What is a Maloney dilator made of?
What is a French Maloney dilator? The Maloney (Medovations, USA) is the most commonly used bougie dilator. Made of rubber and filled with mercury or tungsten, it has a tapered tip and is freely passed without a guidewire.
When is Maloney bougie dilation indicated for septoplasty?
Maloney bougie dilation is appropriate for single, distal strictures where the internal diameter of the lumen at the stricture site is greater than 10 mm and can be traversed by an endoscope. These are typically peptic strictures and Schatzki rings.
Can a Maloney dilator go down through the esophagus without any change?
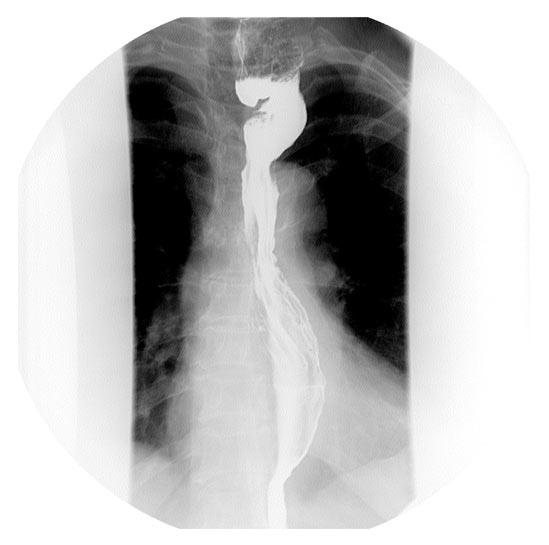
I have a doctor who performed an EGD with a Maloney dilation and dictates, "a 56'French Maloney dilator went down through the esophagus into the stomach without any apparent change. I did not see any tear that was noted because of the dilation. The scop was withdrawn.
What is the best Bougie dilator?
The Maloney (Medovations, USA) is the most commonly used bougie dilator. Made of rubber and filled with mercury or tungsten, it has a tapered tip and is freely passed without a guidewire.
What are Maloney dilators used for?
Maloney dilators were designed as weighted reusable devices with soft, tapered ends for per oral “blind” dilations of esophageal stenosis. Theoretically, this would minimize risk for trauma, given the soft, flexible tip and the ability to gradually dilate up to the desired size.
Is a Maloney dilator a balloon dilator?
Traditionally, mercury-weighted rub- ber bougies (Maloney dilators) are used for simple or mild-to-moderate esophageal strictures, whereas balloon dilators (hydrostatic and pneumatic) and wire-guided polyvinyl bougies have become stan- dard for more complex strictures.
What is a French Savary dilator?
Dilation Procedure Savary-Gilliard hollow-centered dilators were used to dilate esophageal narrowing over an endoscopically placed spring-tipped guide wire under fluoroscopy. The size of first dilator used was chosen based on the initial endoscopic assessment of luminal caliber.
Who makes Maloney dilators?
Medline Industries, Inc.Maloney Dilator Bougies | Medline Industries, Inc.
How can I naturally widen my esophagus?
You can strengthen your esophagus by making certain changes to your lifestyle, such as eating small meals and giving up smoking. These changes help lower your risk of having a narrowed esophagus. Other changes include avoiding foods that trigger acid reflux, such as spicy foods and citrus products.
How many times can esophagus be stretched?
Overall, one to three dilations are sufficient to relieve dysphagia in simple strictures. Only 25–35 % of patients require additional sessions, with a maximum of five dilations in more than 95 % of patients [4]. Complex strictures are usually longer (>2 cm), angulated, irregular, or have a severely narrowed diameter.
How do you clean a Savary dilator?
Savary-gilliard case should be washed throughly with soap and water then wiped dry with a lint-free cloth or air-dried. Note: betadine is not recommended for use on savary-gilliard dilators.
What is a bougie dilator?
Bougie dilation is an approach to widening esophageal strictures. During this procedure, your doctor uses a thin plastic tube (bougie) along with an endoscope to widen your esophagus. Your doctor will first guide an endoscope down your esophagus.
How many types of dilation are there?
There are two broad categories of dilators: mechanical (push-type or bougie) and balloon. Both types may or may not be used with a guidewire.
What is an American dilator?
american-dilation-system american-dilation-system CleanGuide is single-use product that eliminates the need to reprocess the wire. Eliminating reprocessing limits exposure of hazardous material to staff during cleaning and the potential for harm due to the reprocessed wire springing open during cleaning.
What is a Hurst dilator?
Hurst dilators are reusable, flexible silicone-based devices that are more commonly used for dilatation of benign esophageal sphincters but are also used off-label for bougienage. Most pediatric centers will have access to these through their operating or endoscopy suites.
What does it mean to dilate the esophagus?
Esophageal dilation is a procedure that allows your doctor to dilate, or stretch, a narrowed area of your esophagus [swallowing tube]. Doctors can use various techniques for this procedure. Your doctor might perform the procedure as part of a sedated endoscopy.
0.33 mm is converted to 1 of what?
The millimeters unit number 0.33 mm converts to 1 Fr, one French gauge. It is the EQUAL Diameter Size value of 1 French gauge but in the millimeters length unit alternative.
Length, Distance, Height & Depth units
Distance in the metric sense is a measure between any two A to Z points. Applies to physical lengths, depths, heights or simply farness. Tool with multiple distance, depth and length measurement units.
Other applications for this length calculator ..
With the above mentioned two-units calculating service it provides, this length converter proved to be useful also as a teaching tool: 1. in practicing French gauge and millimeters ( Fr vs. mm ) measures exchange. 2. for conversion factors between unit pairs. 3. work with length's values and properties.
Why Is Esophageal Dilation Performed?
Over time, different health problems can cause strictures to form in the esophagus, causing a narrowing of the esophagus. These strictures can make it difficult to swallow and you may have a feeling of food getting stuck in your chest. This feeling is because the food has a difficult time moving past the stricture.
Associated Risks
You should only have esophageal dilation performed by a trained care provider. While esophageal dilation is generally a safe procedure, there are some risks that you should be aware of.
What to Expect
Prior to the esophageal dilation, you will need to fast (not have food or water) for a minimum of six hours. You should follow your healthcare provider’s pre-procedure instructions regarding fasting time.
Will I Need Esophageal Dilation Again?
It is common for symptoms to eventually return after an esophageal dilation. How long it takes for symptoms to recur is variable and dependent on many factors including the severity and cause of the stricture. 2
PREOPERATIVE PLANNING
Candidates for esophageal dilation should be thoroughly evaluated prior to the procedure to determine the cause of the esophageal obstruction as well as the procedural risks associated with the patients’ comorbidities. History should be taken and physical examination performed before making the decision to intervene.
Principles
Despite the specific differences in the technique used, there are some principles that apply to all the types of esophageal dilation.
Positioning
Most commonly, the patient is placed in the left lateral decubitus position, which is the typical for upper endoscopy. This allows the use of all types of esophageal dilators and does not interfere with patient monitoring, while it facilitates the management if intraoperative regurgitation occurs and minimizes the risk of aspiration.
Push Dilators
The guided passage of push dilators, such as the Savary-Gilliard, lowers the risk of perforation. These dilators have a central lumen which allows their advancement over a stiff guidewire with a soft spring tip (Savary guidewire) ( Figs. 35.1 and 35.2 ). Softer guidewires can be used with caution when more complex strictures need to be negotiated.