What is Riedel’s lobe and how is it detected?
The usual detection of Riedel’s lobe is through surgery or autopsy. It can be a result of embryonic heteroplasia or Riedel’s lobe can be a result of any trauma. It is mostly observed in women. The other name of Riedel’s lobe is the floating lobe or constriction lobe.
What causes the Riedel lobes to be formed?
If the Riedel lobe is of congenital origin then it is supported by Dysembryoplastic anomaly which is located in the hepatic bud. This leads to the formation of the Riedel lobe or accessory lobes. These are formed in intrahepatic positions.
How does the prevalence of Riedel's lobe vary by age?
There were no significant differences in the prevalence of Riedel's lobe between sexes. The proportion of individuals in whom the most caudal margin of the liver was inferior to the most caudal costal margin was age-dependent and increased to 65% in the 50-59 age group. The craniocaudal dimension of the liver decreased with age (P < 0.02).
What is the difference between Riedel's lobe and temporal lobe?
Riedel's lobean anomalous tongue-shaped mass of tissue projecting from the right lobe of the liver in some individuals. spigelian lobecaudate lobe. temporal lobea long tongue-shaped process that is the lower lateral portion of each cerebral hemisphere.
Is Riedel's lobe normal?
Riedel's lobe appears to be a common variant of normal anatomy, its prevalence being dependent on age-related changes in liver size and skeletal shape.
What is Riedel's lobe and discuss its clinical significance?
Riedel lobe is a common anatomical variant of the liver to be aware of because it can simulate a mass. Its misidentification as a pathologic abdominal mass has led to surgery. Pathology can also occur within it (e.g. malignancy or even torsion) and cause atypical hepatic symptoms low in the pelvis 1,2.
Can Riedel's lobe cause pain?
Mechanical complications An accessory lobe, and in particular, Riedel's lobe, can simulate a mass in the right upper quadrant, with symptoms such as pain, vomiting, constipation, or bloating [6], [25].
What is Riedel's lobe variant?
Riedel's lobe is a normal variant form of right liver lobe rarely found. Here we report a case of 38 years old female with an incidental finding not revealed in physical examination, but then known to have hepatomegaly by gynecological ultrasonography.
What is the treatment for Riedel's lobe?
Typical Riedel lobe usually has good prognosis considering the early-stage diagnosis, the lack of complications, and the proper treatment such as the resection of the hypertrophic parenchyma in case of torsion with noisy clinical presentation, metastatic lesion, or hepatic hydatide cysts of the Riedel lobe.
How do you get Riedel's lobe?
The etiology of Riedel lobe has been proposed to be either congenital or acquired. The congenital origin of Riedel lobe is supported by a congenital disembrioplasic anomaly in the development of a hepatic bud, which can lead to the formation of accessory lobes, in infrahepatic positions.
What is a Riedel's lobe in the liver?
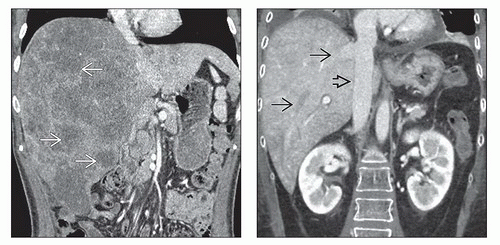
Riedel lobe is a tongue-like, inferior projection of the right lobe of the liver beyond the level of the most inferior costal cartilage on cross-sectional images 1. It is not considered a true accessory lobe of the liver but an anatomical variant of the right lobe of the liver 3.
Is polycystic liver disease curable?
The only definitive treatment of PLD, used in only the most severe cases, is liver transplant [2, 8, 33]. Medication to slow down cyst growth and fluid secretion in the liver (somatostatin analogs, namely octreotide and lanreotide) is also useful in reducing liver volume [7, 10].
What is the meaning hepatomegaly?
An enlarged liver is one that's bigger than normal. The medical term is hepatomegaly (hep-uh-toe-MEG-uh-le). Rather than a disease, an enlarged liver is a sign of an underlying problem, such as liver disease, congestive heart failure or cancer. Treatment involves identifying and controlling the cause of the condition.
What does mild hepatomegaly mean?
Hepatomegaly is an enlarged liver, which means it's swollen beyond its usual size. Your liver has a lot of important jobs. It helps clean your blood by getting rid of harmful chemicals that your body makes.
What is the normal size of liver?
By percussion, the mean liver size is 7 cm for women and 10.5 cm for men (Table 94.1). A liver span 2 to 3 cm larger or smaller than these values is considered abnormal. The liver weighs 1200 to 1400 g in the adult woman and 1400 to 1500 g in the adult man.
What side is your liver on?
The liver is located in the upper right-hand portion of the abdominal cavity, beneath the diaphragm, and on top of the stomach, right kidney, and intestines. Shaped like a cone, the liver is a dark reddish-brown organ that weighs about 3 pounds.
What is the Riedel lobe?
Riedel lobe. Riedel lobe is a common anatomical variant of the liver to be aware of because it can simulate a mass. Its misidentification as a pathologic abdominal mass has led to surgery. Pathology can also occur within it (e.g. malignancy or even torsion) and cause atypical hepatic symptoms low in the pelvis 1,2.
Is the Riedel lobe accessory or lobe?
Some feel that the term Riedel lo be should be abandoned as it is not an accessory lobe but just a variant of the appearance of the right lobe.
Where is the Riedel lobe?
Riedel lobe of the liver is a simple anatomical variation, a downward tongue-like projection of the anterior edge of the right lobe of the liver to the right of the gallbladder with its typical case to be rare.
What is the Riedel lobe of the liver?
Riedel lobe of the liver is a simple anatomical variation, a downward tongue-like projection of the anterior edge of the right lobe of the liver to the right of the gallbladder with its typical case to be rare. We report the case of a 71-year-old woman with typical feature of a nonpalpable Riedel's lobe of the liver, ...
Where is the floating lobe of the liver?
This rare morphologic feature of hepatic lobulation was firstly described by Corbin in 1830 and it was defined by Riedel in 1888, as a “round tumor on the anterior side of the liver, near the gallbladder, to its right.” In the literature, it is also referred as floating lobe, “tongue like,” or constriction lobe. 4 Nowadays, this downward elongation of the liver is frequently observed (mostly in women) by modern imaging techniques, but the typical case of Riedel lobe is rare. 4,7
Where is the hepatic lobulation?
This rare morphologic feature of hepatic lobulation was firstly described by Corbin in 1830 and it was defined by Riedel in 1888, as a “round tumor on the anterior side of the liver, near the gallbladder, to its right.”.
Is Riedel's lobe latent?
Generally, knowledge or suspicion of Riedel's lobe of the liver is important, as it does not always remain clinically latent, as in our case, and it can be complicated by its torsion or hepatic tumors.