Units per milliliter (U/mL) The results of some medical tests are reported in units per milliliter (U/mL). A unit is an arbitrary amount agreed upon by scientists and doctors. A milliliter is a unit of fluid volume equal to one-thousandth of a liter.
Full Answer
What is the meaning of ML in science?
11/03/2020 · What does units per mL mean? Units per milliliter (U/mL) The results of some medical tests are reported in units per milliliter (U/mL). A unit is an arbitrary amount agreed upon by scientists and doctors. A milliliter is a unit of fluid volume equal to one-thousandth of a liter. A liter is slightly larger than a quart.
How do you calculate units in ML?
30/04/2005 · Units per volume (units / volume) concentration equation. C is the desired concentration of the final solution with the concentration unit expressed in units of activity per volume of solution (e.g., Units/mL).
What is a microgram per milliliter?
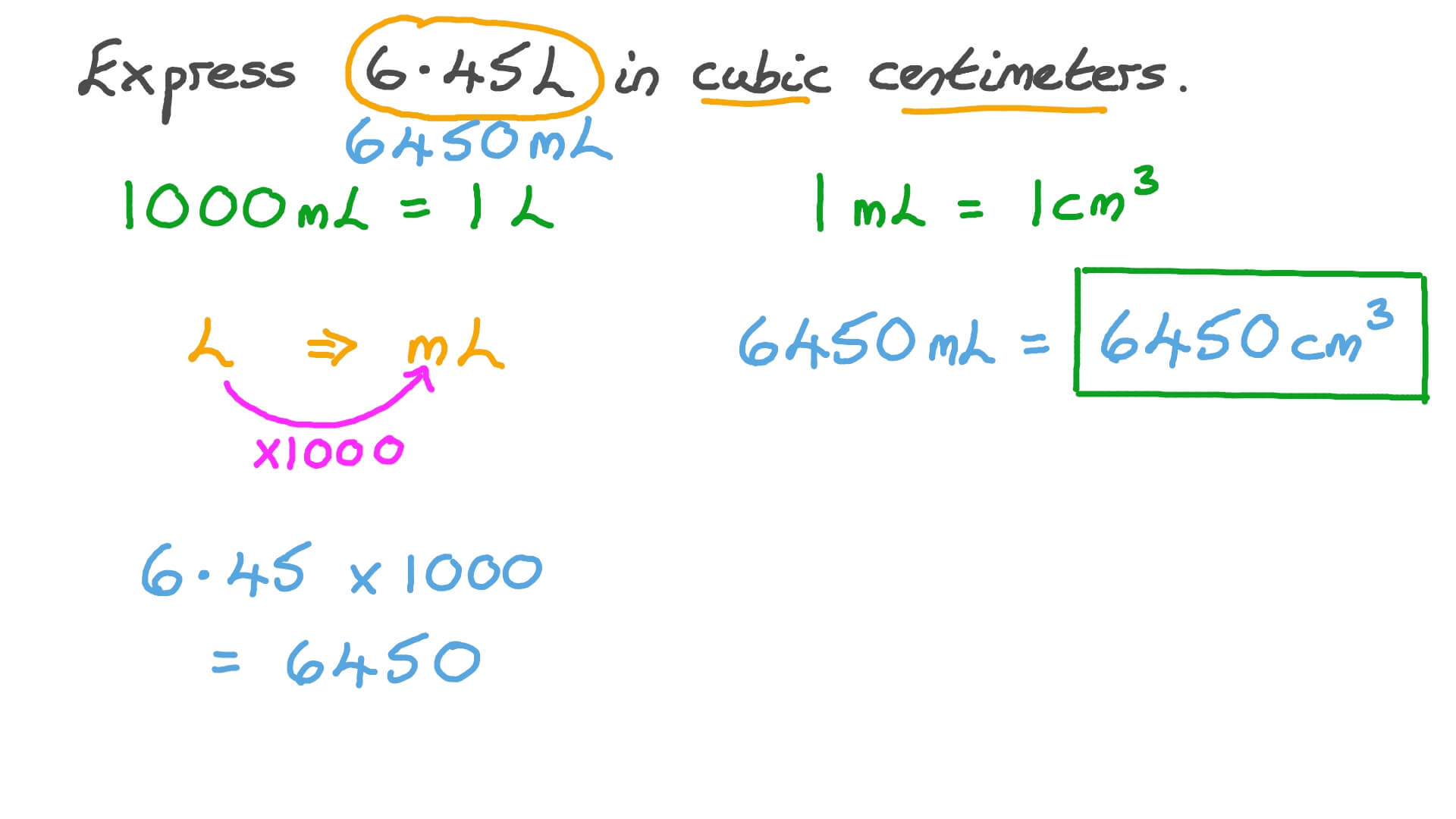
The millilitre (ml or mL, also spelled milliliter) is a metric unit of volume that is equal to one thousandth of a litre. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with the International Systems of Units (SI). It is exactly equivalent to 1 cubic centimetre (cm³, or, non-standard, cc). ›› Sample conversions: ml. ml to US fluid ounce ml to mililitro
How many units are in A 10mL bottle of water?
28/04/2010 · The formula is to take your amount of Heparin and divide it by the amount of fluid in mLs you have. This will give you the amount of units per mL.units/mls= units per mL
What is a unit per mL?
The results of some medical tests are reported in units per milliliter (U/mL). A unit is an arbitrary amount agreed upon by scientists and doctors. A milliliter is a unit of fluid volume equal to one-thousandth of a liter. A liter is slightly larger than a quart.
What is IU per mL?
An international unit is an arbitrary amount of a substance agreed upon by scientists and doctors. A milliliter is a measure of volume that is equal to one-thousandth of a liter (or slightly less than a quarter of a teaspoon).
What is the difference between a unit and a mL?
“U” stands for unit. The numbers 40 or 100 refer to how much insulin (the number of units) is in a set volume of fluid – which, in this case, is one milliliter (1 ml) [referred to as units per ml]. For example, U-100 insulin has 100 units per milliliter and U-40 has 40 units per milliliter.18-Mar-2020
How many mL are in a nursing unit?
So 50 units per ml.20-Aug-2013
How many units is a IU?
Unit ConversionsNutrientCurrent DV Unit*Current Conversion*Vitamin AIU1 IU = 0.3 mcg retinol 1 IU = 0.6 mcg beta-caroteneVitamin EIU1 IU = 0.67 mg for d-alpha-tocopherol (natural) 1 IU = 0.9 mg for dl-alpha-tocopherol (synthetic)Vitamin DIU1 IU = 0.025 mcgFolatemcg1 more row•14-Aug-2017
Is units the same as IU?
U is the international unit of enzyme activity.It is 1 micromole of substrate or product transformed/min. But IU is international units which represents the amount of biological agents(vitamins,vaccines) in different preparations producing the same biological effect. ... You can use any units as long as it is defined.
How many mL is 2 units insulin?
0.5 mL syringes are for 30 to 50 units of insulin and are numbered at 1-unit intervals. 1.0 mL are for doses more than 50 units of insulin and are numbered at 2 units per interval.24-Mar-2021
How many milliliters is 100 units?
The U-100 means there are 100 units in 1 milliliter.02-Mar-2015
Is units more than mL?
Finally, the basic metric unit of volume is the liter. A liter is slightly larger than a quart. The handle of a shovel is about 1 meter....Length, Mass, and Volume.LengthMassVolumekilometerkilogramdekalitercentimetercentigramcentilitermillimetermilligrammilliliter3 more rows
How do you calculate units to mL?
0:373:51Metric Units of Capacity | Convert mL and L - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipMeans again one thousandth of a liter. So one liter equals a thousand milliliters so let's do someMoreMeans again one thousandth of a liter. So one liter equals a thousand milliliters so let's do some conversions. So for number one we have three liters equals how many milliliters.
How do you calculate nursing doses?
A basic formula, solving for x, guides us in the setting up of an equation: D/H x Q = x, or Desired dose (amount) = ordered Dose amount/amount on Hand x Quantity....Dimensional Analysis MethodThe clinician has 2 mg/mL vials in the automated dispensing unit.How many milliliters are needed to arrive at an ordered dose?More items...•07-Mar-2021
How many mL is a teaspoon of nursing?
5 mLHousehold EquivalenciesMeasurement and AbbreviationCommon Conversionsdrop (gtt)15 -20 gtt = 1 mLteaspoon (tsp)1 tsp = 5 mLtablespoon (Tbs)1 Tbs = 3 tsp = 15 mLounce (oz)1 oz = 30 mL5 more rows
Why are serial dilutions of enzymes different?
Serial dilutions of an enzyme solution will have different enzyme activity values , but identical specific activity values because in calculating specific activity the numerator (units/ml) and denominator (mg/ml) are affected equally by sample dilution. Although specific activity is very different from activity, ...
What temperature is an enzyme more active?
Generally speaking, an enzyme will be more active at 37°C than at 20°C. The definition of the enzyme unit would be better expressed thus: 1 unit (U) is the amount if enzyme that catalyses the reaction of 1 nmol of substrate per minute under standard conditions.
Is specific activity dependent on enzyme unit?
Although specific activity is very different from activity, the calculation of specific activity nonetheless is dependent on the activity value , and therefore the stated specific activity value will also be dependent on the enzyme unit definition. Batches that are below the expected specific activity value may contain impurities or enzyme molecules ...
Is the assay linear or non linear?
Most assays are linear if the degree of substrate conversion is less than 15%, assuming that there are no other limiting factors.
What is continuous assay?
acid). However, in continuous assays the appearance of product (less commonly the consumption of substrate) is recorded continuously (e.g. by means of a chart recorder).
Does a 3ml cuvette change the absorbance?
However, absorbance assays are often an exception, and a switch from a 3ml cuvette to 1ml micro-cuvette, for example, will not change the absorbance reading if the width (path length) of the cuvette is still 1 cm (i.e. the light still passes through the same ‘length’ of liquid).
What happens when the protein is pure?
When the protein is pure, the ratio reaches a constant value characteristic of a protein and a function of the catalytic rate constant ( kCAT ). Knowing the specific activity tells you about enzyme's purity in the preparation.
What does knowing the specific activity tell you about enzymes?
Knowing the specific activity tells you about enzyme's purity in the preparation. Your preparation may or may not be pure, but It should indicate the Biological source of the protein (which organism it comes from, it should be in the catalogue, at least).
What is the unit of enzymes?
Popular Answers (1) The enzyme unit (U) is a unit for the amount of a particular enzyme. One U is defined as the amount of the enzyme that produces a certain amount of enzymatic activity, that is, the amount that catalyzes the conversion of 1 micro mole of substrate per minute.
Can U and IU be interchanged?
Vyasa Williams Rajasekar. Enzyme consulting. yes, I agree with Fransisco. U and IU interchangeably used in research, however, when IU is used, it is presumed in most cases that there is a well known activity unit definition where as when it is simply used U, it may infer the method is customized. both can be used.. Cite.
What is 1 U or IU?
Yes, I agree with both of them, 1 U or IU is defined as the enzyme quantity that liberates 1 microgram or micromole of product per ml of the reaction mixture per minute. Cite. 1 Recommendation. 9th Oct, 2014.
What is the difference between U and IU?
But IU is international units which represents the amount of biological agents ( vitamins,vaccines) in different preparations producing the same biological effect. Cite.
What is the enzyme unit?
In pharmacology, the international unit is a unit of measurement for the amount of a substance; the mass or volume that constitutes one international unit varies based on which substance is being measured, and the variance is based on the biological activity or effect, ...
What is the U of Al Qadisiyah?
University of Al-Qadisiyah. U is defined as the amount of the enzyme that produces a certain amount of enzymatic activity, that is, the amount that catalyzes the conversion of 1 micro-mole of substrate per minute.
Definitions of Enzyme Units
What Is ‘Enzyme Activity’
- Activity is quoted in units per ml (U/ml), in other words nmol per min per ml(if unit definition B has been adopted). Thus activity values expressed in units are also subject to an illusory 1000-fold ‘increase’ if one switches from unit definition A to unit definition B. Again there cannot be any confusion if activity is expressed in terms of nmol per min per ml rather than units per ml. Since …
What Is Specific Enzyme Activity?
- Specific enzyme activity (usually stated simply as ‘specific activity’) is the number of enzyme units per ml divided by the concentration of protein in mg/ml. Specific activity values are therefore quoted as units/mg or nmol/min/mg(if unit definition B is applied). Specific activity is an important measure of enzyme purityand values for different batches of a pure enzyme should be the same…
Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
- In this section we discuss why one enzyme may have different measured activity values in different labs. By this we mean real differences in measured activity, not apparent differences caused by the use of different unit definitions. The conditions under which an assay is carried out will influence the reported activity values. For example, assays typically are carried out at a temp…
Developing Assays and The Importance of Linear Range
- The activity value (units/ml) for your enzyme is the most important parameter when you are developing an assay. This is because the volume (i.e. number of units) that you add will determine the amount of substrate that is converted into product. Remember, 1 unit catalyses the conversion of 1 nmol of substrate per min (definition B). The reported units/ml may give you a ro…
Assay Time and Temperature
- These parameters can also influence the linear range as they affect the rate of substrate conversion. For example, an assay may be linear after 15 min, but at 60 minutes too much substrate may have been consumed. In this situation you would have to reduce the amount of enzyme in order to run your assay for 60 minutes. The same considerations apply to assay temp…
Assay Volume/Sensitivity
- From a practical perspective the assay volume is determined/limited by the consumable item that you use for your assays (e.g. cuvettes, tubes, or microplates). The signal for most enzyme assays is proportional to the assay volume and attempts to miniaturise the assay (e.g. to conserve reagents) will usually lead to lower signals. However, absorbance assays are often an exception…
Continuous Assays
- Most assays are carried out for a fixed period time (end point assays) and the reaction is halted by the addition of a stop reagent (e.g. acid). However, in continuous assays the appearance of product (less commonly the consumption of substrate) is recorded continuously (e.g. by means of a chart recorder). The same basic rules apply; a plot of signal versus time for a fixed amount …
What Substrate Concentration Should I use?
- The concentration of substrate will influence the rate of reaction but there are several factors to consider in selecting the ‘right’ concentration. From a practical point of view one key consideration is the amount of product that must be generated in order to give a measurable assay signal. Since the rate of an enzyme reaction is likely to fall when more than about 15% of the substrate has be…
Standard Curves
- A standard curve is always required if you wish to calculate enzyme activity. It is not essential if you are only interested in relative activity values. The standard curve is constructed by measuring the assay signal with standard solutions of the reaction product over a suitable range of concentrations. Ideally you should run a standard curve for every experiment, but if the standard …