Explore
Trachea Treatments
- Tracheostomy: A small hole is cut in the front of the trachea, through an incision in the neck. ...
- Tracheal dilation: During bronchoscopy, a balloon can be inflated in the trachea, opening a narrowing (stenosis). ...
- Laser therapy: Blockages in the trachea (such as from cancer) can be destroyed with a high-energy laser.
What is the opening into the trachea called?
Tracheostomy (tray-key-OS-tuh-me) is a hole that surgeons make through the front of the neck and into the windpipe (trachea). A tracheostomy tube is placed into the hole to keep it open for breathing. The term for the surgical procedure to create this opening is tracheotomy.
What is the opening into the trachea?
- Need for prolonged respiratory support, such as Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia (BPD)
- Chronic pulmonary disease to reduce anatomic dead space
- Chest wall injury
- Diaphragm dysfunction
Why would a patient need a tracheostomy?
What Are The Pros And Cons Of A Tracheostomy? In an emergency, a tracheostomy procedure can save lives when other airway management techniques do not bring good results. 1. There are several potential benefits of using a tracheostomy when compared to a mechanical ventilator because it reduces sedation requirements. 2,3.
What are the pros and cons of a tracheostomy?
What is the surgical incision to larynx and trachea?
Tracheotomy (/ˌtreɪkiˈɒtəmi/, UK also /ˌtræki-/), or tracheostomy, is a surgical procedure which consists of making an incision (cut) on the anterior aspect (front) of the neck and opening a direct airway through an incision in the trachea (windpipe).
What is a surgical opening in the trachea?
A tracheostomy is an opening created at the front of the neck so a tube can be inserted into the windpipe (trachea) to help you breathe. If necessary, the tube can be connected to an oxygen supply and a breathing machine called a ventilator.
What is the difference between a tracheostomy tracheotomy and an intubation?
A tracheostomy (trach) is a procedure in which a doctor surgically makes an incision in the trachea, sometimes called the “windpipe.” Tracheostomy procedures are performed when there is an obstruction in the airway and intubation is medically not possible, a patient has inefficient oxygen delivery or has problems with ...
Is a tracheostomy a serious surgery?
A tracheostomy is a fairly common procedure, and it's especially safe if it's done in a hospital. But there can be complications. Risks during or soon after a tracheostomy include: Bleeding.
Where is the incision for tracheostomy?
Open Tracheostomy A skin incision is then marked in the midline anterior neck 1 to 2 cm inferior to the carotid cartilage. A horizontal or vertical incision may be utilized. The incision is extended through the platysma muscle to expose the strap muscles (sternohyoid and sternothyroid), identifying the median raphe.
Can you eat with a trach?
Most people will eventually be able to eat normally with a tracheostomy, although swallowing can be difficult at first. While in hospital, you may start by taking small sips of water before gradually moving on to soft foods, followed by regular food.
Is it better to be on a ventilator or tracheostomy?
Tracheostomy is recommended for patients receiving mechanical ventilation (MV) for 14 days or more in the intensive care unit (ICU). Nevertheless, many patients undergoing prolonged MV remain intubated via the translaryngeal route.
What is the quality of life after a tracheostomy?
The median survival after tracheostomy was 21 months (range, 0-155 months). The survival rate was 65% by 1 year and 45% by 2 years after tracheostomy. Survival was significantly shorter in patients older than 60 years at tracheostomy, with a hazard ratio of dying of 2.1 (95% confidence interval, 1.1-3.9).
How long can a person be on a ventilator with a trach?
Currently, most clinicians view 1–2 weeks after intubation as the most appropriate timing for tracheostomy [9]. Nonetheless, many patients still undergo MV via a translaryngeal endotracheal tube for more than 2 weeks.
Can you speak again after a tracheostomy?
Your Recovery But it may take at least 2 weeks to adjust to living with your trach (say "trayk"). At first, it may be hard to make sounds or to speak. Your doctor, nurses, respiratory therapists, and speech therapists can help you learn to talk with your trach tube or with other speaking devices.
Can you breathe on your own with a tracheostomy?
Usually air enters through the mouth and nose, goes through the windpipe and into the lungs. In cases with an injury or a blockage to the windpipe, a tracheostomy tube can bypass the damaged part of the windpipe and allow a person to continue to breathe on their own.
How long does a tracheostomy hole take to heal?
After the tracheostomy tube has been removed, the opening in your neck will be covered with a dressing. The opening will usually take one to two weeks to heal and afterwards you may have a small scar where the opening was. If the opening does not close on its own, stitches may be needed to close it.
How is air pulled into the trachea?
Most particles that enter the airway are trapped in the thin layer of mucus on the trachea walls. These are then moved upwards toward the mouth by cilia, where they can be swallowed.
How big is the trachea?
The trachea is roughly 4 to 5 inches long and 1 inch in diameter. It starts just under the larynx (voice box) and runs down the center of the chest behind the sternum (breast bone) and in front of the esophagus. 1 . The trachea is connected to the larynx via a ring of cartilage known as the cricoid cartilage.
What is the trachea vulnerable to?
The trachea is vulnerable to infections, inflammation, and other stresses that can damage cells. This can lead to conditions like tracheal stenosis, in which the trachea narrows and restricts breathing, and tracheal cancer, an extremely rare form of cancer.
How is the trachea connected to the larynx?
The trachea is connected to the larynx via a ring of cartilage known as the cricoid cartilage . As the trachea descends the chest, it is surrounded by 16 to 22 U-shaped rings of cartilage that hold the windpipe open like scaffolding, allowing the flow of air.
What is the posterior wall of the trachea?
The posterior wall of the trachea not covered by cartilage is composed of connective tissue and smooth muscle. The muscle will flex and expand when needed to change the diameter of the trachea. The trachea ends at the carina, a ridge of cartilage that separates and forms the junction into the bronchi.
What are the conditions that affect the trachea?
The trachea, like all parts of the respiratory system, is vulnerable to inhaled substances that can damage tissue and interfere with breathing. Certain infections and diseases can also affect the trachea, undermining its structure and/or function.
What is the name of the tube that delivers air to the bronchi?
The trachea, commonly known as the windpipe, is the large tube that delivers air from the upper respiratory tract (the nasal passages, throat, and larynx) to the bronchi (the two large airways that branch off into each lung).
How is a tracheostomy tube inserted?
A tracheostomy tube is inserted through the hole and secured in place with a strap around your neck. Tracheostomy (tray-key-OS-tuh-me) is a hole that surgeons make through the front of the neck and into the windpipe (trachea). A tracheostomy tube is placed into the hole to keep it open for breathing. The term for the surgical procedure ...
When is a tracheostomy performed?
In rare cases, an emergency tracheotomy is performed when the airway is suddenly blocked, such as after a traumatic injury to the face or neck. When a tracheostomy is no longer needed, it's allowed to heal shut or is surgically closed. For some people, a tracheostomy is permanent. Mayo Clinic's approach.
How to get rid of tracheostomy secretions?
Putting small amounts of saline directly into the tracheostomy tube, as directed, may help loosen secretions. Or a saline nebulizer treatment may help. A device called a heat and moisture exchanger captures moisture from the air you exhale and humidifies the air you inhale.
What is a tracheostomy tube?
Overview. A tracheostomy is a surgically created hole (stoma) in your windpipe (trachea) that provides an alternative airway for breathing. A tracheostomy tube is inserted through the hole and secured in place with a strap around your neck. Tracheostomy (tray-key-OS-tuh-me) is a hole that surgeons make through the front ...
Why do we need a tracheostomy?
A tracheostomy is often needed when health problems require long-term use of a machine (ventilator) to help you breathe. In rare cases, an emergency tracheotomy is performed when the airway is suddenly blocked, ...
What happens if you have a tracheostomy after you leave the hospital?
Infection around the tracheostomy or infection in the trachea and bronchial tubes (tracheobronchitis) and lungs (pneumonia) If you still need a tracheostomy after you've left the hospital, you'll need to keep regularly scheduled appointments for monitoring possible complications.
What are the complications of a tracheostomy?
Long-term complications are more likely the longer a tracheostomy is in place. These problems include: Obstruction of the tracheostomy tube. Displacement of the tracheostomy tube from the trachea.
What is the name of the procedure that is done through the neck into the trachea?
One solution to this problem is a tracheostomy. A tracheostomy is a temporary or permanent opening surgically created through the neck into the trachea (or windpipe) where a tube is then placed so that the patient can breathe. The procedure is also called a tracheotomy, but both terms are often used interchangeably.
When is a tracheotomy tube removed?
As patients continue to be treated and become healthier, the tracheotomy tube is removed as soon as possible. Removing the tube usually requires changing the tube to a smaller tube. The patient then starts capping trials where the tracheotomy tube is capped and the patient observed.
Why do you need a tracheostomy?
There are three major reasons why someone may need a tracheostomy, says Dr. Mehra. They include: 1 To help patients loosen and remove mucus or phlegm from the bronchioles to the upper airways to prevent lung infections. A tracheostomy allows doctors to insert a suction catheter into the lungs to remove mucus. 2 If a patient has been on prolonged ventilation through a tube in the mouth, a tracheostomy tube in the neck may allow the patient to be wide awake and more comfortable as they work towards becoming unhooked from the ventilation equipment and breathe on their own. 3 If a patient has an obstructed upper airway because of a tumor, inflammation, infection, or other blockage, a tracheotomy can easily and safely deliver oxygen directly to the lungs, bypassing the obstruction.
What are the complications of a tracheostomy?
However, the two complications doctors see most often are profuse bleeding or a dislodged tracheotomy tube.
How long does it take to make a tracheostomy?
The procedure to make a tracheostomy usually takes between 20 and 45 minutes.
What is the function of the trachea?
Central to a lot of these function is the trachea, a large membranous tube reinforced by rings of cartilage, that connects the voice box to the lungs. If the trachea is damaged or blocked, it could block airflow from your mouth to your lungs. One solution to this problem is a tracheostomy.
Can a tracheotomy tube be inserted over a catheter?
Then, a catheter is threaded through the needle into the windpipe, and the opening is successively dilated until a tracheotomy tube can be inserted over the catheter. Percutaneous tracheostomies are generally considered less invasive than surgical tracheostomies, but can only be done safely in the properly chosen patient.
Where is a tracheostomy performed?
How is a tracheostomy performed? The tracheostomy procedure is performed in the operating room under general anesthesia. A small incision is made in the skin overlying the trachea in the middle of the neck.
What is a tracheostomy tube?
A tracheostomy tube is the plastic breathing tube that is placed into the hole.
Why do children need tracheostomy?
Two common reasons include: Upper airway obstruction may occur due to bilateral vocal cord paralysis, tracheal or laryngeal stenosis, infection, trauma, or due to a cyst or tumor.
How long does it take to change a tracheostomy tube?
The tracheostomy tube is changed to a new tube by the surgeon several days after the operation. Occasionally, the ties around the neck are changed during the first week after the operation.
How long do tracheostomy tubes stay in place?
Although some tracheostomy tubes stay in place for many months or years, many are temporary and can be removed after a shorter period of time.
Is a tracheostomy better than an endotracheal tube?
A tracheostomy allows for a ventilator to be used without a breathing tube that goes through the mouth or nose (endotracheal tube.) For long-term ventilation, a tracheostomy is considered safer and more comfortable than an endotracheal tube.
Can you swim with a tracheostomy?
When a tracheostomy is present, care must be taken to prevent water or sand from getting into the tracheostomy tube (no swimming.)
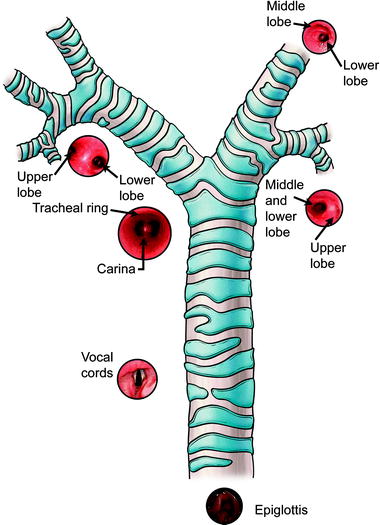
Anatomy
Function
- The trachea serves as the main passageway through which air passes from the upper respiratory tract to the lungs. As air flows into the trachea during inhalation, it is warmed and moisturized before entering the lungs. The U-shaped sections of cartilage that line the trachea are flexible and can close and open slightly as the trachealis muscle at t...
Associated Conditions
- The trachea, like all parts of the respiratory system, is vulnerable to inhaled substances that can damage tissue and interfere with breathing. Certain infections and diseases can also affect the trachea.
Treatment and Rehabilitation
- Injuries, infections, and diseases of the trachea can cause damage to the airway, sometimes irreparably. Tracheal stenosis is one such case in which the development of fibrosis (scarring) is most often permanent. Once the underlying cause of a tracheal injury is treated, efforts may be made to repair the trachea or support its function.
Overview
Why It's Done
- Situations that may call for a tracheostomy include: 1. Medical conditions that make it necessary to use a breathing machine (ventilator) for an extended period, usually more than one or two weeks 2. Medical conditions that block or narrow your airway, such as vocal cord paralysis or throat cancer 3. Paralysis, neurological problems or other conditions that make it difficult to cou…
Risks
- Tracheostomies are generally safe, but they do have risks. Some complications are particularly likely during or shortly after surgery. The risk of such problems greatly increases when the tracheotomy is performed as an emergency procedure. Immediate complications include: 1. Bleeding 2. Damage to the trachea, thyroid gland or nerves in the neck 3. Misplacement or displa…
How You Prepare
- How you prepare for a tracheostomy depends on the type of procedure you'll undergo. If you'll be receiving general anesthesia, your doctor may ask that you avoid eating and drinking for several hours before your procedure. You may also be asked to stop certain medications.
What You Can Expect
- During the procedure
A tracheotomy is most commonly performed in an operating room with general anesthesia, which makes you unaware of the surgical procedure. A local anesthetic to numb the neck and throat is used if the surgeon is worried about the airway being compromised from general anesthesia or i… - After the procedure
You'll likely spend several days in the hospital as your body heals. During that time, you'll learn skills necessary for maintaining and coping with your tracheostomy: 1. Caring for your tracheostomy tube.A nurse will teach you how to clean and change your tracheostomy tube to h…
Results
- In most cases, a tracheostomy is temporary, providing an alternative breathing route until other medical issues are resolved. If you need to remain connected to a ventilator indefinitely, the tracheostomy is often the best permanent solution. Your health care team will help you determine when it's appropriate to remove the tracheostomy tube. The hole may close and heal on its own, …