What is the best R-value for insulation?
High R-Value
- Closed-cell spray foam: Up to R-7 per inch
- Open-cell spray foam: Up to R-3.6 per inch
- Blown-in fibers: Between R-3.1 and R-3.7, depending on fiber type
- Fiberglass batts: Up to R-3.8
- Rock wool: Up to R-3.3
What is the best insulation are value?
The best R-Value insulation for a colder climate will be at least R-29 for an attic or loft and around R-16 for a floor. Choosing the right kind of insulation to suit the climate where you live will make all the difference when it comes to enjoying a warmer living environment and the benefit of lower energy bills.
What is R5 continuous insulation?
Continuous Insulation (Ci) means creating an insulation blanket around the exterior of the structure. When you apply Kingspan GreenGuard R-5 XPS Insulation over studs, you create a wall with reduced energy loss through thermal bridging and less potential for moisture problems. With insulation on the exterior of the wall cavity, the dew point is ...
What is the your rating of insulation?
What is insulation R rating? "R" means resistance to heat flow. The higher the R-value, the greater the insulating power. Almost all insulation products have to tell you their R-value — pipe and duct insulation are the only exceptions. Click to see full answer.
Is R5 insulation effective?
In this laboratory test: After hitting equilibrium, the sample with the layer of R-5 CI used 23% less energy than the standard R-20 stud wall. Throughout the entire 55-hour test, the wall assembly with the CI layer consumed roughly 45% less energy than the R-20 wall.
What does continuous R-value mean?
Continuous R-Value - Enter the R-value of any continuous insulation in the above-grade wall. Continuous insulation is continuous over framing members or furring strips and is free of significant thermal bridging.
What qualifies as continuous insulation?
Continuous Insulation (ci). Insulating material that is continuous across all structural members without thermal bridges other than fasteners and service openings. It is installed on the interior or exterior or is integral to any opaque surface of the building envelope.
Is spray foam considered continuous insulation?
Medium-density, closed cell spray foam insulation provides a high performance wall assembly solution by combining four functions in one material: truly continuous insulation, a continuous air barrier, a full water-resistive barrier, and a vapor barrier.
What is continuous insulation?
Continuous Insulation (Ci) means creating an insulation blanket around the exterior of the structure. When you apply Kingspan GreenGuard R-5 XPS Insulation over studs, you create a wall with reduced energy loss through thermal bridging and less potential for moisture problems. With insulation on the exterior of the wall cavity, the dew point is moved outward, reducing the potential for condensation on the warm side of the wall cavity. And, since XPS Insulation does not absorb water, you create an additional barrier to water penetration from the exterior.
Does XPS insulation absorb water?
And, since XPS Insulation does not absorb water, you create an additional barrier to water penetration from the exterior.
What is Continuous Insulation?
Continuous insulation (ci) (as defined in ASHRAE 90.1, Energy Standard for Buildings Except Low-Rise Residential Buildings):
How many square feet can a fanfold cover?
Two bundles easily unfold to cover up to 400 square feet per at one time. R-Tech fanfold bundles require fewer fasteners than other roof and wall insulations, and require about 60% fewer man hours to install than working with individual insulation sheets.
What is the best insulation for a building envelope?
Among rigid foam insulations, EPS and GPS have the highest R-value per dollar, which makes them well-suited for cost-effective continuous insulation. EPS, such as Insulfoam EPS and R-Tech branded products, is a rigid and tough, closed-cell foam that provides about R 4.6 per inch of thickness. Due to the way it is made, unlike other rigid foam insulations, EPS retains its R-Value throughout its time in service. EPS is the most versatile of rigid insulations because it can be used anywhere in the building envelope – roof, walls, floors, and below grade since it dries quickly and assists with moisture management requirements.
What is the IECC code for building insulation?
Building owners benefit through reduced heating and cooling energy costs. Since 2012 the International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) has required continuous insulation in the building envelope in most all Climate Zones (as defined by ASHRAE 90.1).
What is the R value of polyiso?
Polyiso panels provide up to R 6.5 (aged value) per inch of thickness. Polyiso R-Values start at about R-7 per inch, but (like XPS) degrade over time as the thermal-enhancing blowing agents used to make them diffuse out of the material. Polyiso thermal warranties also reflect this R-Value decline.
What is GPS insulation?
GPS, graphite-infused polystyrene, insulation provides R 5 per inch of thickness. Found in Insulfoam’s R-Tech Platinum R5 and R10 GPS, it combines factory laminated specially-treated metalized polymeric facer and premium insulation into one product, creating a semi-vapor permeable (breathable) shield to efficiently meet the latest building and energy code requirements for continuous insulation.
How does CI help a building?
In addition to enhancing a building’s energy efficiency, CI helps reduce moisture damage in the building envelop by lowering condensation within the envelope assembly resulting from vapor diffusion.
What is Continuous Insulation?
Continuous insulation, also known as outsulation, is defined in American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-conditioning Engineers 90.1 (ASHRAE 90.1), as:
How does continuous insulation help the building industry?
In the long run, continuous insulation not only dramatically reduces building management costs, but the improvements in efficiency, help the building industry move closer to carbon neutrality and a more sustainable environment.
What is rigid foam insulation?
Rigid foam plastic sheathing materials are commonly used for continuous insulation because of their relatively high R-value per inch and low cost to meet or exceed energy code requirements . [We discuss the pros and cons of Rigid Foam Sheathing here and here .]
What is CI in building?
To help ensure well-insulated buildings, since 2012, the International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) has required continuous insulation (CI) in the building envelope. The 2012 IECC prescribes how much insulation is required for each of the 8 U.S. climate zones, for various types of above-grade walls, below-grade walls, roofs, and floors.
How much does thermal bridging reduce insulation?
Furthermore, studies done by the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) found that thermal bridging through framing components reduces insulation performance by as much as 15-20 percent in wood frame construction and by 40-60 percent in metal framed buildings.
What is thermal bridge?
If you’ve been around the construction and insulation industry you probably know the term. T hermal bridging, also known as cold bridges or heat bridges, are penetrations in a building’s insulation layer that allow heat (a.k.a. energy) to escape and cold to intrude during winter. Vice versa in the summer. In an airtight and insulated home, thermal bridges can account for heat loss of up to 30 percent.
How much heat loss is due to thermal bridges?
Vice versa in the summer. In an airtight and insulated home, thermal bridges can account for heat loss of up to 30 percent. As more stringent legislation and energy awareness lead to increased insulation levels in walls, roofs, and floors, heat losses due to thermal bridging become increasingly important.
What is continuous insulation?
Continuous insulation, also known as CI, is defined by ASHRAE 90.1 as “insulation that is continuous across all structural members without thermal bridges other than fasteners and service openings. It is installed on the interior, exterior, or is integral to any opaque surface of the building envelope.”
What is the R value of a 2x4 stud?
A 2x4 stud (i.e., 3.5" deep) has an R-value of 4.4.
Where is rigid insulation used?
Over the last few years, New England and other cold regions of the U.S. have seen a growth in the use of rigid insulation on the exterior of buildings. This use of exterior rigid foam first started appearing in commercial buildings and was driven primarily by the International building codes which required steel-stud buildings to place rigid foam on the exterior of the structure.
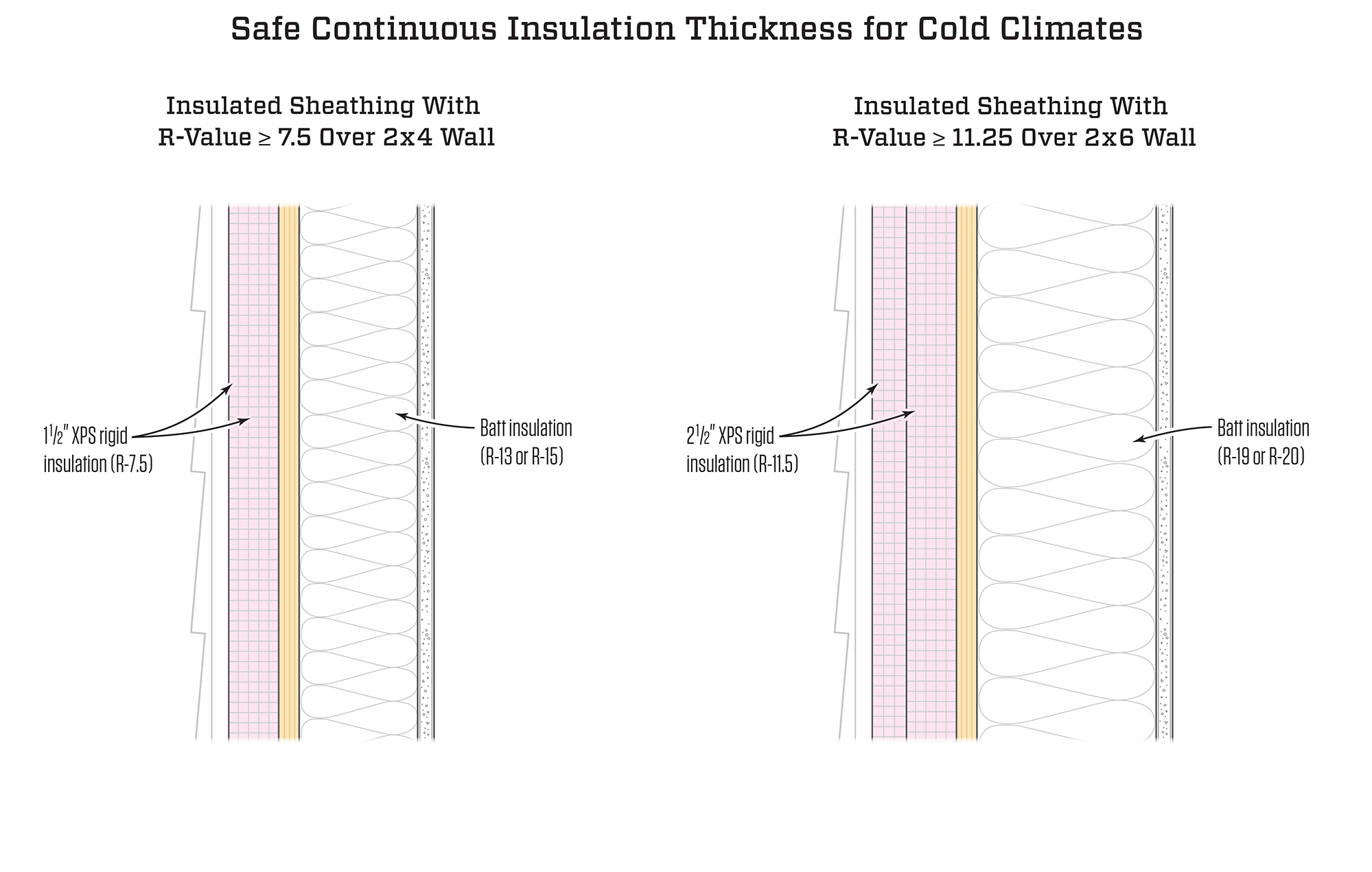
What is the insulation code for a 2x6 wall?
This insulation method is now gradually entering the residential marketplace, driven by the newer International Residential Codes which beginning in 2009 started recommending (in colder climate zones) a 2×4 wall with R-13 in the cavity and R-5 on the exterior as an alternative to a 2×6 wall with R-20 insulation in the cavity.
How to reduce thermal bridging?
So, by putting rigid insulation over the sheathing and studs , you reduce this bridging effect (thermal bridging).
Why put insulation on the outside?
In addition to reducing heat loss and increasing the R-value of the wall system, there are other benefits to putting insulation on the outside. These include reducing the chance for the moisture in the cavity (water vapor) to condense on the inside face of the sheathing, which happens when the sheathing temperature is below the dew point. This moisture can lead to mold and mildew, and can reduce the effectiveness of the cavity insulation and ultimately shorten the life of the wall through rot.
Why are steel studs good insulation?
Why? Steel studs are great thermal conductors, and these thermal bridges were conducting the heat from the inside to the outside in the winter and the reverse in the summer . This was making the insulation in the cavities between the studs practically useless and causing the R-value of the walls to be 50% lower than many people assumed. So builders decided to skip the insulation in the cavity (unless needed for sound suppression) and put all the insulation on the outside.
Is exterior insulation better than foam insulation?
This can save you money in construction as well as giving you more space inside. The exterior insulation on the wall can make it perform up to 50 percent better than the same wall without the rigid foam.