- The chromatin begins to condense into visible chromosomes.
- The nucleolus disappears.
- The centrioles begin to move to opposite sides of the cell.
- The mitotic spindle begins to form.
What are facts about the centriole?
Let’s Know
- Euglena has a red eyespot. The eyespot (eye-like marking) of Euglena is also known as the stigma and is red in color due to the presence of a red-colored ...
- They are both autotrophs and heterotrophs. Eating in Euglena is more like consuming (absorbing). ...
- It can survive in both fresh and salt water. ...
- They can also survive in the dark. ...
What function do centrosomes perform during mitosis?
Centrosomes are small cytoplasmic organelles that function as major microtubule-organizing centres during interphase and mitosis. Numerous studies have reported centrosome aberrations in human tumors where they frequently increase with malignant progression and advanced disease stage.
What is happening to the centrioles during prophase?
- Prophase I is the beginning phase of Meiosis I while Prophase II is the beginning phase of Meiosis II.
- There is a long interphase before Prophase I, whereas Prophase II occurs without an interphase. ...
- The pairing of homologous chromosomes occurs in Prophase I, whereas such process cannot be seen in Prophase II.
What is the function of the centrioles during metaphase?
The main parts of a cell, which are involved in the cell division are:
- Nucleus – It is the control centre of the cell.
- Centrioles – Centrioles are present in the animal cells.
- Microtubules – They help in aligning and separating the chromosomes during the metaphase and anaphase stage of cell division.
What happens to the centrioles during mitosis quizlet?
What happens to the centrioles during mitosis? What happens in Prophase I? Centrioles separate, spindle fibers are formed, nuclear envelope disappears, chromosomes become visible, tetrads form, crossing over takes place.
What happens to centrioles in telophase in mitosis?
An electron-dense halo, which surrounds only the mother centriole and is the site where spindle microtubules converge, disappears at the end of telophase. In metaphase and anaphase, the mother centriole is situated perpendicular to the spindle axis.
Do centrioles separate during mitosis?
In late mitosis/G1, the two centrioles separate from each other. This process is called 'centriole disengagement' (depicted in the enlargement at the right) and is regulated by the protease separase.
What happens to the centrioles during prophase in mitosis?
During prophase, chromatin condenses into chromosomes, and the nuclear envelope, or membrane, breaks down. In animal cells, the centrioles near the nucleus begin to separate and move to opposite poles (sides) of the cell. As the centrioles move, a spindle starts to form between them.
What phase do centrioles disappear?
During metaphase, the nuclear membrane disappears and the chromosomes become aligned half way between the centrioles. The centromere of each doubled chromosome becomes attached by thread-like spindle fibers to the centrioles which are at polar opposite sides of the cell.
What happens to the centrioles in interphase?
During interphase, the centrioles are static and have not started to play a role in cell division. In prophase, the centrioles move to opposite poles of the cell and start sending out microtubules which attach to the chromosomes.
What does the centriole do?
Centrioles are primarily involved in forming two structures-centrosomes and cilia. Centrioles bias the position of spindle pole formation, but because spindle poles can self-organize, the function of the centriole in mitosis is not obligatory.
What is the function of centrioles during cell division?
The main function of centrioles is to produce cilia during interphase and the aster and the spindle during cell division.
What are centrioles in meiosis?
Centrioles - Organizing Chromosomes Every animal-like cell has two small organelles called centrioles. They are there to help the cell when it comes time to divide. They are put to work in both the process of mitosis and the process of meiosis.
What happens to the centrioles during cytokinesis?
During cytokinesis, centrioles show increased mobility and either one centriole or the complete centrosome is frequently associated with the nuclear envelope. After abscission centrioles increase their mobility and frequently detach from the nuclear envelope.
In what stage of mitosis are the centrioles visible?
ProphaseProphase is the first stage of mitosis, during which the cell begins to position itself in order to separate the chromatids and divide. During prophase, the nuclear envelope and nucleolus are dissolved and the chromosomes condense. The centrioles and spindle fibers begin to form at opposite poles of the cell.
What happens during each stage of mitosis?
1) Prophase: chromatin into chromosomes, the nuclear envelope break down, chromosomes attach to spindle fibres by their centromeres 2) Metaphase: chromosomes line up along the metaphase plate (centre of the cell) 3) Anaphase: sister chromatids are pulled to opposite poles of the cell 4) Telophase: nuclear envelope ...
What do centrioles do in metaphase?
In metaphase, centrioles help to position polar fibers as they extend from the centrosome and position chromosomes along the metaphase plate. In keeping with the highway analogy, this keeps the lane straight.
What are centrioles in biology?
Updated September 01, 2019. In microbiology, centrioles are cylindrical cell structures that are composed of groupings of microtubules, which are tube-shaped molecules or strands of protein. Without centrioles, chromosomes would not be able to move during the formation of new cells. Centrioles help to organize the assembly ...
What are the functions of centrosomes?
Two Main Functions. During mitosis or cell division, the centrosome and centrioles replicate and migrate to opposite ends of the cell. Centrioles help to arrange the microtubules that move chromosomes during cell division to ensure each daughter cell receives the appropriate number of chromosomes. Centrioles are also important for the formation ...
What is the name of the structure that surrounds the centrioles?
Prophase and Asters and the Mitotic Spindle. In prophase, each centrosome with centrioles migrates toward opposite ends of the cell. A single pair of centrioles is positioned at each cell pole. The mitotic spindle initially appears as structures called asters which surround each centriole pair. Microtubules form spindle fibers ...
How do microtubules form spindle fibers?
Microtubules form spindle fibers that extend from each centrosome, thereby separating centriole pairs and elongating the cell. You can think of these fibers as a newly paved highway for the replicated chromosomes to move into the newly formed cell. In this analogy, the replicated chromosomes are a car along the highway.
How many sets of microtubules are in a centriole?
Composition. Most centrioles are made up of nine sets of microtubule triplets, with the exception of some species, such as crabs which have nine sets of microtubule doublets. There are a few other species that deviate from the standard centriole structure.
What happens to spindle fibers in telophase?
In telophase, the spindle fibers disperse as the chromosomes are cordoned off into distinct new nuclei. After cytokinesis, which is the division of the cell's cytoplasm, two genetically identical daughter cells are produced each containing one centrosome with one centriole pair.
Answer
During mitosis the four centrioles appear visibly and move to the ends of the nucleus one pair at each end then they produce a series of threads that attach to the chromosomes During cell division the threads split the chromosomes and drew them towards the centrioles.
New questions in Biology
Directions: Identify the models in each picture as an element or a compound. and there's more to it just answer the rest pls I need this test done thi …
What is the function of centrioles?
The main function of the centriole is to help with cell division in animal cells. The centrioles help in the formation of the spindle fibers that separate the chromosomes during cell division (mitosis). This occurs during the anaphase stage of mitosis in which the chromosomes move towards the different poles of the cell. Without centriole's, the chromosomes would not be able to move. In the picture above you can see the chromosomes moving to the opposite poles and also the spindle fibers (the lines).
What is the centrosome in G1?
G1 phase: Right after mitotic exit, G1 cells contain one centrosome that consists of two centrioles and the pericentriolar material (PCM). These two centrioles are attached at the base (the proximal end) by a proteinaceous linker (indicated by C-Nap1). At this stage, only the mother centriole contains subdistal and distal appendages. As G1 progresses, the mother centriole accumulates various components required for procentriole assembly.
Where Centrioles Are Found
Composition
- Most centrioles are made up of nine sets of microtubule triplets, with the exception of some species, such as crabs which have nine sets of microtubule doublets. There are a few other species that deviate from the standard centriole structure. Microtubules are composed of a single type of globular protein called tubulin.
Two Main Functions
- During mitosis or cell division, the centrosome and centrioles replicate and migrate to opposite ends of the cell. Centrioles help to arrange the microtubules that move chromosomesduring cell division to ensure each daughter cell receives the appropriate number of chromosomes. Centrioles are also important for the formation of cell structures known...
Important Role in Cell Division
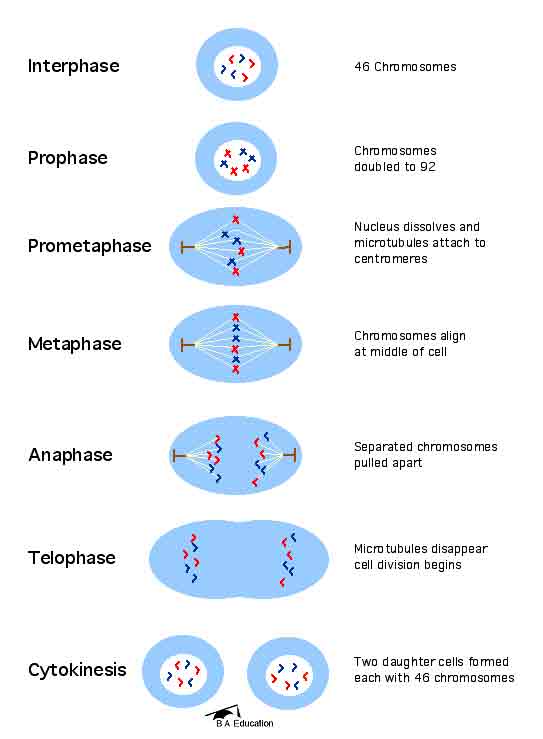
- Centrioles are located outside of, but near the cell nucleus. In cell division, there are several phases: in order of occurrence they are interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Centrioles have a very important role to play in all phases of cell division. The end goal is in moving replicated chromosomes into a newly created cell.
Interphase and Replication
- In the first phase of mitosis, called interphase, centrioles replicate. This is the phase immediately prior to cell division, which marks the start of mitosis and meiosis in the cell cycle.
Prophase and Asters and The Mitotic Spindle
- In prophase, each centrosome with centrioles migrates toward opposite ends of the cell. A single pair of centrioles is positioned at each cell pole. The mitotic spindle initially appears as structures called asters which surround each centriole pair. Microtubules form spindle fibersthat extend from each centrosome, thereby separating centriole pairs and elongating the cell. You can think …
Metaphase and Positioning of Polar Fibers
- In metaphase, centrioles help to position polar fibers as they extend from the centrosome and position chromosomes along the metaphase plate. In keeping with the highway analogy, this keeps the lane straight.
Anaphase and The Sister chromatids
- In anaphase, polar fibers connected to chromosomes shorten and separate the sister chromatids(replicated chromosomes). The separated chromosomes are pulled toward opposite ends of the cell by polar fibers extending from the centrosome. At this point in the highway analogy, it is as if one car on the highway has replicated a second copy and the two cars begin …
Telophase and Two Genetically Identical Daughter Cells
- In telophase, the spindle fibers disperse as the chromosomes are cordoned off into distinct new nuclei. After cytokinesis, which is the division of the cell's cytoplasm, two genetically identical daughter cellsare produced each containing one centrosome with one centriole pair. In this final phase, using the car and highway analogy, the two cars look exactly the same, but are n…