What is a grounding electrode?
ground electrode. A conductor buried in the ground, used to maintain conductors connected to it at ground potential and dissipate current conducted to it into the earth, or to provide a return path for electric current in a direct-current power transmission system. Also known as earth electrode; grounding electrode. Click to see full answer.
How do grounding electrodes work?
Things You'll Need
- Ground rod
- Ground rod clamp
- Grounding electrode conductor
- Sledge hammer, hammer drill with a ground rod bit, or a manual pile driving tool
- Shovel or post hole digger
- Screwdriver
- Drill
- Hammer
What is Article 250 NEC?
The National Electrical Code (NEC) covers grounding and bonding in several articles, but the primary coverage is in Article 250. Typical commercial electrical systems are grounded systems. Within the system, some things are grounded… some things are bonded. The terms grounding and bonding are used throughout the NEC.
What is the grounding electrode conductor?
“Grounding Electrode Conductor is run from the service equipment to one of the grounding electrodes that are bonded together. NEC Section 250-24 (c), is a requirement to connect the equipment grounding conductors, the service-equipment enclosures, and where the system is grounded, the grounded service conductor to a grounding electrode.
What is the purpose of the ground electrode in EEG?
The ground is used for common mode rejection. The primary purpose of the ground is to prevent power line noise from interfering with the small biopotential signals of interest. By design, amplifiers should not be affected by large changes in potential at both the active and reference sites.
What does ground electrode do in EMG?
Reference electrode placement. The signal from the EMG detecting surfaces is gathered with respect to a reference. An EMG reference electrode acts as a ground for this signal. It should be placed far from the EMG detecting surfaces, on an electrically neutral tissue [15].
What is ground or earth electrode?
An Earth Electrode is a conducting element buried directly in the ground, facilitating the flow of fault currents towards the ground. This means that Earth Electrodes are metallic and, since they have to be buried for long periods of time, they need to be resistant to corrosion as well.
What is the electrical service grounding electrode system?
The “Grounding Electrode System” includes metal underground water pipes, metal frames of buildings, concrete-encased electrodes and ground rings. The general requirement is that a bonding jumper must be installed between the grounding electrodes to bond them together.
What is the ground lead on an ECG?
Right lower electrode serves as the ground as in standard 12 lead ECG.
How do electrodes pick up signals?
Electrodes placed on or within a nerve can read and stimulate nerve signals. Penetrating electrodes are more selective than non-penetrating ones because they target individual nerve fibers called axons.
Why does electricity need a ground?
Why Does Electricity Go to Ground? The negatively charged ground wire attracts the excess positive charge in your electrical lines, providing a safe outlet for the energy. This is called grounding, and it eliminates the dangers of fire and electrocution, which are high in ungrounded home electrical systems.
Where do you connect grounding electrode conductor?
It says the grounding electrode conductor connection shall be made at any accessible point from the load end of the service drop or service lateral to and including the terminal or bus to which the grounded service conductor is connected at the service disconnecting means.
What happens if ground wire is not connected?
The appliance will operate normally without the ground wire because it is not a part of the conducting path which supplies electricity to the appliance. In fact, if the ground wire is broken or removed, you will normally not be able to tell the difference.
Is a grounding rod necessary?
A fundamental component of safety and protection for your business and/or home's electrical system is proper grounding. For this reason, one or more ground rods are required on your property by the National Electrical Code (NEC) and local building codes.
Where should a grounding rod be placed?
Install the rod in a location near the electrical panel. Ground rods need to be installed in the ground outside in a spot where they can be hammered 8 feet (2.4 m) into the ground.
How many grounding electrodes are required?
two grounding electrodesThe NEC requires a minimum of two grounding electrodes, unless one electrode has a resistance to earth less than 25 ohms. However, commonly in construction, the ground resistance is not measured again after a supplemental grounding electrode is installed.
How Electrodes Assist Grounding Systems
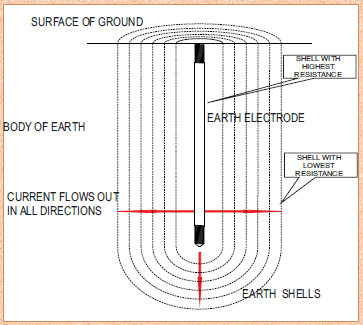
There are two functions of a grounding system that depend heavily on these electrodes. The first and most hazardous is taking the high amperage of a lightning strike off the facility and dissipating it into the earth, (Figure 1).
Grounding Electrode Requirements & Restrictions
There are multiple types of electrodes authorized for use in electrical systems. They are listed in Article 250 of the National Electrical Code. Basically, the code says any grounding electrode listed for use in grounding can be used. However, the code identifies the following along with their installation requirements and restrictions:
Where is the ground electrode placed for EEG?
A ground electrode for EEG recordings is often placed on the forehead (but could be placed anywhere else on the body; the location of the ground on the subject is generally irrelevant).
Why do amplifiers need ground?
The primary purpose of the ground is to prevent power line noise from interfering with the small biopotential signals of interest. By design, amplifiers should not be affected by large changes in potential at both the active and reference sites.
Is ground a reference?
The terminology for electrical connections to human subjects is not universally agreed upon. “Ground” and “reference” are often used interchangeably. This is not a good practice as there are different purposes for different connections.
How long is a ground rod?
There are ground rods manufactured and commercially available that do not meet the minimum 8-foot requirement, although the manufacturer may claim the rod to be 8 feet nominal in length.
What is the NEC code for ground rods?
There are several misconceptions with interpretation of the National Electrical Code as it relates to ground rod electrode compliance. The section of the NEC that deals with ground rods is 250.52. The wording of this portion of the Code presently includes conflicting terms, dimensions and interpretations, which hopefully will be addressed in the next code proposal cycle.
What is a free ground rod gage?
A free ground rod gage is available to be used to see if the rod has to be listed or not.
How much copper is needed for a ground rod?
In order for a copper ground rod to meet the requirements of the product standard and be listed, it must also have a protective coating of 10 mils minimum of copper. If a rod does not have at least 10 mils of copper and is less than 0.625, the rod does not meet Code.
What are the disadvantages of cutting off a non-fully driven rod?
Another disadvantage for the contractor is if he would choose to cut a non-fully driven rod off at ground level, the craft would be cutting off the listed marking on one of the two rod sections, not allowing one of the parts to be used.
Can you inspect a ground rod after it has been installed?
A simple and creative technique to inspect the ground rod after it has been installed in the ground, as other inspectors have done in many areas, is to require the contractor to leave a shovel full of dirt away from the rod with the listed marking showing.
How are neutral and ground connected?
At the main service, the neutral and ground are connected via the main bonding jumper. If the ground path has a low enough resistance, it may prove to be a satisfactory return path, and the imbalance current will travel through the main bonding jumper into the grounding electrode. Since the transformer neutral is grounded by the utility, ...
How does current exit a building?
The current exits the building with the open neutral through the metallic pipes and finds its way back up through the grounding electrode conductors in your building. Any grounded electrically conductive path between buildings can serve as a return path for current for a building with an open neutral.
What is neutral current?
For a 3-phase system, the neutral current is the imbalance between all three hot phases.
Is a grounding electrode conductor dangerous?
Always assume the grounding electrode conductor is “hot,” and treat it as such, until proven otherwise. Even though the system you're working on may be functioning correctly, and have a good neutral, a dangerous condition may still exist if there is an open neutral in a neighboring building.
Is there a shock hazard with grounding electrodes?
In any and all cases, shock hazards can exist with all electrical conductors, including grounding electrode conductors. Osoliniec is a private consulting engineer located in Warren, N.J. He is a licensed professional engineer and electrical contractor in the state of New Jersey.
When is a 240V series a neutral?
When the neutral is open, and there is no return path at all, the entire system becomes a 240V series system. In the case of an open neutral, when the ground path is of high resistance, the open neutral becomes evident as the voltage difference between the phases.
Do electrical conductors only present during faults?
With that assumption, and based on that incorrect interpretation, many electricians assume that in a properly functioning electrical system, currents in grounding electrode conductors are only present during faults — and only for a very short time.
Calculation
Continuous resistance of a conductor is RC = ρ l / s , i.e. RC = 1.7 mΩ for a 10 m long cylindrical copper conductor with a 100 mm2 cross-section. As frequency increases, the skin effect strengthens this resistance.
Premium Membership
Get access to premium HV/MV/LV technical articles, electrical engineering guides, research studies and much more! It helps you to shape up your technical skills in your everyday life as an electrical engineer.
Edvard Csanyi
Electrical engineer, programmer and founder of EEP. Highly specialized for design of LV/MV switchgears and LV high power busbar trunking (<6300A) in power substations, commercial buildings and industry facilities. Professional in AutoCAD programming.
What is ground electrical?
Ground (electricity) A typical earthing electrode (left of gray pipe), consisting of a conductive rod driven into the ground, at a home in Australia. Most electrical codes specify that the insulation on protective earthing conductors must be a distinctive color (or color combination) not used for any other purpose.
Why are exposed conductive parts of electrical equipment connected to ground?
Exposed conductive parts of electrical equipment are connected to ground, so that failures of internal insulation which create dangerous voltages on the parts which could be a shock hazard will trigger protective mechanisms in the circuit such as fuses or circuit breakers which turn off the power.
How does a distribution system work?
Distribution power systems may be solidly grounded, with one circuit conductor directly connected to an earth grounding electrode system. Alternatively, some amount of electrical impedance may be connected between the distribution system and ground, to limit the current that can flow to earth. The impedance may be a resistor, or an inductor (coil). In a high-impedance grounded system, the fault current is limited to a few amperes (exact values depend on the voltage class of the system); a low-impedance grounded system will permit several hundred amperes to flow on a fault. A large solidly grounded distribution system may have thousands of amperes of ground fault current.
What is PE conductor?
In electric power distribution systems, a protective earth (PE) conductor is an essential part of the safety provided by the earthing system . Connection to ground also limits the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices.
Why is a distribution system insulated from earth ground?
A distribution system insulated from earth ground may attain a high potential due to transient voltages caused by static electricity or accidental contact with higher potential circuits. An earth ground connection of the system dissipates such potentials and limits the rise in voltage of the grounded system.
What happens when a ground connection has a significant resistance?
Where a real ground connection has a significant resistance, the approximation of zero potential is no longer valid. Stray voltages or earth potential rise effects will occur, which may create noise in signals or produce an electric shock hazard if large enough.
Do radio antennas need grounding?
Radio antennas. Certain types of radio antennas (or their feedlines) require a connection to ground. Since the radio frequencies of the current in radio antennas are far higher than the 50/60 Hz frequency of the power line, radio grounding systems use different principles from AC power grounding.