Protective Systems
- Sloping involves cutting back the trench wall at an angle inclined away from the excavation.
- Shoring requires installing aluminum hydraulic or other types of supports to prevent soil movement and cave-ins.
- Shielding protects workers by using trench boxes or other types of supports to prevent soil cave-ins.
What is sloping in construction?
Sloping a method of protecting employees from caveins by excavating to. form sides of an excavation that are inclined away from the. excavations so as to prevent cave ins. In practice, it may be difficult to accurately determine these sloping angles.
What is sloping and benching in excavation?
What is sloping in excavation? This appendix contains specifications for sloping and benching when used as methods of protecting employees working in excavations from cave-ins. Actual slope means the slope to which an excavation face is excavated. Distress means that the soil is in a condition where a cave-in is imminent or is likely to occur.
What is a slope in an excavation?
For excavations greater than 20 ft depth, the slope or bench shall be designed by a registered professional engineer. Sloping means a method of protecting employees from cave-ins by excavating to form sides of an excavation that are inclined away from the excavation so as to prevent cave-ins.
Is the slope of bedding plane stable during excavation?
However, if the slope of bedding plane is away from the excavation area or horizontal, then vertical slope of the excavation wall would be stable. With regard to shattered rocks, it could lead to the collapse of the excavation wall.
What is slope in excavation?
Maximum allowable slope means the steepest incline of an excavation face that is acceptable for the most favorable site conditions as protection against cave-ins, and is expressed as the ratio of horizontal distance to vertical rise (H:V).
How do you calculate excavation slope?
For example, if the trench is 6 ft deep and 20 ft wide across the end of the trench and the bottom of the trench is 2 ft wide, the slope can be calculated as follows: Horizontal distance = 20 ft – 2 ft ÷ 2 = 9 and the Vertical depth = 6 ft; Slope = 9 ÷ 6 = 1.5 to 1, which is the slope needed for type C soil.
At what depth is sloping required?
1. All simple slope excavations 20 feet or less in depth shall have a maximum allowable slope of 1:1. 3. All excavations 20 feet or less in depth which have vertically sided lower portions shall be shielded or supported to a height at least 18 inches above the top of the vertical side.
What is a trench slope?
Sloping involves cutting back the trench wall at an angle inclined away from the excavation. Shoring requires installing aluminum hydraulic or other types of supports to prevent soil movement and cave-ins. Shielding protects workers by using trench boxes or other types of supports to prevent soil cave-ins.
What is safe slope for excavation?
1. Type 1 and 2 soil must be sloped to within 1 . 2 metres (four ft .) of the bottom of the excavation or trench, with a slope at an angle not steeper than one horizontal to one vertical, or 450 measured from the horizontal .
What is a slope ratio?
In math, slope is the ratio of the vertical and horizontal changes between two points on a surface or a line. The vertical change between two points is called the rise, and the horizontal change is called the run. The slope equals the rise divided by the run: . This simple equation is called the slope formula.
How do you dig a sloping trench?
In order to dig a drainage trench, follow these steps:Plan your drainage trench. ... Measure your slope to ensure the ground falls at least 1 inch every 10 feet. ... Dig your trench. ... Line your trench with water-permeable landscape fabric.Lay 3 inches of gravel in the bottom of the trench.More items...
What is the OSHA standard for excavation?
OSHA requires employers to provide ladders, steps, ramps, or other safe means of egress for workers working in trench excavations 4 feet (1.22 meters) or deeper. The means of egress must be located so as not to require workers to travel more than 25 feet (7.62 meters) laterally within the trench.
What is shielding in excavation?
Shielding. Shielding systems include trench boxes, steel plates, and/or combination of protective systems. Shielding does not protect against soil failures. Shielding systems do not support the face of excavations, rather they protect the workers inside of them.
What is sloping and shoring?
A shoring system is used to support the face of an excavation and to prevent movement of soil, underground utilities, roads, and foundations. A shoring system is typically used when sloping is an inadequate solution due to the depth of the cut or the location.
What is the slope ratio for sand?
Excavation SlopesType of SoilSlope (x : y)Solid rock, shale or cemented sand and gravels0 : 1Compact angular gravels1/2 : 1Recommended slope for average soils1 : 1Compact sharp sand1 1/2 : 11 more row
How do you calculate excavation volume and slope?
At = Wt * Lt, where Wt and Lt are the width and length of the top of the excavation. In our example, Wb = Lb = 5 and Wt = Lt = 15, so Ab = 5 * 5 = 25 and At = 15 * 15 = 225, and D = 5. Therefore, the volume is: = 542 cf or 20.0 cy.
Soil Classification
An adequate identification of the type of soil is necessary through visual and manual tests to identify the correct solution of the protection system. The type of soil will determine the trench protection system to be used. Any time the site conditions change the soil will need to be reevaluated.
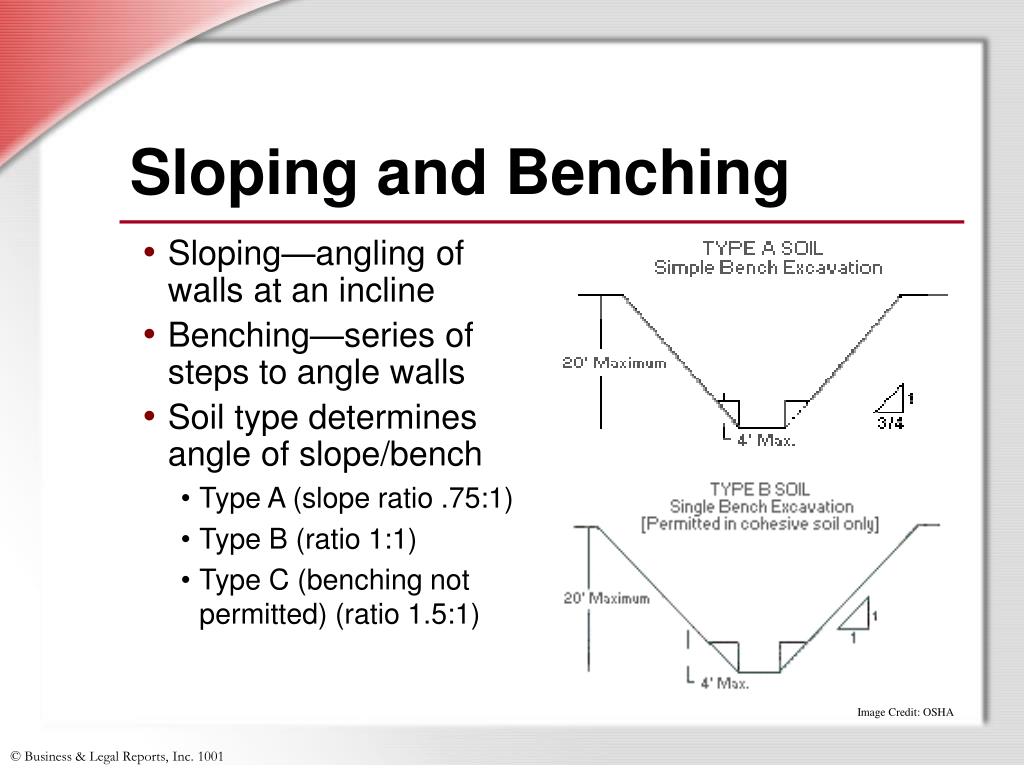
Sloping and Benching
Sloping, benching, or other approved cave-in protection systems must be utilized in excavations 5 feet or greater in depth. For excavations greater than 20 ft depth, the slope or bench shall be designed by a registered professional engineer.
Benching
Benching is a method of protecting employees from cave-ins by excavating the sides of an excavation to form one or a series of horizontal levels or steps, usually with vertical or near-vertical surfaces between levels. There are two basic types of benching, simple and multiple.
When is the actual slope less steep than the maximum allowable slope?
The actual slope shall be less steep than the maximum allowable slope when there are signs of distress. If that situation occurs, the slope shall be cut back to an actual slope which is at least 1/2 horizontal to one vertical (1/2H:1V) less steep than the maximum allowable slope.
How deep is a simple slope?
All simple slope excavations 20 feet or less in depth shall have a maximum allowable slope of 1 1/2:1. Simple Slope. All excavations 20 feet or less in depth which have vertically sided lower portions shall be shielded or supported to a height at least 18 inches above the top of the vertical side.
How high should a vertically sided excavation be?
All excavations 20 feet or less in depth which have vertically sided lower portions shall be shielded or supported to a height at least 18 inches above the top of the vertical side. All such excavations shall have a maximum allowable slope of 1:1. Vertically-Sided Lower Portion.
What is the maximum slope allowed for a simple slope?
All simple slope excavations 20 feet or less in depth shall have a maximum allowable slope of 3/4:1. Simple Slope Exception: Simple slope excavations which are open 24 hours or less (short term) and which are 12 feet or less in depth shall have a maximum allowable slope of 1/2:1. Short Term Slope.
Engineering ToolBox - SketchUp Extension - Online 3D modeling!
Add standard and customized parametric components - like flange beams, lumbers, piping, stairs and more - to your Sketchup model with the Engineering ToolBox - SketchUp Extension - enabled for use with the amazing, fun and free SketchUp Make and SketchUp Pro .Add the Engineering ToolBox extension to your SketchUp from the SketchUp Pro Sketchup Extension Warehouse!.
Privacy
We don't collect information from our users. Only emails and answers are saved in our archive. Cookies are only used in the browser to improve user experience.
Advertise in the ToolBox
If you want to promote your products or services in the Engineering ToolBox - please use Google Adwords. You can target the Engineering ToolBox by using AdWords Managed Placements.
Citation
Engineering ToolBox, (2010). Excavation Slope. [online] Available at: https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/excavation-slope-d_1717.html [Accessed Day Mo. Year].
Protective Systems
All excavations are hazardous because they are inherently unstable. If they are restricted spaces, they present the additional risks of oxygen depletion, toxic fumes, and water accumulation. If you are not using protective systems or equipment while working in trenches
Other Safety Precautions
The OSHA standard requires you to provide support systems such as shoring, bracing, or underpinning to ensure that adjacent structures such as buildings, walls, sidewalks, or pavements remain stable. The standard also prohibits excavation below the base or footing of any foundation or retaining wall unless:
What is sloping in trenching?
Sloping. Sloping involves cutting back the trench wall at an angle that is inclined away from the work area of the excavation. The angle of slope required depends on the soil conditions. Benching is a similar method to sloping.
What is trench excavation?
What is meant by a trench and an excavation? Generally speaking, an excavation is a hole in the ground as the result of removing material. A trench is an excavation in which the depth exceeds (is bigger than) the width.
Why do trench boxes tilt?
They can support trench walls if the space between the box and the trench wall is backfilled with soil and compacted properly. Otherwise, a cave-in or collapse may cause the trench box to tilt or turn over. Workers should not be present in the box when it has to be moved.
What is the term for falling into a trench?
Falling into the trench or excavation. Flooding or water accumulation. Exposure to a hazardous atmosphere (e.g., gas, vapour, dust, or lack of oxygen). Contact with buried service lines such as electrical, natural gas, water, sewage, telecommunications, etc. Contact with overhead electrical lines.
What is temporary protective structure?
Saskatchewan Labour defines a temporary protective structure as “a structure or device in an excavation, trench, tunnel or excavated shaft that is designed to provide protection from cave-ins, collapse, sliding or rolling materials, and includes shoring, trench boxes, trench shields and similar structures.”
What is the purpose of soil type?
When a soil type is defined, the purpose is to try to identify or predict the potential for the soil to move and cause a collapse while the work is being done.
How deep is a trench?
In general, trenches that are 1.2 metres (4 feet) deep or greater require a protective system unless the excavation is made entirely in stable rock. The factors to consider include: Surcharge loads (e.g., spoil, other materials to be used in the trench) and.
What happens if the slope of the bedding plane is away from the excavation area?
However, if the slope of bedding plane is away from the excavation area or horizontal, then vertical slope of the excavation wall would be stable. With regard to shattered rocks, it could lead to the collapse of the excavation wall.
Why is slope slippage in stiff fissured clay small falls?
The slope slippage in stiff fissured clay is either small falls due to crumbling or slipping along fissure plan or rotational shear slide of sizable mass of clay soil. When the slipping does not impose server risks to ...
What factors affect slope stability?
Factors Affecting Slope Stability in Open Excavation 1 Types of soil 2 Time during which the excavation is required to be open 3 Allowable degree of risk of slipping which is determined based on the existing structures and new constructed buildings around the excavation area.
What type of soil is slope stability?
Excavation Slope stability in Cohesionless or Partially Cohesive Soil. In this section, the slope stability of excavations in various types of soil such as dry sand and gravel, dump sand, sandy gravel, water bearing sand, water bearing sandy soil, silt and silty sand, dry silt, and wet silt.
Why does clay stand vertically?
Slope Stability in Stiff Clay. It can stand almost vertically with small soil mass fall due to erosion and frost damage from sandy lenses in the clay. However, if pocket lenses of water bearing sand and gravel are present in clay or when the excavation is dug steeply and cuts fissures in the clay, then a major risk would be highly likely ...
Why is water bearing sand more problematic?
This is because clay or silt layer may bleed from the face and consequently jeopardize the stability of other strong layers.
Why is it so hard to stabilize slopes in silt?
So, stability of slopes in wet silt is considerably difficult because erosion due to water lead to the collapse of the excavation until a stable angle is reached.
General Requirements For All Excavations
- All employees working in an excavation must receive initial training.
- A competent person must be clearly identified for all excavations. This person must be knowledgeable in assessing soil conditions, the use of protective systems, and OSHA requirements.
- Before beginning excavation, establish the locations of underground and overhead utilities a…
- All employees working in an excavation must receive initial training.
- A competent person must be clearly identified for all excavations. This person must be knowledgeable in assessing soil conditions, the use of protective systems, and OSHA requirements.
- Before beginning excavation, establish the locations of underground and overhead utilities and services.
- Use Personal Protective Equipment:
Soil Classification
- An adequate identification of the type of soil is necessary through visual and manual tests to identify the correct solution of the protection system. The type of soil will determine the trench protection system to be used. Any time the site conditions change the soil will need to be reevaluated. The soil type must be identified by the competent person on site. 1. Stable Rock ar…
Sloping and Benching
- Sloping, benching, or other approved cave-in protection systems must be utilized in excavations 5 feet or greater in depth. For excavations greater than 20 ft depth, the slope or bench shall be designed by a registered professional engineer. 1. Sloping 1.1. Sloping means a method of protecting employees from cave-ins by excavating to form sides of ...
Benching
- Benching is a method of protecting employees from cave-ins by excavating the sides of an excavation to form one or a series of horizontal levels or steps, usually with vertical or near-vertical surfaces between levels. There are two basic types of benching, simple and multiple. The type of soil determines the horizontal to vertical ratio of the benched side. As a general rule, the …
Scope and Application
Definitions
- Actual slopemeans the slope to which an excavation face is excavated. Distressmeans that the soil is in a condition where a cave-in is imminent or is likely to occur. Distress is evidenced by such phenomena as the development of fissures in the face of or adjacent to an open excavation; the subsidence of the edge of an excavation; the slumping of m...
Requirements
- Soil Classification Soil and rock deposits shall be classified in accordance with the Soil Classification Procedures. Maximum Allowable Slope The maximum allowable slope for a soil or rock deposit shall be determined from Table 1of this part. Actual Slope 1. The actual slope shall not be steeper than the maximum allowable slope. 2. The actual slope shall be less steep than t…
Slope Configurations
- All slopes stated below are in the horizontal to vertical ratio. Hyperlinks are to .gif images. Excavations made in Class "A" soil All simple slope excavations 20 feet or less in depth shall have a maximum allowable slope of 3/4:1. Simple Slope Exception: Simple slope excavations which are open 24 hours or less (short term) and which are 12 feet or less in depth shall have a maximum …