can quantitative attributes be measured in interval scales?
All quantitative attributes can be measured in interval scales. Measurements belonging to this category can be counted, ranked, added, or subtracted to take the difference, but it does not give any sense to take the ratio between two measurements. A good example of this category is the measurements made in the Celsius scale.
Why is temperature at interval scale?
For example, temperature in Celsius or Fahrenheit is at an interval scale because zero is not the lowest possible temperature. In the Kelvin scale, a ratio scale, zero represents a total lack of thermal energy.
What are the two types of estimates of a population?
Using descriptive and inferential statistics, you can make two types of estimates about the population: point estimates and interval estimates. A point estimate is a single value estimate of a parameter. For instance, a sample mean is a point estimate of a population mean.
Answer
The difference between an interval schedule of reinforcement and a ratio schedule of reinforcement is the following:
Answer
In an interval schedule of reinforcement, a certain period of time must pass between reinforcements. In a ratio schedule of reinforcement, a certain number of successful demonstrations of the target behavior must occur before reinforcement is provided.
New questions in English
Which of these passages includes an example of an analogy? A.) The sun set amid the paper-thin clouds that slowly changed colors from bright pinks and …