What temperature equals the dew point?
The dew point temperature is always less than or equal to the air temperature. At the dew point, the relative humidity is 100% (at constant pressure). When the relative humidity is 100 the air temperature is equal to? Relative humidity of 100% indicates the dew point is equal to the current temperature and that the air is maximally saturated with water. For example, at 22°C and 100% RH the air will have a dew point of 22°C also.
What factors determine the dew point?
The dew point is the temperature to which air must be cooled to become saturated with water vapor, assuming constant air pressure and water content.When cooled below the dew point, moisture capacity is reduced and airborne water vapor will condense to form liquid water known as dew.When this occurs via contact with a colder surface, dew will form on that surface.
Can the dew point be higher than the temperature?
When this is achieved, the temperature of the air has reached the dew point temperature. It is also called the condensation temperature. The dew point temperature can never be higher than the air temperature.
What happens when temperature drops below the dew point?
What happens when temperature drops below dew point? The temperature can never go below the dew point. The dew point is the temperature that 100% relative humidity is reached, based on the amount of water vapour in the air. That means that once the temperature drops to that point, the air cannot hold any more water vapour so condensation occurs.
How do you read dew point chart?
1:208:15Relative Humidity & Dew Point Charts- HOW TO - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou look up the dry bulb on your table. And you look up the difference on your table the dry bulbMoreYou look up the dry bulb on your table. And you look up the difference on your table the dry bulb information will be listed along the left hand side of your chart.
How do you find the dew point temperature?
You can physically determine the dew point temperature with a device called a hygrometer. For it to work, a smooth, shiny surface, like a mirror, is cooled until water vapor in the air begins to condense on it. When that happens, you have the dew point temperature.
What does dew point tell you?
The dew point temperature tells us the absolute quantity of moisture that is in the air, thereby indicating how humid it will feel outside to our bodies. On the other hand, relative humidity only tells us how saturated the air is compared to how much it can hold.
How do you read the dew point temperature of moist air on a psychrometric chart?
Take a ruler and draw a vertical line at the dry bulb temperature of 70 and draw a horizontal line where the dew point is 50. The point where these two lines intersect is known as a 'state point'. Plot the state point and you can also read the rel- ative humidity, wet bulb, enthalpy, vapor pressure and humidity ratio.
What is the unit of dew point?
WHAT IS DEW POINT? As the term implies, it is the climate point at which the relative air humidity equals 100% and begins to condense. The dew point is given in °C Td. The dew point temperature is a measurement of the water vapor content in a gas.
What is dew point vs humidity?
Dew point is the temperature at which the air becomes saturated (100 percent relative humidity). It is dependent on only the amount of moisture in the air. Relative humidity is the percent of saturation at a given temperature; it depends on both moisture content and temperature.
Can dewpoint be higher than temperature?
Dew point temperature is NEVER GREATER than the air temperature. Therefore, if the air cools, moisture must be removed from the air and this is accomplished through condensation. This process results in the formation of tiny water droplets that can lead to the development of fog, frost, clouds, or even precipitation.
Is dew point the same as saturation temperature?
Is Dew Point and Saturation Point Same? The dew point and saturation point are not the same; there is a variation in the temperature and the density of the system at both points. At saturation point, the density of the water vapors in the air is very high and the temperature is equal to the atmospheric temperature.
How do you read a psychrometric chart?
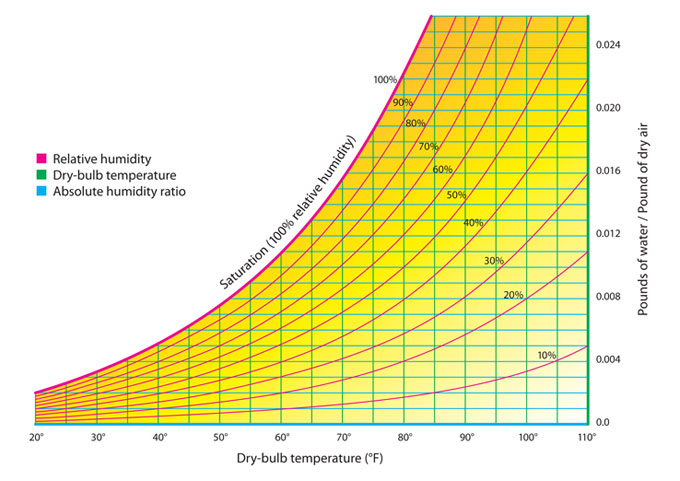
Reading A Psychrometric ChartDry Bulb Temperature: the axis along the bottom.Humidity Ratio and Vapor Pressure: the right axis.Saturation Temperature or Dew Point: the curved left axis.Enthalpy: the slanted left axis.Relative Humidity: the lines that curve up from left to right.More items...•
What is the range of DBT on the psychrometric chart usually used?
from -6 to 45°C.What is the range of DBT on the psychrometric chart usually used? Explanation: Generally, the temperature range of dry bulb temperature lines on the psychrometric chart is from -6 to 45°C. These lines are drawn with a difference of every 5°C of DBT.
Plotting Lines of Constant Relative Humidity
Lines of constant relative humidity can be superimposed on to the same chart. For example, say the 60 percent RH line. First, locate the point of 60 percent RH on the 80°F DB line, as follows. Since at 80°F is 156 gr/lb, the moisture content at 60 percent RH = 0.60 X 156 = 93.5 gr per pound of dry air. This condition is plotted as point A.
Lines of Constant Wet-Bulb Temperature
To locate lines of constant wet-bulb temperature, at saturation, dry-bulb temperature = dew point temperature = wet bulb temperature, one point on each wet bulb line is already located, that is, the point of intersection of each dry-bulb line with the saturation line.
Mixtures of Air Quantities
The process of mixing two air streams occurs in air conditioning systems, and it is necessary to determine the properties of the resultant mixture. An example would be mixing outside air with space or return air.
How to determine dewpoint temperature?
When air is cooled, the relative humidity increases until saturation is reached and condensation occurs. Condensation occurs on surfaces which are at or below the dewpoint temperature. Dewpoint temperature is determined by moving from a state point horizontally to the left along lines of constant humidity ratio until the upper, curved, saturation temperature boundary is reached.
Why do we use psychrometric charts?
Understanding psychrometric charts can help you visualize environmental control concepts, such as why heated air can hold more moisture or, conversely, how allowing moist air to cool will result in condensation. This fact sheet explains how characteristics of moist air are used in a psychrometric chart.
What is dry bulb temperature?
is the commonly measured temperature from a thermometer. It is called "dry-bulb" since the sensing tip of the thermometer is dry (see "wet bulb temperature" for comparison). Dry-bulb temperature is located on the horizontal, or x-axis, of the psychrometric chart and lines of constant temperature are represented by vertical chart lines. Since this temperature is so commonly used, assume that temperatures are dry-bulb temperatures unless otherwise designated.
How does evaporative cooling work?
Evaporative cooling uses heat contained in the air to evaporate water. Air temperature (dry-bulb) drops while water content (humidity) rises to the saturation point. Evaporation is often used in hot weather to cool ventilation air. The process moves upward along the line of constant enthalpy or constant wet-bulb temperature, for example, from point D to point E in Figure 5. Notice that hot dry air (points D to E with a 24° F temperature drop) has more capacity for evaporative cooling than hot humid air (points F to G with only a 12° F temperature decrease).
How much humidity can a greenhouse have in winter?
A rule of thumb for inside typical greenhouses or animal buildings during winter conditions is that a 10°F rise in air temperature can decrease relative humidity 20 percent. Use of a psychrometric chart will show that this is roughly true.
What are psychrometric properties?
Psychrometric properties also are available as data tables, equations, and slide rulers. A psychrometric chart packs a lot of information into an odd-shaped graph. If we consider the components piece by piece, the usefulness of the chart will be clearer.
What is the difference between warm and cool air?
Warm air is less dense than cool air, which causes warmed air to rise. This phenomena is known as thermal buoyancy. By similar reasoning, warmer air has greater specific volume and is hence lighter than cool air. On the psychrometric chart, lines of constant specific volume are almost vertical lines with scale values written below the dry-bulb temperature scale and above the upper boundary's saturation temperature scale. On this chart, values range from 12.5 to 15.0 cubic feet/ pound of dry air. Greater specific volume is associated with warmer temperatures (dry-bulb).
Why does humidity rise at ground level?
If all the other factors influencing humidity remain constant, at ground level the relative humidity rises as the temperature falls; this is because less vapor is needed to saturate the air. In normal conditions, the dew point temperature will not be greater than the air temperature, since relative humidity cannot exceed 100%.
What does 100% humidity mean?
A relative humidity of 100% indicates the dew point is equal to the current temperature and that the air is maximally saturated with water. When the moisture content remains constant and temperature increases, relative humidity decreases, but the dew point remains constant.
What happens when barometric pressure increases?
This means that, if the pressure increases, the mass of water vapor per volume unit of air must be reduced in order to maintain the same dew point.
What is the dew point?
t. e. The dew point is the temperature to which air must be cooled to become saturated with water vapor. When cooled further, the airborne water vapor will condense to form liquid water ( dew ). When air cools to its dew point through contact with a surface that is colder than the air, water will condense on the surface.
What is the device used to measure dew point?
Devices called hygrometers are used to measure dew point over a wide range of temperatures. These devices consist of a polished metal mirror which is cooled as air is passed over it. The temperature at which dew forms is, by definition, the dew point.
What is the dew point in temperature?
Most inhabitants of temperate areas will consider dew points above 21 °C (70 °F) oppressive and tropical-like, while inhabitants of hot and humid areas may not find this uncomfortable. Thermal comfort depends not just on physical environmental factors, but also on psychological factors. Dew point.
What is the rate of condensation at a temperature below the dew point?
At temperatures below the dew point, the rate of condensation will be greater than that of evaporation, forming more liquid water. The condensed water is called dew when it forms on a solid surface, or frost if it freezes.
How many measurements do you need to read a psychrometric chart?
When solving a problem involving a psychrometric chart, you only need 2 measurements to read the chart. Pick any 2 known measurements available and plot them on the chart where the lines intersect. Normally, you should give preference to measurements of dry temperature, absolute humidity, dew point, or vapor pressure.
What can you use a ruler for?
For example, if you know the dry temperature and absolute humidity readings, you can use a ruler to gather information about the dew point, relative humidity, specific volume, enthalpy, and vapor pressure. ...
What is a psychrometric chart?
Psychrometric charts are used by engineers and scientists to visualize the relationships of gases and vapors. While the charts may look complex, they’re relatively easy to read when you know what each part of the graph is representing. By identifying the axes and reading the markings on the interior of the chart, ...
How to find dew point on a graph?
1. Look on the right side of the chart to find the vertical dew point line. Just to the right of the Y-axis, find the line with the dew point measurement in degrees Fahrenheit or Celsius. If you’re having trouble seeing the lines on the chart, use a ruler to align the hash marks with the lines on chart.
How to measure wet bulb temperature?
Wet Bulb Temperature can be measured with a thermometer that has the bulb covered with a water-moistened bandage with air flowing over the thermometer. Wet-Bulb Temperatures are always lower than dry bulb temperatures with less than 100% relative humidity in the air.
What is the temperature at which water vapor starts to condense in the air?
Dew Point is the temperature at which water vapor starts to condense in the air - the temperature at which air becomes completely saturated. Above this temperature the moisture stays in the air.
What is relative humidity?
Relative humidity can also be expressed as the ratio of water vapor pressure - pw, to the water vapor pressure of saturated air at the same temperature - pws . Relative humidity is expressed as a percentage. The moisture-holding capacity of air increases with air temperature. In practice the relative humidity will indicate the moisture level ...
What is the science of studying thermodynamic properties of moist air?
Psychrometry is the science of studying thermodynamic properties of moist air and the use of these to analyze humid air conditions and processes. Air conditioning processes can be determined with psychrometric charts and Mollier diagrams. Common properties in the charts includes.
Where is enthalpy on psychrometric chart?
Enthalpy in the psychrometric chart can read from where the appropriate wet-bulb line crosses the diagonal scale above the saturation curve. Air with the same amount of energy may either be drier hotter air (higher sensible heat) or cooler moister air (higher latent heat).
What does specific volume mean on a psychrometric chart?
Specific Volume represents the space occupied by a unit weight of dry air ( ft3/lb, m3/kg ). Specific volume is indicated along the bottom axis of the psychrometric chart with the constant-volume lines slanting upward to the left.