How to analyze TLC?
always between zero and one. A TLC analysis might be summarized something like, "Using a silica gel plate and ethyl acetate as the development solvent, unknown mixture X showed three spots having Rf's of 0.12, 0.25, and 0.87". Comparing these Rf's with the Rf's of known compounds might enable a tentative identification to be made.
How to read TLC results?
Watch TLC’s Jazz Jennings Confront Her Complex Feelings About Weight Loss
- Celebrity Coming Out Stories. “I honestly feel beautiful every shape and size. ...
- Celebrities' Weight Loss and Transformations: Before and After Photos. ...
- Lady Gaga, Miley Cyrus and More Celebrity LGBTQ Allies. ...
- Celebrity LGBTQ Allies
How to interpret TLC?
Step by Step Guide
- A Quick Infographic Guide for Thin Layer Chromatography. After lining up the entire procedure for running a TLC, I want to cut to a quick reference graphical guide that we ...
- Thin Layer Chromatography for Reaction Monitoring. The main use of TLC is monitoring chemical reactions. ...
- TLC for Column Chromatography Purification. ...
How does solvent affect TLC?
How does solvent affect TLC? The eluting power of solvents increases with polarity. Therefore, low polarity compounds can be eluted with low polarity solvents, while higher polarity compounds require solvents of higher polarity. The stronger a compound is bound to the adsorbent , the slower it moves up the TLC plate. Click to read more on it.
What is the purpose of an eluent?
The eluent or eluant is the "carrier" portion of the mobile phase. It moves the analytes through the chromatograph. In liquid chromatography, the eluent is the liquid solvent; in gas chromatography, it is the carrier gas.
Is water an eluent?
In ambient conditions water is too polar to be efficient eluent in chromatographic analysis. However, with increase of temperature it can be observed dramatically decrease of water polarity. Such high critical point of water allows wide spectrum of temperature and pressure values to choose.
Which solvents are used in TLC?
Solvent Systems for Thin Layer ChromatographyPolar compounds: 100% EtOAc or 5% MeOH/dichloromethane.Normal compounds: 10-50% EtOAc/Hexane.Nonpolar compounds: 5% EtOAc/hexane, 5% ether/hexane, 100% hexane.
How do you choose a solvent for TLC?
The solvent should be 2–3 mm deep so that the spotted sample and the line are not submerged. This ensures the sample does not dissolve into the solvent and travel up the TLC plate with the solvent.
What is elute in chromatography?
[ ĭ-lōō′shən ] n. The chromatographic process of using a solvent to extract an adsorbed substance from a solid adsorbing medium. The removal of antibody from the antigen to which it is attached.
What is meant by elution?
: to wash out or extract specifically : to remove (adsorbed material) from an adsorbent by means of a solvent.
How does TLC choose eluent?
If you want the Rf of your TLC spot to be smaller, i.e., the spot to be lower down on the plate, you must decrease the eluent polarity. Either choose a different eluent (solvent) or adjust the solvent ratio by increasing the percentage of the nonpolar solvent relative to the polar solvent in the eluent.
What is the solute and solvent in TLC?
There are three components in TLC: (1) the TLC plate (stationary phase), the development solvent (mobile phase), and the sample to be analyzed (solute). In our experiment the TLC plate consists of a thin plastic sheet covered with a thin layer of silica gel, a portion of the structure of which is shown below.
What are the polar solvent in TLC?
0:041:2411. Solvent Polarity- Effect on Rf - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipExample of a TLC is shown here. Let's assume it was developed using a 90/10 mixture of hexane aMoreExample of a TLC is shown here. Let's assume it was developed using a 90/10 mixture of hexane a nonpolar alkane and ethyl acetate a polar ester.
Why is solvent important in TLC?
The solvent, which is in the bottom of the container, travels up the layer of adsorbent by capillary action, passes over the spot and, as it continues up, moves the compounds in the mixture up the plate at different rates resulting in separation of the compounds.
Why are two solvents used in paper chromatography?
Why are two solvents used in the process? Different pigments will be soluble in one solvent but not another. Better separation of pigment bands will result if a combination of solvents is used.
Is silica polar or non polar?
polarSilica gel is a polar adsorbent. This allows it to preferentially adsorb other polar materials. When it comes to polarity, materials interact more with like materials. This principle is particularly important to many laboratories, which use silica gel as the stationary phase for column chromatography separations.
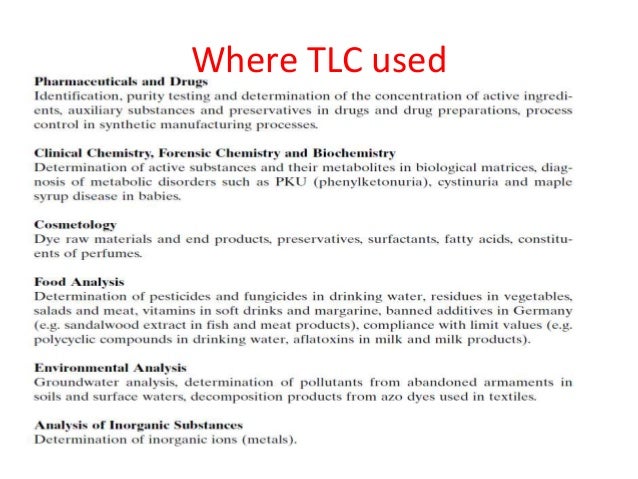
What is TLC used for?
Examining reactions and compound stability. TLC is also used for the identification of the completion of any chemical reaction. To determine this it is observed that at the beginning of a reaction the entire spot is occupied by the starting chemicals or materials on the plate.
What is TLC in chemistry?
Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) is a chromatography technique used to separate non-volatile mixtures. Thin-layer chromatography is performed on a sheet of an inert substrate such as glass, plastic, or aluminium foil, which is coated with a thin layer of adsorbent material, usually silica gel, aluminium oxide (alumina), or cellulose.
How are TLC plates made?
They are prepared by mixing the adsorbent, such as silica gel, with a small amount of inert binder like calcium sulfate (gypsum) and water. This mixture is spread as a thick slurry on an unreactive carrier sheet, usually glass, thick aluminum foil, or plastic. The resultant plate is dried and activated by heating in an oven for thirty minutes at 110 °C. The thickness of the absorbent layer is typically around 0.1–0.25 mm for analytical purposes and around 0.5–2.0 mm for preparative TLC.
Why is TLC used in chemical reactions?
Because of its simplicity and speed, TLC is often used for monitoring chemical reactions and for the qualitative analysis of reaction products.
What is the purpose of two dimensional TLC?
Furthermore, two-dimensional TLC is frequently used as a method to check if a compound is stable in the stationary phase (such as silica gel, which is usually slightly acidic).
How to run thin layer chromatography?
To run a thin layer chromatography plate, the following procedure is carried out: Using a capillary tube, a small spot of solution containing the sample is applied to a plate, about 1.5 centimeters from the bottom edge.
Why do chemists use thin layer chromatography?
Thin-layer chromatography can be used to monitor the progress of a reaction, identify compounds present in a given mixture, and determine the purity of a substance.
Most recent answer
1. The first consideration is that the sample concentration is too high. This can be verified by directly reducing the sample concentration.
All Answers (4)
As you are seeing the increasing polarity increases the trailing, (methanol + ethyl acetate gives significant tailing of the spots. 1 + 1 methanol + water gives dreadful tailing!). Why don't you try with some low polar solvent (like DEE)+ methanol?
What is TLC in chemistry?
TLC is a simple, quick, and inexpensive procedure that gives the chemist a quick answer as to how many components are in a mixture. TLC is also used to support the identity of a compound in a mixture when the R f of a compound is compared with the R f of a known compound (preferably both run on the same TLC plate).
What is the purpose of TLC chromatography?
Since TLC is a much faster procedure than column chromatography, TLC is often used to determine the best solvent system for column chromatography.
How to get a TLC plate to rise up?
The solvent will rise up the TLC plate by capillary action. Make sure the solvent does not cover the spot. Allow the plate to develop until the solvent is about half a centimeter below the top of the plate. Remove the plate from the beaker and immediately mark the solvent front with a pencil. Allow the plate to dry.
How to make a TLC chamber?
Step 1: Prepare the developing container. The developing container for TLC can be a specially designed chamber, a jar with a lid, or a beaker with a watch glass on the top (the latter is used in the undergrad labs at CU). Pour solvent into the chamber to a depth of just less than 0.5 cm.
What is a TLC plate?
A TLC plate is a sheet of glass, metal, or plastic which is coated with a thin layer of a solid adsorbent (usually silica or alumina). A small amount of the mixture to be analyzed is spotted near the bottom of this plate. The TLC plate is then placed in a shallow pool of a solvent in a developing chamber so that only the very bottom ...
Why can't you see spots after a TLC plate is developed?
If the solvent level in the developing jar is deeper than the origin (spotting line) of the TLC plate, the solvent will dissolve the compounds into the solvent reservoir instead of allowing them to move up the plate by capillary action. Thus, you will not see spots after the plate is developed.
How does a TLC plate work?
The TLC plate is then placed in a shallow pool of a solvent in a developing chamber so that only the very bottom of the plate is in the liquid. This liquid, or the eluent, is the mobile phase, and it slowly rises up the TLC plate by capillary action.
What is the difference between an eluate and an eluent?
It specifically includes both the analytes and solutes passing through the column, while the eluent is only the carrier.
What is the elution time of a solute?
The " elution time" of a solute is the time between the start of the separation (the time at which the solute enters the column) and the time at which the solute elutes. In the same way, the elution volume is the volume of eluent required to cause elution. Under standard conditions for a known mix of solutes in a certain technique, the elution volume may be enough information to identify solutes. For instance, a mixture of amino acids may be separated by ion-exchange chromatography. Under a particular set of conditions, the amino acids will elute in the same order and at the same elution volume.
What is an eluotropic series?
An eluotropic series is listing of various compounds in order of eluting power for a given adsorbent. The "eluting power" of a solvent is largely a measure of how well the solvent can "pull" an analyte off the adsorbent to which it is attached. This often happens when the eluent adsorbs onto the stationary phase, displacing the analyte. Such series are useful for determining necessary solvents needed for chromatography of chemical compounds. Normally such a series progresses from non-polar solvents, such as n-hexane, to polar solvents such as methanol or water. The order of solvents in an eluotropic series depends both on the stationary phase as well as on the compound used to determine the order.
What is the process of removing analytes from an adsorbent?
Elution then is the process of removing analytes from the adsorbent by running a solvent, called an "eluent", past the adsorbent/analyte complex. As the solvent molecules "elute", or travel down through the chromatography column, they can either pass by the adsorbent/analyte complex or they can displace the analyte by binding to ...
Overview
Technique
The process is similar to paper chromatography with the advantage of faster runs, better separations, and the choice between different stationary phases. Because of its simplicity and speed, TLC is often used for monitoring chemical reactions and for the qualitative analysis of reaction products. Plates can be labeled before or after the chromatography process using a pencil or other im…
Plate preparation
TLC plates are usually commercially available, with standard particle size ranges to improve reproducibility. They are prepared by mixing the adsorbent, such as silica gel, with a small amount of inert binder like calcium sulfate (gypsum) and water. This mixture is spread as a thick slurry on an unreactive carrier sheet, usually glass, thick aluminum foil, or plastic. The resultant plate is dried and activated by heating in an oven for thirty minutes at 110 °C. The thickness of the absor…
Analysis
As the chemicals being separated may be colorless, several methods exist to visualize the spots:
• Fluorescent analytes, like quinine, may be detected under blacklight (366 nm)
• Often a small amount of a fluorescent compound, usually manganese-activated zinc silicate, is added to the adsorbent that allows the visualization of spots under UV-C light (254 nm). The adsorbent layer will thus fluoresce light-green by itself, but spots of analyte quench this fluorescence.
Applications
In organic chemistry, reactions are qualitatively monitored with TLC. Spots sampled with a capillary tube are placed on the plate: a spot of starting material, a spot from the reaction mixture, and a cross-spot with both. A small (3 by 7 cm) TLC plate takes a couple of minutes to run. The analysis is qualitative, and it will show if the starting material has disappeared, i.e. the reaction is complete, if any product has appeared, and how many products are generated (although this mi…
See also
• Radial chromatography
Bibliography
• F. Geiss (1987): Fundamentals of thin layer chromatography planar chromatography, Heidelberg, Hüthig, ISBN 3-7785-0854-7
• Justus G. Kirchner (1978): Thin-layer chromatography, 2nd edition, Wiley
• Joseph Sherma, Bernard Fried (1991): Handbook of Thin-Layer Chromatography (= Chromatographic Science. Bd. 55). Marcel Dekker, New York NY, ISBN 0-8247-8335-2.