What is meant by manufacturing process flow?
What is meant by manufacturing process flow? In a manufacturing process, material and information must move throughout the facility between manufacturing points and storage locations. The path that both material and information take as they move through the facility defines the process flow.
Why is assessing process flow in manufacturing critical?
You can identify the high risk processes with the following criteria but not limited to:
- Lengthy process with more stages
- High risk of failures in the process
- Top failed product in the history
- Process that is heavily dependent on human intervention
- Process executed in the oldest facility
- Process/facility with rapid changes
What are the four types of manufacturing processes?
The Four Basic Process Types:
- Job Shop Manufacturing Process. A job shop is used to process low volume high customized goods. ...
- Batch Manufacturing Process. A batch process is used to produce a moderate amount of fairly standardized goods. ...
- Repetitive Manufacturing Process. Repetitive processing is used to produce high volume standardized goods. ...
- Continuous Manufacturing Process. ...
What are the basics of the manufacturing process?
process manufacturing
- Process manufacturing vs. discrete manufacturing. ...
- Types of manufacturing processes. Within the manufacturing industry, various processes are used -- in addition to process and discrete manufacturing -- to determine how a company will produce its products.
- Process manufacturing software. ...
- Examples of process manufacturing. ...
What are the 4 types of manufacturing processes?
What are the 4 types of manufacturing process?Casting and molding.Machining.Joining.Shearing and forming.
What is the process flow of process?
A business process flow is a sequential representation of a process and its components, including operations, timelines, people involved, and resources needed. The main objective of process flows is to help you standardize and optimize your processes and help your team better understand how your business works.
What are the 5 manufacturing processes?
Five types of manufacturing processesRepetitive manufacturing.Discrete manufacturing.Job shop manufacturing.Process manufacturing (continuous)Process manufacturing (batch)
What are the types of process flow?
Other commonly used flowchart types include:PERT chart.Workflow flowchart.Swimlane diagram.Data Flow Diagram (DFD)Process Flow Diagram (PFD)Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN 2.0)Specification and Description Language Flowchart (SDL)Event-Driven Process Chain Flowchart (EPC)
What do you call a process flow?
Also called: process flowchart, process flow diagram. Variations: macro flowchart, top-down flowchart, detailed flowchart (also called process map, micro map, service map, or symbolic flowchart), deployment flowchart (also called down-across or cross-functional flowchart), several-leveled flowchart.
What are the 6 main manufacturing processes?
Six types of manufacturing processesJob shop manufacturing. ... Repetitive manufacturing. ... Discrete manufacturing. ... Batch process manufacturing. ... Continuous process manufacturing. ... 3D printing. ... Machining. ... Joining.More items...•
What is main manufacturing process?
A manufacturing process uses manufacturing methods, operations scheduling software, machinery, and labor to transform raw material into the finished product. Broadly, there are five manufacturing processes, and most businesses that create products will fall into one of these five categories.
What are the 6 different types of manufacturing processes?
The Six Types of Manufacturing – Complete GuideRepetitive Manufacturing.Discrete Manufacturing.Job Shop Manufacturing.Continuous Process Manufacturing.Batch Process Manufacturing.3D Printing.Related Articles.
Why is lean manufacturing important?
This is often necessary because of processes that are not available internally, but this is also the reason that Lean factories tend to be more vertically integrated, so that that they can perform as much work as possible in-house, in a flow.
What is one by one production?
One-by-one Production is one of the core principles of the Toyota Production System, in the interest of achieving optimum flow (and catching problems early).
What happens when work cannot advance smoothly?
What happens when the work cannot advance smoothly is that workers will either be blocked or waiting, and both flow and productivity will be negatively affected. The action to address variability (but not eliminate it) is called Heijunka or Smoothing, along with the prudent use of IPKs or In-Process Kanbans. 4.
What is a lean tool that can be applied to a product?
Imagine having to flow a river back upstream! A Lean tool that can be applied, in addition to good product design, is called Poke Yoke or Error-Proofing. Another simple and inexpensive practice is called Check-Do-Check or operator-based inspection.
Process manufacturing vs. discrete manufacturing
Process manufacturing is the exact opposite of discrete manufacturing. Whereas process manufacturing follows recipes or formulas and creates products that cannot be broken down at the end of the production cycle, discrete manufacturing uses a bill of materials ( BOM) and follows instructions to create finished, assembled goods.
Types of manufacturing processes
Within the manufacturing industry, various processes are used -- in addition to process and discrete manufacturing -- to determine how a company will produce its products. The three other common manufacturing processes include:
Process manufacturing software
Because it's a complex and often highly specialized activity, most manufacturers use enterprise resource planning ( ERP) software systems that have specific functions for process manufacturing.
What is continuous flow in manufacturing?
Continuous flow in a manufacturing industry focus on optimum movement of material. Material movement path usually designed in ‘U’ shape or straight line for reducing the zig zag movement. Which will drastically reduce the movement path and hence saves energy and time.
What are the restrictions on manufacturing?
Restrictions to the flow in manufacturing industry 1 Changeovers 2 Breakdowns 3 Material shortages 4 Defective parts 5 Unorganized work stations 6 Lack of proper communication of demand 7 Unbalanced cycle time of operations 8 Poorly designed layout
What are the different types of manufacturing processes?
There are several different ways to approach the classification of types of manufacturing processes: By the scale of production: job-shop (individual), batch (serial), and mass production. By the nature of the product: discrete or process manufacturing. By the role of the process: basic, auxiliary, serving, managerial.
How to classify manufacturing processes?
There are not only different types of manufacturing processes but also several ways to classify them: by the scale of production, by the nature of the product, by the role of the process, by the level of automation.
What are the three manufacturing processes categorized by the scale of production?
Manufacturing processes categorized by the scale of production are: job shop manufacturing, batch/serial manufacturing, and mass production. Manufacturing processes categorized by the nature of the product are discrete manufacturing and process manufacturing.
What is job shop production?
A job-shop production process is characterized by: The manufacturing of products in single copies or in small series (one to two dozen per month ). A wide range of products. The use of universal equipment, universal devices, cutting and measuring tools for general purposes.
What are the norms of manufacturing?
A manufacturing process must also have established norms such as quality measurements, tolerances, and performance metrics to keep all areas of production – including machine operation, labor, material flow, and others – coordinated to achieve consistency and efficiency.
What is managerial process?
Managerial processes, in which decisions are developed and made, regulation and coordination of production progress, control over the accuracy of program implementation, analysis and accounting of work performed; these processes are often intertwined with the course of production processes.
When to use make to stock?
The Make to Stock model is mostly used when producing consumer goods with predictable demand. However, it is also used when demand for the products is uncertain, but customers require short lead times.
What is flow in a system?
Flow is how work progresses through a system . When a system is working well, or having “good” flow, it tends to move steadily and predictably, whereas, “bad” flow means the work starts and stops. Every time there is a breakdown in the flow, chances of accumulating waste increase. One goal is to Sstrive for a consistent flow which generates more ...
How to improve flow?
Develop an action plan. Actively monitor the new processes put into place by creating performance measures. A final point to make about improving flow is the necessity of training and educating employees. All employees must understand, and appreciate, how essential it is to keep a good flow going!
Why is it important to keep production running?
Keeping production running, in such a smooth fashion, also helps to ensure that a company is creating efficiencies. There is a direct relationship between creating efficiencies that enhance overall business performance and increasing profitability. These are just some of the ways that a company implementing lean manufacturing can put notable ...
What is manufacturing process?
Manufacturing processes typically follow a strict set of rules or guidelines in order to turn raw materials into a quality finished product. Any deviation from standard manufacturing processes can lead to machine malfunction, elongated lead times or excessive scrap rates. In-depth and detailed analysis of manufacturing processes can be reinforced through the use of flow charts – a few examples:
How to describe manufacturing processes?
Manufacturing processes typically follow a strict set of rules or guidelines in order to turn raw materials into a quality finished product. Any deviation from standard manufacturing processes can lead to machine malfunction, elongated lead times or excessive scrap rates. In-depth and detailed analysis of manufacturing processes can be reinforced through the use of flow charts – a few examples: 1 Standardize Production Run Setup Activities: Inefficient manufacturing setup procedures can be very costly (financial and otherwise) to an organization. A well-documented and detailed flow chart describing the exact steps required to prepare a new production run is pivotal for reducing lead times and increasing machine utilization. 2 Create Flow Charts for Preventative Maintenance Procedures and Notification: Develop standard preventative maintenance (PM) processes for each machine in the manufacturing process. Following these processes and developing protocols for notifying machine operators of PM schedules will allow employees to plan ahead and do other work while machines are being inspected. 3 Identify Root Causes of Defects Using Flow Charts: Flow charts can enable manufacturers to analyze their manufacturing process step-by-step in detail, which can help in diagnosing which activities are leading to higher defect and scrap rates.
What is process flow?
What is a Process Flow? Process flows (or process diagrams) provide a visual overview or workflow diagram of all the tasks and relationships involved in a process.
What is the goal of process improvement?
This is the goal of process improvement —to improve the efficiency and accuracy of a process by reviewing its current state and finding ways of improving it.
Is a process opaque?
Most processes tend to be fairly opaque with a lot of institutional or "tribal" knowledge moving things forward. If you work in an environment like this you probably hear a lot of comments that sound like this:
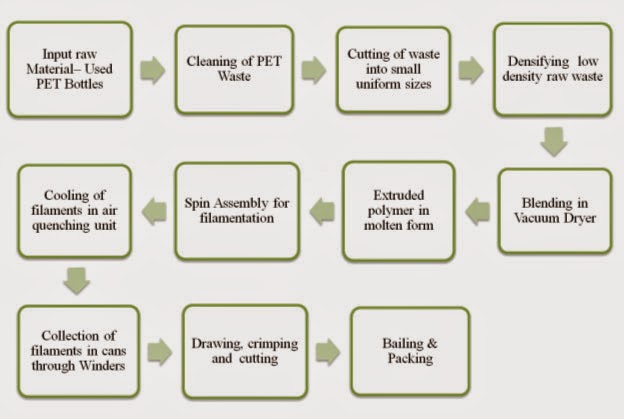
Manufacturing Process Engineering
- Manufacturing process engineering came from the technological development and profound change of the steel industry. Ferrous metallurgy is a process of iron-coal chemical engineering at high temperature. The manufacturing process consists of many procedures and consumes plen…
Production Line
- A production line is a traditional method which people associate with manufacturing. The production line is arranged so that the product is moved sequentially along the line and stops at work centres along the line where an operation is performed. The item may move along some kind of conveyor, or be moved manually by staff or forklift. For example, operations along the pr…
Custom Manufacturing
- If a company manufactures a wide range of products that can be modified based on the customers’ requirements, then a custom manufacturing process is a good fit. The custom manufacturing facility has a number of skilled employees and a range of equipment that can be used to manufacture and modify a wide range of items. The facility should be set up with a num…
Fixed Position Manufacturing
- Fixed position manufacturing is different from other manufacturing processes as it involves the finished product not moving from its fixed position from the beginning to the end of the process. This is the method used in large-scale manufacturing such as the manufacture of an aircraft or ship but is also used for products that are being constructed in place for the customer, such as …
Process Manufacturing vs. Discrete Manufacturing
- Process manufacturing is the exact opposite of discrete manufacturing. Whereas process manufacturing follows recipes or formulas and creates products that cannot be broken down at the end of the production cycle, discrete manufacturing uses a bill of materials (BOM). It follows instructions to create finished, assembled goods. At the end of the discrete manufacturing proc…
Types of Manufacturing Processes
- Within the manufacturing industry, various processes are used — in addition to process and discrete manufacturing — to determine how a company will produce its products. The three other common manufacturing processes include: 1. repetitive manufacturing (REM) 2. job shop manufacturing 3. 3-D printing Repetitive manufacturing is used for repeated production that is c…
Process Manufacturing Software
- Because it’s a complex and often highly specialized activity, most manufacturers use enterprise resource planning (ERP) software systems that have specific functions for process manufacturing. Various enterprise software vendors produce these systems, including: 1. SAP 2. Oracle 3. Microsoft 4. Infor 5. IFS 6. Sage 7. IQMS 8. Plex Systems 9. Syspro Each vendor may s…
Examples of Process Manufacturing
- Some of the top process manufacturing markets include: 1. food and beverage 2. oil and gas 3. pharmaceuticals 4. personal care and cosmetics 5. plastics 6. metals Beer brewing is one example of process manufacturing in the food and beverage industry. Key ingredients in beer making include grains, malt, hops, yeast and sugar; various recipes are available to guide the pro…
Composite Materials Manufacturing
- The manufacturing process is very important with regard to the final properties of a composite material. The manufacturing processes employed to realize brake friction materials or thermoset matrix composites have a crucial impact on their future properties. This is especially related to the level and stability of friction and wear during braking in the case of brake friction materials. …