What is the Frankfort plane of the skull?
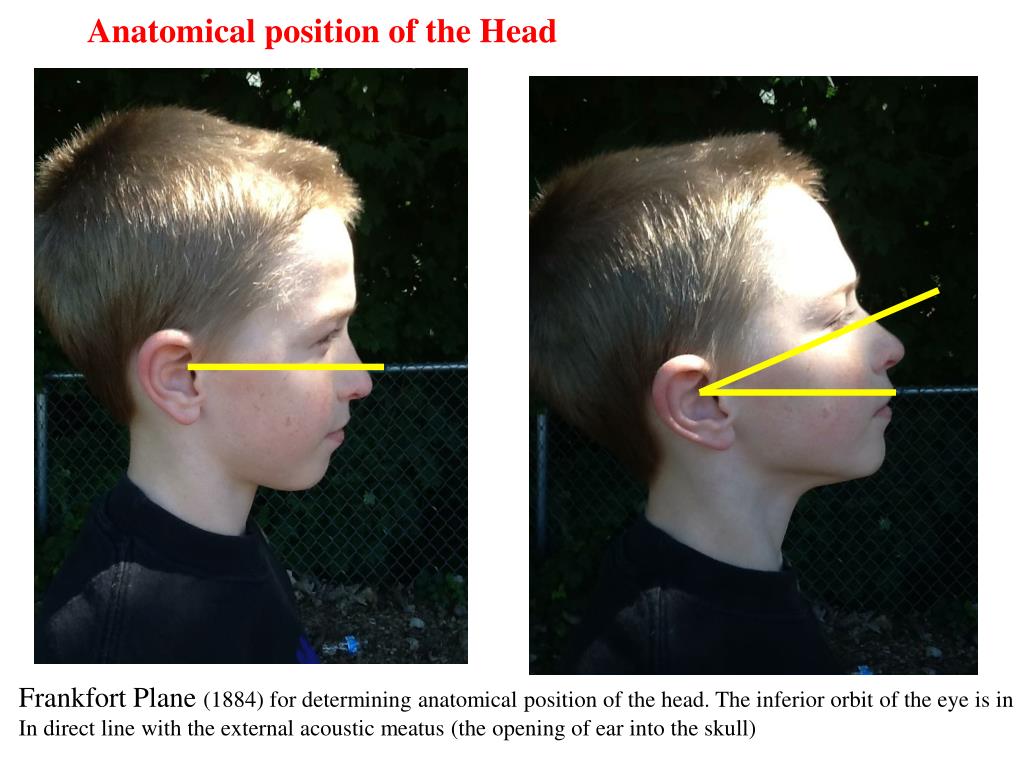
In humans, the anatomical position of the skull has been agreed by international convention to be the Frankfurt plane or Frankfort plane, a position in which the lower margins of the orbits, the orbitales, and the upper margins of the ear canals, the poria, all lie in the same horizontal plane. Popular Trending About Us Asked by: Cauzar Causera
What is the Frankfort-mandibular plane angle?
The Frankfort-mandibular plane angle (FMA) is formed by the intersection of the Frankfort horizontal plane and the mandibular plane. This angle can be traced and measured by means of a diagnostic overlay.
What is the Frankfurt plane?
The Frankfurt plane was established at the World Congress on Anthropology in Frankfurt am Main, Germany in 1884, and decreed as the anatomical position of the human skull.
What is the FMA of the Frankfort-mandibular plane?
The Frankfort-mandibular plane angle (FMA) is formed by the intersection of the Frankfort horizontal plane and the mandibular plane. This angle can be traced and measured by means of a diagnostic overlay. An FMA of 25 +/- 5 degrees is within normal range.
Where was the Frankfurt plane established?
What plane is the skull on?
What is the standard anatomical position?
What is the standard position of a human body?
What is the position of the skull in dogs?
Is a straight position assumed when describing the proximo-distal axis?
See more
About this website
What is the Frankfort horizontal plane?
In profile view, a plane connecting the highest point of the opening of the external auditory canal with the lowest point on the lower margin of the orbit, used to orient a human skull or head so that the plane is horizontal.
What is the Frankfort line?
Frankfort horizontal line, Reid's base line Reconstructive surgery An imaginary line that projects from the median line of the occipital bone and upper rim of the external auditory canal–the auricular point, to the lower rim of the orbit–the infraorbital point; the FHL divides the head into upper and lower halves from ...
Why we use Frankfort horizontal plane?
The Frankfort plane was employed for orientation of the patient and was chosen as the best anatomic indicator of the true horizontal line. It is also closely related to the natural head position (NHP) (3, 4).Sep 7, 2017
What is an occlusal plane?
Occlusal plane is the average plane established by the incisal and occlusal surfaces of the teeth; it is not a plane but represents the planar mean of the curvature of the surfaces [3].
What does vertical plane mean?
Definition of vertical plane 1 : a plane that passes through a vertical line. 2 : a plane of perspective passing through the point of sight and perpendicular to the ground plane and to the picture.
What does transverse plane mean in medical terms?
Axial Plane (Transverse Plane) - A horizontal plane; divides the body or any of its parts into upper and lower parts. Median plane - Sagittal plane through the midline of the body; divides the body or any of its parts into right and left halves.
What is true horizontal plane?
The true horizontal (physiological) is the perpendicular line to the true vertical16. Frankfort plane (FHP) It is the line created by the opening of the externalauditory meatus (Porion) and the low point on the lower margin of the infraorbital rim. Point N (Nasion)
What is palatal plane?
Palatal plane : The plane joined by forming ANS to PNS. Occlusal plane : The plane formed by the line passing through the overlapping cusps of the premolars and molars. Mandibular plane : The plane formed by joining the gonion and menton.
What is FMA angle?
The Frankfort-mandibular plane angle (FMA) is formed by the intersection of the Frankfort horizontal plane and the mandibular plane. This angle can be traced and measured by means of a diagnostic overlay. An FMA of 25 +/- 5 degrees is within normal range.
What are the three landmarks used to determine the plane of occlusion?
Different intra- and extra-oral landmarks used by clinicians to define the level of the occlusal plane include the upper lip, corners of mouth, lateral margins of tongue, Camper's plane and interpupillary line, the parotid papilla and the retromolar pad (RMP).
What is the ALA tragus line?
A line from the lower border of the ala of the nose to the upper border of the tragus of the ear. It is used as a reference line in orthodontics, radiography, and the construction of complete dentures. Also known as Camper's line [P. Camper (1722–89), Dutch anatomist]. Ala-tragal line.
What is the Retromolar pad?
Introduction. The retromolar pad is a mass of soft tissue located at the posterior end of the mandibular alveolar ridge. This pad covers the underlying bone with surrounding attached muscle fibers. Sicher described retromolar pad as a triangular soft elevation of mucosa that lies distal to third molar [1].
Anatomical Position - Definition and Function | Biology Dictionary
Anatomical Position Definition. Standard anatomical position is a way of describing the anatomy of an organism so that it is easy to understand what part of the body is being talked about no matter what direction the organism is facing or where its appendages/limbs are. In humans, standard anatomical position is defined as standing up straight with the body at rest.
Standard Anatomical Position - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Hollie Kirwan, Rose Pignataro, in Pathology and Intervention in Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation (Second Edition), 2016. Clock Method. The clock method is one of the most common methods of wound measurement. The wound is considered as a face of a clock with the position of the wound based on the standard anatomical position of the patient (Figure 2-2).For wounds on the torso and extremities, the ...
Anatomical Position: What Is It, Significance, Regions, Planes, and ...
Back Anatomical Position What Is It, Significance, Regions, Planes, and More. Author: Ashley Mauldin, MSN, APRN, FNP-BC. Editor s: Ahaana Singh, Lisa Miklush, PhD, RN, CNS. Illustrator: Aileen Lin. What is anatomical position? Anatomical position, or standard anatomical position, refers to the specific body orientation used when describing an individual’s anatomy.
Anatomical position | definition of anatomical position by Medical ...
position [pŏ-zish´un] 1. a bodily posture or attitude. 2. the relationship of a given point on the presenting part of the fetus to a designated point of the maternal pelvis; see accompanying table. See also presentation. Common examination positions. From Lammon et al., 1995. anatomical position that of the human body standing erect, palms facing ...
Where was the Frankfurt plane established?
Frankfurt plane. The Frankfurt plane was established at the World Congress on Anthropology in Frankfurt am Main, Germany in 1884, and decreed as the anatomical position of the human skull.
What plane is the skull on?
In humans, the anatomical position of the skull has been agreed by international convention to be the Frankfurt plane or Frankfort plane, a position in which the lower margins of the orbits, the orbitales, and the upper margins of the ear canals, the poria, all lie in the same horizontal plane.
What is the standard anatomical position?
The standard anatomical position, or standard anatomical model, is the scientifically agreed upon reference position for anatomical location terms. Standard anatomical positions are used to standardise the position of appendages of animals with respect to the main body of the organism.
What is the standard position of a human body?
Human anatomy. The standard anatomical position in a male and female. In standard anatomical position, the human body is standing erect and at rest. Unlike the situation in other vertebrates, the limbs are placed in positions reminiscent of the supine position imposed on cadavers during autopsy.
What is the position of the skull in dogs?
This is a good approximation to the position in which the skull would be if the subject were standing upright and facing forward normally. In dogs, the skull is the more diverse within the species than any other mammal so the dorsal, ventral, and lateral views are the most important positions.
Is a straight position assumed when describing the proximo-distal axis?
However, a straight position is assumed when describing the proximo-distal axis. This helps avoid confusion in terminology when referring to the same organism in different postures. For example, if the elbow is flexed, the hand remains distal even if it approaches the shoulder.
Where was the Frankfurt plane established?
Frankfurt plane. The Frankfurt plane was established at the World Congress on Anthropology in Frankfurt am Main, Germany in 1884, and decreed as the anatomical position of the human skull.
What plane is the skull on?
In humans, the anatomical position of the skull has been agreed by international convention to be the Frankfurt plane or Frankfort plane, a position in which the lower margins of the orbits, the orbitales, and the upper margins of the ear canals, the poria, all lie in the same horizontal plane.
What is the standard anatomical position?
The standard anatomical position, or standard anatomical model, is the scientifically agreed upon reference position for anatomical location terms. Standard anatomical positions are used to standardise the position of appendages of animals with respect to the main body of the organism.
What is the standard position of a human body?
Human anatomy. The standard anatomical position in a male and female. In standard anatomical position, the human body is standing erect and at rest. Unlike the situation in other vertebrates, the limbs are placed in positions reminiscent of the supine position imposed on cadavers during autopsy.
What is the position of the skull in dogs?
This is a good approximation to the position in which the skull would be if the subject were standing upright and facing forward normally. In dogs, the skull is the more diverse within the species than any other mammal so the dorsal, ventral, and lateral views are the most important positions.
Is a straight position assumed when describing the proximo-distal axis?
However, a straight position is assumed when describing the proximo-distal axis. This helps avoid confusion in terminology when referring to the same organism in different postures. For example, if the elbow is flexed, the hand remains distal even if it approaches the shoulder.