Suture granuloma
Granuloma
A granuloma is a structure formed during inflammation that is found in many diseases. It is a collection of immune cells known as macrophages. Granulomas form when the immune system attempts to wall off substances it perceives as foreign but is unable to eliminate. Such substances include infectious organisms including bacteria and fungi, as well as other materials such as foreign object…
What suture materials are used in microsurgery?
sutures used typically for microsurgery such as ophthalmic brown and sharpe (B&S sizing) used for stainless steel wire gauges non absorbable suture suture used when continued support is needed silk suture suture commonly used for ligating blood vessels monofilament due to capillarity which suture should be used in presence of infection
What is a continuous suture?
A running suture, also known as a continuous suture, consists of one strand of suture material that runs for a lengthy distance along a wound, normally in a zigzag pattern, which is tied at either end. This suture resembles those used on baseballs, and so, they are sometimes called baseball sutures.
How to treat suture reaction?
“Suture granulomas can resolve on their own and simply monitoring it or using an anti-inflammatory agent may be all that’s needed,” says Dr. Mamelak. However, if the growth is painful, continues to grow, or is an aesthetic concern, the suture (and granuloma) can simply be removed.
What is basilar suture?
n. 1. a. The process of joining two surfaces or edges together along a line by sewing. b. The material, such as thread, gut, or wire, that is used in this... Basilar suture - definition of basilar suture by The Free Dictionary https://www.thefreedictionary.com/basilar+suture Printer Friendly
Do suture granulomas go away?
“Suture granulomas can resolve on their own, and simply monitoring it or using an anti-inflammatory agent may be all that's needed,” says Dr. Mamelak, our dual board-certified dermatologist. In other cases, where the growth continues to get worse or becomes painful, the suture and granuloma can both be removed.
How long do suture granulomas last?
The time duration between the operation and the occurrence of the granulomatous mass has been reported to vary between a few months to several years (2, 12). The diagnosis of suture granuloma is particularly important in patients treated for cancer because the condition may resemble local tumor recurrence.
Is suture granuloma painful?
Although keloids may be painful, the pain usually is not associated with menses, and the lesions do not bleed. A suture granuloma essentially is a foreign body reaction to suture remaining in the tissue after surgery. It is generally a tender, erythematous nodule that occurs several days to weeks after surgery.
Can you have a suture granuloma?
It is rare but possible that a suture granuloma may occur several years following a surgery. The occurrence of delayed suture granulomas has varied about from 4 months to 7 years in the literature [3,7,8].
How do you fix a suture granuloma?
“Suture granulomas can resolve on their own and simply monitoring it or using an anti-inflammatory agent may be all that's needed,” says Dr. Mamelak. However, if the growth is painful, continues to grow, or is an aesthetic concern, the suture (and granuloma) can simply be removed.
Why is it hard under my stitches?
You may feel bumps and lumps under the skin. This is normal and is due to the dissolvable sutures under the surface of the skin. These deep sutures take months to completely dissolve and the scar will not be smooth until this time.
When do suture granulomas form?
Although suture granulomas have been reported to develop several years after surgery, those in the two cases reported by Nomiya et al. developed as early as 9 and 2 months after surgery, respectively. The granuloma in the present case also developed only 9 weeks after surgery.
What happens if part of a suture is left in?
If the stitches are left in the skin for longer than is needed, they are more likely to leave a permanent scar. Nonabsorbable sutures also are ideal for internal wounds that need to heal for a prolonged time.
Why does my scar have a bump?
In some people, the scar tissue keeps forming long after the wound heals. This extra scar tissue causes the raised area on your skin that is called a keloid. Doctors still aren't sure why some people's skin scars this way. Many different types of skin injuries can lead to a keloid.
How common are suture granulomas?
Silk sutures are non-absorbable yarn which has a particularly high incidence of granuloma formation of 0.6–7.1 % [2, 3].
Can suture granuloma be cancerous?
Suture granuloma is a rare benign tumor caused by suture material, which usually appears several years after surgery.
Do suture granulomas bleed?
They may bleed easily and, in some cases, can be tender. Very rarely, more than one lesion of pyogenic granuloma may develop at the same time at the same site.
Why do suture granulomas form?
A suture granuloma forms as a result of the body’s immune system attempting to wall off the foreign substance from surrounding body tissues.
Where can you find a suture granuloma?
A suture granuloma, for example, can normally be found on or near the site of past surgery. Suture granulomas are a mass or cluster of immune cells that develop at the site of surgical sutures, or stitches.
What does granuloma look like?
The granuloma can look red and swollen in some cases. “Sometimes the body even trys to eliminate the foreign material through the skin’s surface, which can look like a boil or pimple in the area,” Dr. Mamelak states.
What are abnormal skin growths?
Abnormal skin growths – lumps, ridges, or other seemingly random growths on or below the surface of the skin – can be very concerning. This is especially true if they come up at the site of a previously treated skin cancer. However, not all of these growths are worrisome.
Can granulomas be removed?
However, if the growth is painful, continues to grow, or is an aesthetic concern, the suture (and granuloma) can simply be removed. Suture granulomas may reoccur. For this reason, any patient who has had even one incident should discuss this with their physician and surgeon before any subsequent medical procedure.
Can suture granulomas be treated on their own?
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, there are a variety of ways to treat suture granulomas. “Suture granulomas can resolve on their own and simply monitoring it or using an anti-inflammatory agent may be all that’s needed,” says Dr. Mamelak.
What is suture granulomas?
Suture granulomas are localized inflammatory reactions in response to retained suture material. A similar process may also occur in certain situations with mesh repairs 5 . Ultrasound is often used as a first-line imaging modality.
What is granuloma in sutures?
A suture granuloma represents a benign granulomatous proliferation in response to a retained foreign body. They less commonly occur with absorbable sutures, but may still occur.
What is the treatment for retained suture?
The treatment of choice is resection of the retained suture and surrounding inflammatory tissue.
What is a granuloma?
A granuloma is a little lump, or nodule. It is a clump of immune cells or white blood cells.
How to diagnose internal granulomas?
To do this, they may: ask a series of questions about the person’s symptoms. carry out a blood test. carry out an imaging test, such as an X-ray or CT scan. carry out a genetic test.
What causes granulomas in the intestine?
Sometimes, long-term conditions such as Crohn’s disease and sarcoidosis can cause granulomas.
What causes a foreign body granuloma?
When something penetrates the skin, eye, or other parts of the body, it can lead to a foreign body granuloma. This looks like a little lump at the site of the damage. Things that can lead to foreign body granulomas include: irritating substances, such as silica or some tattoo inks.
Where do granulomas develop?
A granuloma is a cluster of white blood cells and other tissues. They tend to develop in the lungs, on the head, or on the skin. Granulomas are not cancerous. This article will explain what a granuloma is, how and why they develop, and how to treat them.
What is the purpose of clumping cells together?
When the cells clump together, they protect the body from potential threats in two ways. The first is keeping an infection in one place to stop it from spreading to other parts of the body. The second is isolating an irritant or foreign object so it cannot do any further damage to the body.
Does granuloma annulare hurt?
Subcutaneous granuloma annulare is often just one lump underneath the skin. It tends to affect children more than adults, and it does not hurt.
What is a granuloma?
A granuloma is a tiny cluster of white blood cells and other tissue that can be found in the lungs, head, skin or other parts of the body in some people. Granulomas are not cancerous. They form as a reaction to infections, inflammation, irritants or foreign objects.
What causes granulomas?
Granulomas form when immune cells clump together and create tiny nodules at the site of the infection or inflammation.
How are granulomas diagnosed?
Your doctor or specialist will take a medical history and examine you if they suspect you might have granulomas. They may ask for tests such as a blood test, x-rays or CT scans, genetic tests or a needle biopsy.
What is the name of the disease that causes granulomas in the lungs?
sarcoidosis — a non-infectious disease that can cause multiple granulomas in different parts of the body, but especially in the lungs. chronic granulomatous disease — an inherited immunodeficiency condition that starts in childhood and leads to recurring bacterial and fungal infections.
What are the bumps under my skin?
Several types of granuloma can affect the skin. The most common is granuloma annulare, a harmless skin condition that causes raised pink or flesh-coloured bumps under the skin. The bumps are usually found over bony areas, like the elbow, and may have a distinctive ring shape. They often affect hands and arms, but can also affect legs, feet, trunk or face.
What is a foreign body granuloma?
Foreign body granulomas. This type of granuloma develops when the body's immune system reacts to an object or irritant that penetrates the skin, eye or body. They can form in reaction to: substances that irritate the person, including red tattoo ink and the silica in talcum powder.
Can a granuloma be seen on a scan?
Scans may show numerous minute granulomas in an organ such as the lungs. These can help diagnose the underlying cause. With skin granulomas, your doctor may only need to do a physical examination to confirm a diagnosis.
What is a granuloma on an X-ray?
A granuloma is a tiny lump of inflamed tissue in the body that gets its name from looking like a grain of sand or sugar. Sometimes granulomas harden and can be seen on an X-ray.
Why do we have granulomas?
The body produces granulomas as a way to block out certain irritants that it is unable to ward off, and these lumps can form in tissues throughout the body , affecting how organs, like the lungs or eyes, work. Certain diseases are characterized by the formation of granulomas.
How do you know if you have a granuloma?
A granuloma is a tiny lump of inflamed tissue in the body that gets its name from looking like a grain of sand or sugar. Sometimes granulomas harden and can be seen on an X-ray. To confirm the diagnosis, a tissue sample is taken through a biopsy and examined under a microscope.
What is the name of the disease that causes granulomas to form in the kidneys and lungs?
Granulomas that form in the lungs, kidneys and small blood vessels are characteristic of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (formerly known as Wegener granulomatosis), a rare autoimmune disease. Symptoms of the disease depend on where the granulomas have formed.
Can granulomas be treated with sarcoidosis?
Topical treatments and medications can be prescribed to treat sarcoidosis. However, not all people with sarcoidosis will need treatment.
Can granulomas be found during colonoscopy?
They can't be found during a colonoscopy but can be seen in a biopsy. The presence of granulomas can help doctors make a diagnosis, as granulomas do not form in people with ulcerative colitis, another major form of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Is sarcoidosis a granuloma?
Sarcoidosis is just one condition where granulomas are present in the body. There are other granulomatous conditions commonly seen by doctors:
What is a granuloma on an X-ray?
A granuloma is a small area of inflammation. Granulomas are often found incidentally on an X-ray or other imaging test done for a different reason. Typically, granulomas are noncancerous (benign). Granulomas frequently occur in the lungs, but can occur in other parts of the body and head as well.
Why do I have granulomas?
Granulomas seem to be a defensive mechanism that triggers the body to "wall off" foreign invaders such as bacteria or fungi to keep them from spreading. Common causes include an inflammatory condition called sarcoidosis and infections such as histoplasmosis or tuberculosis.
Do you need to follow up on granulomas?
Granulomas in people without symptoms almost never require treatment or even follow-up imaging tests.
What is a stoma granuloma?
One of the most common reasons for this is a little thing called a granuloma, this usually occurs at the junction of where the stoma joins onto the skin.
Why is it important to have a bag for a granuloma?
It is really important that the bag is as neat a size as possible to the stoma as the more contact with the mucocutaneous junction or the peristomal skin can develop other problems. If you are diagnosed that you do have a granuloma you will be wondering what the best treatment for this is.
What is the first line of treatment for a stoma?
According to the most recent guidelines for the stoma care nurses the first line of treatment would be using a silver nitrate pencil. What the nurse will do is just press the pencil down on the granuloma causing it to reduce in size.
How long does it take to go back to the hospital for granuloma?
You will need to go back to the hospital for around 4 weeks, 1 day each week to have the treatment repeated. Another tip that works well is once the nurse has treated the granuloma, put on a seal or a washer over the top of the treatment area helping to press down on the granuloma.
Can granulomas be prevented?
There is no real way to prevent granulomas occurring. They can re occur again even though they have been treated.
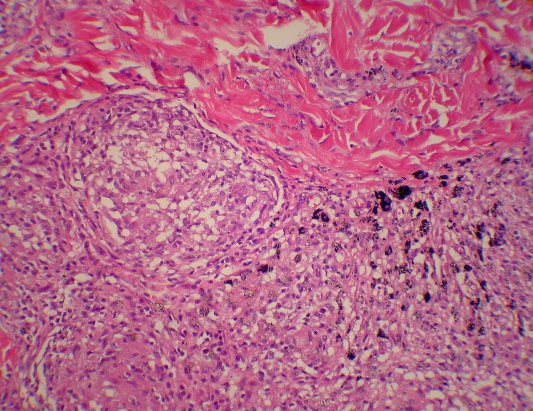
Signs and symptoms
- Abnormal skin growths lumps, ridges, or other seemingly random growths on or below the surface of the skin can be very concerning. This is especially true if they come up at the site of a previously treated skin cancer. However, not all of these growths are worrisome.
Types
- A suture granuloma, for example, can normally be found on or near the site of past surgery. Suture granulomas are a mass or cluster of immune cells that develop at the site of surgical sutures, or stitches.
Causes
- These granulomas are most commonly associated with embedded suture material, or material inadvertently left under the skin following the removal of surgical sutures or staples, explains Dr. Adam Mamelak, board certified Dermatologist and Mohs Micrographic Surgeon at Sanova Dermatology. However, these growths can also appear where dissolvable or absorbable suture material has been used under the skin to repair a wound. Suture granulo…
Pathophysiology
- A suture granuloma forms as a result of the bodys immune system attempting to wall off the foreign substance from surrounding body tissues. Immune system cells cluster around the foreign body or the site where a foreign body has been removed, encapsulating the area with immune cells. The granuloma can look red and swollen in some cases. Sometimes t...
Treatment
- Of course, with any sudden, unexplained skin growth, you should have it evaluated by your dermatologist as soon as possible. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, there are a variety of ways to treat suture granulomas. Suture granulomas can resolve on their own and simply monitoring it or using an anti-inflammatory agent may be all thats needed, says Dr. Mamelak. However, if the growth is painful, continues to grow, or is an aesthetic concern, …
Prognosis
- Suture granulomas may reoccur. For this reason, any patient who has had even one incident should discuss this with their physician and surgeon before any subsequent medical procedure.
Diagnosis
- If you are concerned your skin is not healing properly after surgery, please contact us. Our skilled physicians are available to address any questions and concerns you may have.