What is interception in geography? Interception refers to precipitation that does not reach the soil, but is instead intercepted by the leaves, branches of plants and the forest floor. It occurs in the canopy (i.e. canopy interception ), and in the forest floor or litter layer (i.e. forest floor interception ).
What is interception in biology?
Interception occurs when one of the edges of a particle touches the surface of the respiratory tract and is a major determinant of the deposition of fibers. Interception is the part of the rainfall that is intercepted by the Earth's surface and which subsequently evaporates.
Where does interception occur in a forest?
Some rain collecting on an acer leaf. Interception refers to precipitation that does not reach the soil, but is instead intercepted by the leaves, branches of plants and the forest floor. It occurs in the canopy (i.e. canopy interception ), and in the forest floor or litter layer (i.e. forest floor interception ).
What is the effect of interception on evaporation?
Interception (water) Because of evaporation, interception of liquid water generally leads to loss of that precipitation for the drainage basin, except for cases such as fog interception, but increase flood protection dramatically, Alila et al., (2009). Intercepted snowfall does not result in any notable amount of evaporation,...
What is inter Intercepted snowfall and why is it important?
Intercepted snowfall does not result in any notable amount of evaporation, and most of the snow falls off the tree by wind or melts. However, intercepted snow can more easily drift with the wind, out of the watershed. Conifers have a greater interception capacity than hardwoods.
What is a interception in the water cycle?
Interception refers to all processes that prevent rainfall from immediately reaching the soil. Vegetation intercepts water in two ways: by catching rainfall on leaf surfaces throughout the canopy, and through the litter that it deposits on the ground.
What is infiltration in geography?
Infiltration - Water soaks or filters into the soil. Surface runoff - Water moves across the surface of the earth becoming a stream, tributary or river.
What is interception and infiltration?
The highest level of interception occurs when it snows on conifer forests and hardwood forests that have not yet lost their leaves. INFILTRATION. Infiltration is the physical process involving movement of water through the boundary area where the atmosphere interfaces with the soil.
What is interception simple?
1a : to stop, seize, or interrupt in progress or course or before arrival. b : to receive (a communication or signal directed elsewhere) usually secretly. 2a : to gain possession of (an opponent's pass) b : to intercept a pass thrown by (an opponent)
What is interception in geography GCSE?
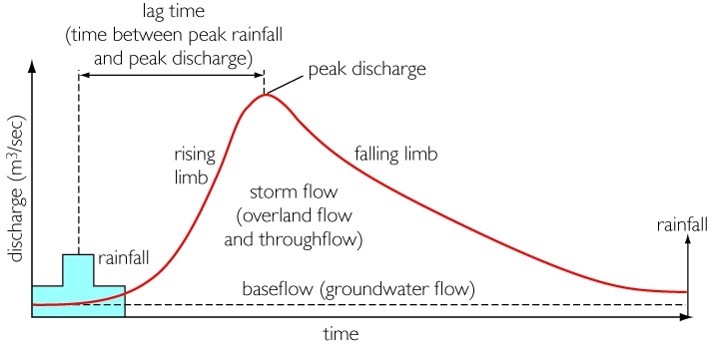
This is known as precipitation . Stores: How water is stored or held for a period of time within the drainage basin system - interception (by vegetation), soil moisture, surface storage (lakes), groundwater.
Is interception a flow?
Stores include puddles, rivers, lakes (surface storage), glaciers, soil storage and groundwater storage along with water stored on vegetation (interception) following precipitation. Transfers or flows include percolation, overland flow, infiltration, stemflow, throughflow and overland flow.
Why is interception important in geography?
Overall, we can conclude that interception has different roles in the hydrological cycle. The most important role is as a rainfall reducer, causing a significant amount of rainfall to be directly fed back to the atmosphere which is not available for infiltration.
What affects interception?
Interception varies with the species, its age and density of stands. About 10 to 20% of precipitation occurring in the growing season is intercepted. It is lost substantially by way of evaporation from leaves. In dense tall vegetation interception is quite substantial.
What is interception losses in hydrology?
Interception loss is the portion of the precipitation that is returned to the atmosphere through evaporation from plant surfaces or is absorbed by the plant. It is the diffe- rence between the precipitation actually occurring over an area and the part that reaches the soil.
What is intercept in a graph?
What are intercepts? The x-intercept is the point where a line crosses the x-axis, and the y-intercept is the point where a line crosses the y-axis.
What does interception look like?
An interception is when you have a house larger than 30 degrees AND it is engulfing an entire sign. A sign is totally enclosed in a house, and, as a result, they do not appear at the beginning of any house. An interception is NOT when you have two signs in one house–every chart has that naturally.
How does interception help in soil conservation?
Second, interception plays an important role in protecting the mineral soil surface from the energy of rainfall. Reduction of raindrop energy by interception minimizes soil detachment and subsequent erosion as well as protects soil structure and infiltration capacity.
What is the interception of rainfall?
Interception is the rainfall intercepted by the vegetation canopy and subsequently evaporated back to the atmosphere. This widely-used Gash analytical model is modified, referred to as the RS-Gash model (remote sensing based Gash model), by introducing remote sensing observations of vegetation area index (VAI), FVC, and rainfall rate. The Gash analytical model was first established based on the dense forest in the middle-high latitude forest regions, and was further adapted to be applied in sparse forest canopy (Gash, 1979; Gash et al., 1995 ). It basically assumes that intercepted rainfall happen in discrete storms and intercepted water lose completely before the next storm. There are three phases for rainfall interception loss: (1) wetting phase that rainfall reach the canopy; (2) saturation phase that the canopy reach its maximum water storage capability; and (3) drying phase that after rainfall has ceased. And evaporation is calculated for each phase with an average evaporation rate for all rainfall events. Although it is an event-based model, it successfully applied on a daily basis with the assumption of one storm per rain day. It is generally assumed that there is one rainfall event per day so that the Gash model can be used to calculate the interception loss on a daily scale.
What is the effect of interception of precipitation?
Interception of precipitation by low vegetation such as shrubs or grass, or by litter on the ground, results in a redistribution of the water flux on a small scale. Amounts of stored water might be large, and in the sheltered location water is not rapidly removed by evaporation, most of it eventually going as liquid to the soil.
What are the phases of interception loss?
There are three phases for rainfall interception loss: (1) wetting phase that rainfall reach the canopy; (2) saturation phase that the canopy reach its maximum water storage capability; and (3) drying phase that after rainfall has ceased. And evaporation is calculated for each phase with an average evaporation rate for all rainfall events.
What is the interception of radiation by a cone?
The interception of radiation by a cone is an interesting problem, relevant to the distribution of radiant energy when leaves on a single tree (Figure 7.8) or on the foliage of a crop are distributed randomly with respect to the points of the compass.
How does vegetation intercept water?
Vegetation intercepts water in two ways: by catching rainfall on leaf surfaces throughout the canopy, and through the litter that it deposits on the ground.
Is light interception proportional to leaf area?
Crop light interception is no more proportional to leaf area when the canopy is dense. In homogeneous conditions (that is to say most cases), a crop can be considered as a turbid environment and light interception is well described by Lambert–Beer law (Figure 7 ).
What is the interception of water?
Interception refers to precipitation that does not reach the soil, but is instead intercepted by the leaves, branches of plants and the forest floor. It occurs in the canopy (i.e. canopy interception ), and in the forest floor or litter layer (i.e. forest floor interception ).
Why does interception of water cause loss of precipitation?
Because of evaporation, interception of liquid water generally leads to loss of that precipitation for the drainage basin, except for cases such as fog interception, but increase flood protection dramatically, Alila et al., (2009). Definition of canopy and forest floor interception.
What trees have an intercept of approximately 38% of the gross precipitation in temperate climate?
Trees like Norway maple and a small-leaved lime have an interception of approximately 38% of the gross precipitation in temperate climate.
Infiltration
When water from a rainstorm or a period of snowmelt reaches the ground, some or all of it will infiltrate the soil. The rate of infiltration depends on the intensity of the input, the initial moisture condition of the surface soil layer, and the hydraulic characteristics of the soil.
Evapotranspiration
Rates of evapotranspiration of water back to the atmosphere depend on the nature of the surface, the availability of water, and the “evaporative demand” of the atmosphere (i.e., the rate at which water vapour can be transported away from the surface under the prevailing meteorologic conditions).
Soil moisture
The soil provides a major reservoir for water within a catchment. Soil moisture levels rise when there is sufficient rainfall to exceed losses to evapotranspiration and drainage to streams and groundwater. They are depleted during the summer when evapotranspiration rates are high.