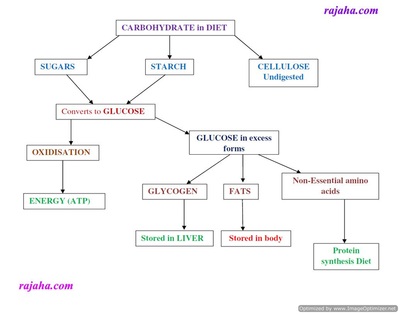
What foods contain disaccharides?
There are three types of disaccharides:
- Sucrose (ordinary table sugar) is made up of two sugars: glucose and fructose.
- Lactose (glucose Plus galactose) is the main sugar in milk.
- maltose (glucose + glucose) is a byproduct of starch digestion.
What are the three disaccharide and their respective monomers?
Three common disaccharides:
- sucrose — common table sugar = glucose + fructose.
- lactose — major sugar in milk = glucose + galactose.
- maltose — product of starch digestion = glucose + glucose.
What is the difference between monosaccharides and disaccharides?
What Is the Difference Between a Monosaccharide and a Disaccharide?
- Chemical Formula. The general formula for a monosaccharide is (CH2O)n, where n is an integer greater than or equal to three.
- Functional Group. ...
- Isomers. ...
- Absorption and Metabolism. ...
What is the least common disaccharide?
Related Biology Terms
- Carbohydrate – An organic molecule consisting of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen with a hydrogen to oxygen ratio of 2:1.
- Glucose – A monosaccharide used for energy; it is found in the blood of animals and created during photosynthesis by plants.
- Monosaccharide – Simple carbohydrates; two of them join to form a disaccharide.
What are 3 disaccharides and the monosaccharides that form them?
...
Common disaccharides.
| Disaccharide | Units | Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Kojibiose | two glucose monomers | α(1→2) |
| Nigerose | two glucose monomers | α(1→3) |
| Isomaltose | two glucose monomers | α(1→6) |
What are most common disaccharides?
What are 3 common monosaccharides?
What are the 3 polysaccharides?
What are the examples of disaccharide?
What is a monosaccharide vs disaccharide?
What are Anomeric carbons?
Which monosaccharide is commonly found in all disaccharides?
What is the General Formula of Carbohydrates?
The general formula for carbohydrates is Cx(H2O)y. Carbohydrates (or sugars) were originally believed to be “hydrates of carbon,” because they hav...
What is the molecular formula of the most common disaccharide?
Disaccharides are the carbohydrates that on hydrolysis gives two same or different carbohydrates. Their general formula is C12H22O11.
What Is Maltose?
Maltose which is also known as a disaccharide made up of two alpha D glucose unit. The two-unit of glucose are linked with an alpha 1,4 glycosidic...
Is maltose a monosaccharide or disaccharide?
Maltose is a disaccharide.
Does maltose give Fehling’s test?
Yes, maltose gives a positive Fehling’s test.
What are the three monosaccharides?
The three major monosaccharides are galactose, glucose, and fructose. Sucrose, lactose, and maltose are the three disaccharides. Galactose is known as the milk sugar, because it is found in milk.
What is the formula for disaccharides?
disaccharide) is broken down. These sugars have the general formula C12H22O11. they are formed when two monosaccharide molecules combine together with the elimination of a water molecle in a condensation reaction. . three disaccharides are: Maltose, sucrose, lactose.
What is a disaccharide?
Disaccharide s are a specialized type of glycoside in which the anomeric hydroxyl group of one sugar has combined with the... Sucrose, which is formed following photosynthesis in green plants, consists of one molecule of glucose and one of fructose bonded via an α-,β-linkage.
Which disaccharide is found in single-celled organisms and in many insects?
Another important disaccharide, trehalose, which is found in single-celled organisms and in many insects, also consists of two molecules of glucose and an α-linkage, but the linkage is distinct from the one found in maltose.
What is double sugar?
Disaccharide, also called double sugar, any substance that is composed of two molecules of simple sugars ( monosaccharides) linked to each other. Disaccharides are crystalline water-soluble compounds. The monosaccharides within them are linked by a glycosidic bond (or glycosidic linkage), ...
What is the linkage between glucose and maltose?
Maltose, a product of the breakdown of starches during digestion, consists of two molecules of glucose connected via an α-linkage.
What are some examples of disaccharides?
Examples of Disaccharides. 1. Sucrose. Sucrose being dextrorotatory in nature gives dextrorotatory glucose as well as laevorotatory fructose on hydrolysis. The overall mixture is laevorotatory and this is because the laevorotation of fructose (-92.4) is more than the dextrorotation of glucose (+52.5). 2.
What are Disaccharides?
Disaccharides are those carbohydrates that on hydrolysis with acids or enzymes give two molecules of monosaccharides which can either be the same or different.
What is the structure of a disaccharide?
Structure of Disaccharides (Sucrose) The most common disaccharide is sucrose which gives D - (+)- glucose and D- (-)- fructose on hydrolysis. Both the monosaccharides i.e. glucose and fructose are connected through the glycosidic linkage between alpha glucose and second carbon beta fructose. Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar as both ...
Which disaccharide has two -D-glucose units?
Maltose. Maltose is also one of the disaccharides which have two α -D-glucose units which are connected by the first carbon of the glucose and also linked to the fourth carbon of another glucose unit. In the solution, a free aldehyde can be produced at the first carbon of the second glucose of the solution and it is a reducing sugar as it shows ...
What is the name of the sugar that is produced at the first carbon of the second glucose of the solution?
In the solution, a free aldehyde can be produced at the first carbon of the second glucose of the solution and it is a reducing sugar as it shows reducing properties. 3. Lactose. Commonly it is called milk sugar as this disaccharide is found in milk.
How are Disaccharides Formed?
There are three basic monosaccharides (many more exist, but these three are the main building blocks of disaccharides in carbohydrates):
Sucrose (Saccharose)
Sucrose, or table sugar, is a disaccharide that is made from the monosaccharides glucose and fructose. The glycosidic bond is between the carbon 1 on glucose and carbon 2 on fructose.
Maltose
Maltose is a disaccharide that is made from two glucose molecules. The two glucose molecules are linked with an alpha 1,4 glycosidic bond. This means that one glucose molecule is linked at carbon 1, and the second glucose molecule is linked at carbon 4, and that both groups are pointing up or both are pointing down.
Lactose
Lactose is a disaccharide that is made from a galactose and glucose molecule, with a beta 1,4 glycosidic link. Carbon 1 from the galactose molecule is bound to carbon 4 from the glucose molecule. Since it is in the beta formation, one group is pointing up and the other group is pointing down.