Denatured protein loses its shape, which in turn affects its ability to function, but that doesn’t change its value. Since the amino acids remain intact, your body still absorbs, uses and benefits from denatured protein. In fact, protein must be denatured during digestion for proper digestion and maximum absorption.
What happens to a protein if it becomes denatured?
- Place an egg white into a clean bowl
- Observe the colour and texture of the egg white
- Now add 3ml of lemon juice to the egg white and stir
- Record what happens to the colour and texture of the egg white
What would be affected when a protein is denatured?
When a protein becomes DENATURED, some of its bonds begin to break, and it ufolds. Bonds that held the folding weaken. Bonds that created the spirals and pleats weaken. Covalent bonds that held the amino acids together remain. How is a denatured protein different from a normal protein?
What is Protein denaturing and why is it bad?
- For proteins to be utilized by the body, they need to be metabolized, or broken down to amino acids.
- We have enzymes or proteases to break down protein molecules into amino acid residues that are further utilized by the human body.
- When partially digested food reach the gut, the acidic environment is already going to have an impact on the struc
What are three conditions that can denature a protein?
What conditions denature proteins quizlet?
- Denaturation. refers to the physical changes that take place in protein exposed to abnormal conditions in the environment.
- Heat/Temperature. Disrupts H-bonds and hydrophobic interactions between non-polar reactions. …
- Acid/Bases. …
- Organic Compounds. …
- Heavy Metal Ions. …
- Agitation.
What happens when a protein is denatured quizlet?
When a protein is denatured, it disrupts the hydrogen, ionic, and disulfide bridges within it, as well as affecting its temperature, pH (hydrogen structure) and salinity. Of a protein folded, and after denaturation. Other chemicals that can break the bonds inside the protein that help it keep its shape.
What is denaturation of protein and what is its effect?
When a native protein is subjected to change in pH, temperature or chemicals, the tertiary structure of protein gets unfolded, the protein gets denatured. This causes the protein to change biological activity.Jan 14, 2019
What does a protein lose when it becomes denatured?
In secondary structure denaturation, proteins lose all regular repeating patterns such as alpha-helices and beta-pleated sheets, and adopt a random coil configuration. Primary structure, such as the sequence of amino acids held together by covalent peptide bonds, is not disrupted by denaturation.
What are the effects of denaturation?
Denaturation leads to the loss of protein function. In a protein-based enzyme, it could be a small change in the conformation of the active site, which renders it incapable of catalyzing a reaction. For proteins like antibodies, the loss of shape removes their ability to recognize and bind to antigens.Apr 28, 2017
What is the effect of denaturation on the structure?
Denaturation referred to as distruction and disruption of protein structure. Secondary and tertiary structures are destroyed, however primary structure remains as it is. Denaturation occur due to heating. Denaturation unfold the globular structure and open the helix.
How will denaturing an enzyme protein affect its function explain?
Denaturation involves the breaking of many of the weak H bonds within an enzyme, that are responsible for the highly ordered structure of the enzyme. Most enzymes lose their activity once denatured , because substrate can no longer bind to the active site.Sep 20, 2016
How do proteins become denatured?
A protein becomes denatured when its normal shape gets deformed because some of the hydrogen bonds are broken. Weak hydrogen bonds break when too much heat is applied or when they are exposed to an acid (like citric acid from lemon juice).
Why is protein denaturation important?
The way proteins change their structure in the presence of certain chemicals, acids or bases - protein denaturation - plays a key role in many important biological processes. And the way proteins interact with various simple molecules is essential to finding new drugs.
1. What is the process to turn egg whites from clear to white?
Objects like eggs change colour when exposed to heat or high temperature. The protein structure conforms to the most important component of a livin...
2. Name the factors that cause denaturation of proteins?
Various reasons cause the denaturation of protein. Some of them are an increased temperature that ruptures the protein molecules' structure, change...
3. How is the process of denaturation of proteins important to human beings?
The process of denaturation is extremely important to live beings. When we ingest food, and it goes to our stomach, the acids present over there, t...
How does denaturation affect protein?
Heavy salts disrupt the protein molecule structure in the same manner as the salts and the bases. Denaturation breaks the covalent bonds and disrupts the amino acid chains. For instance, alcohol of a very high concentration can disrupt the hydrogen bonding in amide groups in the secondary or tertiary protein structure in various amino acid ...
Why do proteins denaturate?
Various reasons cause denaturation of protein. Some of them are an increased temperature that ruptures the protein molecules' structure, changes in pH level, adding of heavy metal salts, acids, bases, protonation of amino acid residues, and exposure to UV light and radiation.
Why is denaturation important?
When we ingest food, and it goes to our stomach, the acids present over there, that is, HCL breaks down the protein molecule components so that the body can easily consume the nutrition. Without breaking the secondary and tertiary protein structure, facilitate the working ability of pepsin enzymes to convert it into peptides. Thus, digestion would not have been properly possible without denaturation of proteins.
What is the process of breaking down the bonds that make up a protein?
Denaturation of protein is a process that breaks down the strong links or bonds that makes up the protein molecules. Protein molecules in their native or natural form have strong bonds and a highly ordered and stable structure.
What causes denaturation of proteins?
Causes of Denaturation of Proteins 1 Temperature maintains stability to a great extent. The heat can disrupt hydrogen bonds and non-polar hydrophobic interactions. When heat is applied, it causes the molecules to vibrate, and it increases the kinetic energy, which disrupts the molecular structure. 2 Due to certain changes in the pH level, temperature, and chemical structure, the hydrogen bonds are disrupted, which results in the unfolding of globular proteins and uncoiling of the helix structure. Thus, the denaturation of proteins takes place, and the secondary and the tertiary structures are destroyed. Heavy salts disrupt the protein molecule structure in the same manner as the salts and the bases. 3 Denaturation breaks the covalent bonds and disrupts the amino acid chains. For instance, alcohol of a very high concentration can disrupt the hydrogen bonding in amide groups in the secondary or tertiary protein structure in various amino acid combinations.
Why does food become firmer after cooking?
For instance, when food is cooked, like egg or meat, it becomes firm due to the change in the protein molecules after it receives adequate heat. This process can be reversed to regain the original structure. If the denaturation agent is removed, the original structure will be restored.
What happens to the hydrogen bonds in a protein?
Due to certain changes in the pH level, temperature, and chemical structure, the hydrogen bonds are disrupted, which results in the unfolding of globular proteins and uncoiling of the helix structure. Thus, the denaturation of proteins takes place, and the secondary and the tertiary structures are destroyed.
What is the property of denatured proteins?
Denaturation does not involve identical changes in protein molecules. A common property of denatured proteins, however, is the loss of biological activity —e.g., the ability to act as enzymes or hormones.
What happens when denaturing agents are removed from a protein solution?
When denaturing agents are removed from a protein solution, the native protein re-forms in many cases. Denaturation can also be accomplished by reduction of the disulfide bonds of cystine—i.e., conversion of the disulfide bond (―S―S―) to two sulfhydryl groups (―SH).
How do cysteines become denaturated?
Reoxidation of the cysteines by exposure to air sometimes regenerates the native protein. In other cases, however, the wrong cysteines become bound to each other, resulting in a different protein. Finally, denaturation can also be accomplished by exposing proteins to organic solvents such as ethanol or acetone.
What happens when you boil a protein?
When a solution of a protein is boiled, the protein frequently becomes insoluble—i .e., it is denatured—and remains insoluble even when the solution is cooled. The denaturation of the proteins of egg white by heat—as when boiling an egg—is an example of irreversible denaturation.
Which peptide bonds are inaccessible in the native proteins?
The peptide bonds that can be split by trypsin are inaccessible in the native proteins but become accessible during denaturation. Similarly, denatured proteins give more intense colour reactions for tyrosine, histidine, and arginine than do the same proteins in the native state.
What is the process of regenerating a protein?
In some instances the original structure of the protein can be regenerated; the process is called renaturation. De naturation can be brought about in various ways. Proteins are denatured by treatment with alkaline or acid, oxidizing or reducing agents, and certain organic solvents.
Is ribonuclease stable in heat?
Some of the smaller proteins, however, are extremely stable, even against heat; for example, solutions of ribonuclease can be exposed for short periods of time to temperatures of 90 °C (194 °F) without undergoing significant denaturation. Denaturation does not involve identical changes in protein molecules.
What is the Denaturation of Protein?
Proteins are complex molecules made of amino acids. They are present in all organisms and play a vital role in cellular functions and processes. Denaturation of proteins occurs when the secondary and tertiary structure of a protein is altered and the protein is no longer capable of performing its function.
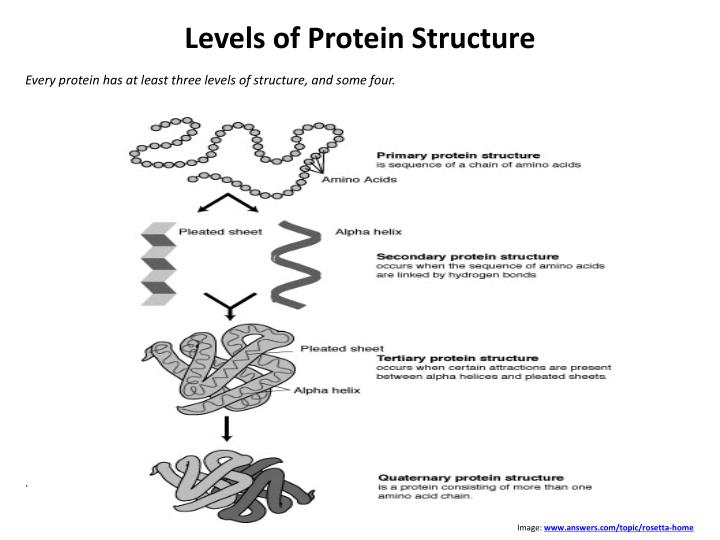
The Structure of Proteins
Proteins are composed of very long strands of amino acids linked together by covalent peptide bonds. Once the strands are formed, they fold into a 3-D shaped protein. The shape of the 3-D protein is determined by the amino acid sequence. Hydrophobic elements do not mix with water. These elements of the protein get buried inside the 3-D shape.
What Happens When a Protein is Denatured?
Reactions that occur during denaturing are not strong enough to disrupt the peptide bonds found in the primary structure of a protein. Denaturing can, however, affect both the secondary and tertiary structure of a protein.
Denaturation in Action
Denaturation of proteins causes the protein structure to degrade and subsequently the protein loses its shape. As you read in the lesson, an egg is a great model for protein denaturation because the white is composed mostly of the protein albumin.
What is denaturation in biology?
Denaturation can be defined as the disruption of the secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure of the native protein resulting in the alterations of the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of the protein by a variety of agents.
What is the process of denaturation used for?
When properly controlled, this process of denaturation is used to make yogurt and fresh cheese. Denatured proteins are involved in a number of diseases, from Parkinson’s disorder, Alzheimer’s to Huntington’s chorea.
What happens to proteins when they are boiled?
When it is boiled, heat denatures the proteins and makes them lose solubility. Denatured proteins aggregate and form a mass that is now opaque and solid. Similarly, altering the pH of milk by adding acids such as citric acid from lemon juice denatures milk proteins and curdles the milk.
What is the term for the disorganization of native protein structure?
The phenomenon of disorganization of native protein structure is known as Denaturation of protein. In other words, the denaturation of proteins is defined as any noncovalent changes in the structure of the protein. Denaturation results in the loss of the secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins.
What are the properties of native proteins?
They possess many characteristic properties such as solubility, viscosity, optical rotation, sedimentation rate, electrophoretic mobility etc.
Is protein denaturation harmful?
Though protein denaturation is detrimental for cell survival, it is often encountered in daily life. For instance, egg white is primarily made of soluble proteins and is liquid and translucent in fresh eggs. When it is boiled, heat denatures the proteins and makes them lose solubility.
Is denaturation irreversible?
Denaturation is irreversible however experimental evidence suggested that certain globular proteins denatured by heat, extremes of pH, or denaturing reagents will regain their native structure and their biological activity if returned to conditions in which the native conformation is stable. This process is called renaturation.