What is the difference between cellulose starch and glycogen?
Key Difference Between Cellulose, Starch, and Glycogen. Cellulose constitutes their glucose residues as β(1-4) glycosidic bonds, with the molar mass of 162.1406g/mol, while starch contains glucose residues as α(1-4) glycosidic bonds in amylose, while in amylopectin α(1-6) glycosidic linkages at branching points, otherwise α(1-4) linkages.
What is the difference between cellulose and chitin?
The structural polysaccharides provide the rigidity to the cells, hence cellulose is the structural polysaccharide found in plants, while chitin is found in some insects or crustaceans. Click to see full answer. Also, what do Starch glycogen cellulose and chitin have in common?
What is the difference between starch and amylose and glycogen?
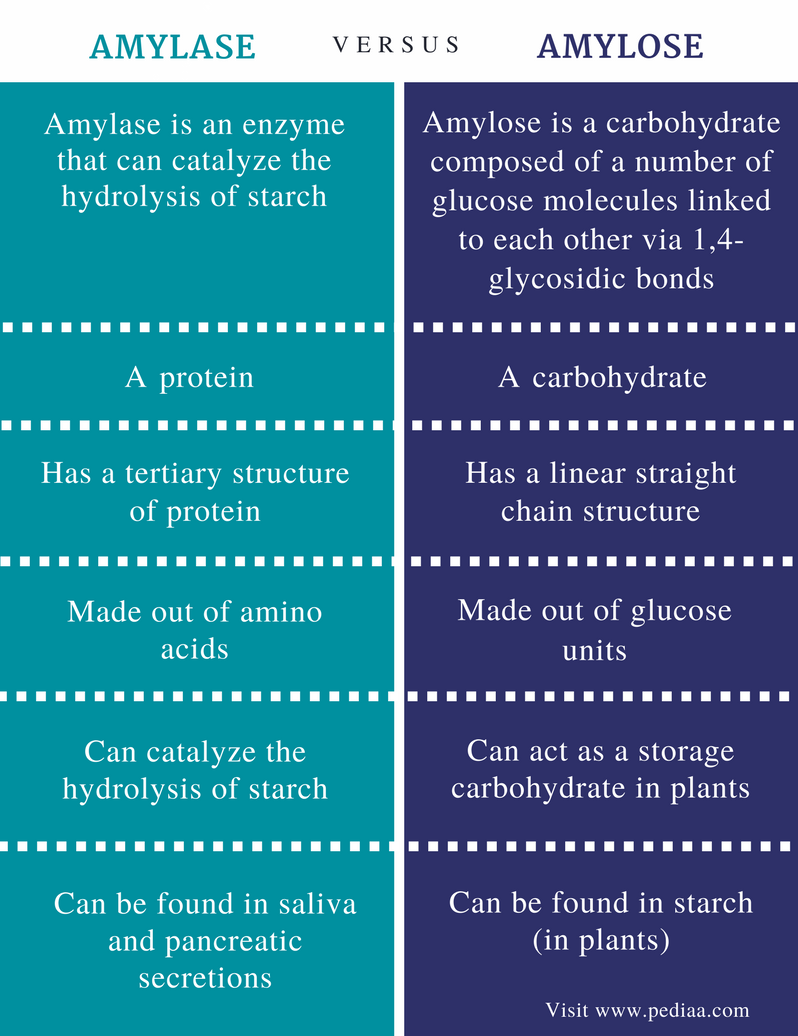
Starch is present in two forms- Amylose- which is linear chain of glucose and Amylopectin is a branched chain polymer of glucose. Glycogen is found in animals and is stored in liver. How are cellulose and starch similar? Starch and cellulose are two very similar polymers.
Does starch have glucose residues?
Starch contains glucose residues as α (1-4) glycosidic bonds in amylose, while in amylopectin α (1-6) glycosidic linkages at branching points, otherwise α (1-4) linkages. Glycogen also contains α (1-4) and α (1-6) (at branching points) glycosidic bonds between their monomers. The molar mass of starch varies.
What are the similarities and differences between starch cellulose and glycogen?
Starch, cellulose and glycogen are all polysaccharides made up of glucose subunits. Starch and glycogen are made up of 𝜶-glucose subunits, whereas cellulose is made up of 𝛃-glucose subunits. Cellulose is unbranched and a straight-chain polymer of glucose, whereas starch and glycogen are branched.
What do starch glycogen cellulose and chitin have in common?
Complex carbohydrates, or polysaccharides, consist of hundreds or even thousands of monosaccharides. They include starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin. They generally either store energy or form structures, such as cell walls, in living things. Starch is a complex carbohydrate that is made by plants to store energy.Sep 4, 2021
What are the similarities and differences between cellulose and chitin?
Chitin is the structural component of the fungal cell wall and the exoskeleton of arthropods. Cellulose is the structural component of the plant and algal cell wall. The strength of chitin is higher than that of cellulose. The main difference between chitin and cellulose is the occurrence and strength of the molecules.Jul 9, 2018
What is the difference between starch cellulose and chitin?
Key Difference – Chitin vs Cellulose Cellulose is a polysaccharide made from linear chains of D-glucose monomers. Chitin is also an organic compound composed of modified glucose monomers which are derivatives of glucose known as N-acetylglucosamines. Cellulose is the most abundant organic polymer found on Earth.Dec 13, 2017
What do cellulose and chitin have in common?
Chitin and cellulose are both made from glucose monomers. Both are structural polymers. Both are linear polymers. Both are polysaccharides.Nov 28, 2021
What are the similarities between starch and cellulose?
Starch and cellulose are two very similar polymers. In fact, they are both made from the same monomer, glucose, and have the same glucose-based repeat units. There is only one difference. In starch, all the glucose repeat units are oriented in the same direction.
What are the differences between starch and glycogen?
Glycogen is made up of only one molecule while starch is made up of two. 2. While both are polymers of glucose, glycogen is produced by animals and is known as animal starch while starch is produced by plants.
How is starch and glycogen similar?
Both starches and glycogen are polymers formed from sugar molecules called glucose. Each independent molecule of glucose has the formula C6H12O, and joining these subunits together in a certain way forms the long chains that make up glycogen and starch.Apr 19, 2018
What is difference between starch and cellulose?
For starch, glucose repeat units are located in the same direction, and each successive glucose unit is rotated 180 degrees in cellulose. Cellulose is thicker than sugar, which is water-insoluble....Difference Between Starch And Cellulose.PropertiesStarchCelluloseConnectionBy alpha linkageBy beta linkageDigestionEasily digestedDifficult to digest7 more rows
What is the difference between glycogen and chitin?
As nouns the difference between chitin and glycogen is that chitin is chitin while glycogen is (carbohydrate) a polysaccharide that is the main form of carbohydrate storage in animals; converted to glucose as needed.
Is cellulose similar to chitin?
1 Answer. The structure of chitin is similar to the polysaccharide cellulose, only difference between the hydroxyl groups in each repeating unit is substituted by N-acetyl groups.Jun 3, 2015
What is the difference between cellulose and glycogen?
Glycogen is a storage form of energy in animals. It is a branched polymer composed of glucose units. It is more highly branched than amylopectin. Cellulose is a structural polymer of glucose units found in plants.Oct 26, 2016
What are the similarities and differences between glycogen and starch?
2. While both are polymers of glucose, glycogen is produced by animals and is known as animal starch while starch is produced by plants. 3. Glycoge...
What are the similarities between glucose and starch?
In humans both glucose and starch both are stored in glycogen. The human body contains extra glucose molecules as compared to starch molecules.
What are the similarities between glycogen and glucose?
Glucose and glycogen are both carbohydrates, but glucose is classified as a monosaccharide and sugar. As a single unit, it is a much smaller molecu...
What are the similarities and differences between glycogen and glucose?
1. Glycogen is a bigger (described as a dendrimer of several hundreds or thousands of glucose molecules) and is a more complex sugar being a polysa...
Is starch and glycogen the same thing?
Starch is a storage form of energy in plants. It contains two polymers composed of glucose units: amylose (linear) and amylopectin (branched). Glyc...
What is the difference between cellulose, starch and glycogen?
Starting from the cellulose which is the monomer of beta glucose and is found in plant cell wall only. While Starch and Glycogen act as the carbohydrate reserve in plants and animals respectively .
What is starch made of?
Another type of polysaccharide, acting as the chief carbohydrate reserve for the plants, and the principal dietary source for the animals and humans. Starch occurs in two types of polymer amylose and amylopectin. Both the polymers are composed of the D-glucose, with the alpha glycosidic bonds known as glucan or glucosan.
What is glycogen in plants?
Definition of Glycogen. Glycogen, often termed as animal starch, though found in plants that do not contain chlorophyll like yeast, fungi, etc. It is also the homopolysaccharide having the glycogen bonds or linkages similar to that of the amylopectin, with the more branches.
Where is glycogen found?
Glycogen is also homopolysaccharide and found in animals as their carbohydrate reserve; it is also found in fungi and plants that do not contain chlorophyll. Cellulose is found only in plants (cell wall). Starch is found in plants. Present in animals and the plants that do not contain chlorophyll like fungi.
Is glycogen a monomer?
Similar to starch (amylopectin), Glycogen also contains α (1-4) and α (1-6) (at branching points) glycosidic bonds between their monomers. Though the molar mass of the starch varies but the glycogen has 666.5777 g/mol. Cellulose constitutes long, straight, unbranched chains forming H-bonds with the adjacent chains and are insoluble in water.
Does cellulose have a glycosidic bond?
Cellulose constitu tes their glucose residues as β (1-4) glycosidic bonds, with the molar mass of 162.1406g/mol, while starch contains glucose residues as α (1-4) glycosidic bonds in amylose, while in amylopectin α (1-6) glycosidic linkages at branching points, otherwise α (1-4) linkages. Similar to starch (amylopectin), ...
Is amylopectin soluble in water?
Amylose is insoluble in water. On the other hand, amylopectin contains highly branched chains, with the α (1-4) glycosidic bond and α (1-6) linkages at their branching point (occurring at every 24 to 30 residues). Amylopectin has high molecular weight and is soluble in water. Starch is mainly found in cereals, vegetables, roots, tubers, etc.
Difference between Starch, Cellulose and Glycogen
The table below shows the main differences between starch, cellulose and glycogen.
Structure of Starch
Starch is the main storage carbohydrate of plants. It is made up of 𝜶-glucose subunits. It contains two types of polymers, amylose and amylopectin.
Structure of Cellulose
Cellulose is the main structural component of the plant cell wall. It is exclusively present in plants. Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound of the plant kingdom. It is made up of 𝛃-glucose subunits that are joined by 1–4 glycosidic bonds. It is a straight and unbranched polymer of glucose.
Structure of Glycogen
It is the main storage carbohydrate in animals and fungi. It is highly branched and the structure is similar to that of amylopectin. It is a polymer of 𝜶-glucose subunits joined together by 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds. It has branching after around every 10 subunits.
Polysaccharides
This video is about Starch vs Glycogen. Difference between starch and glycogen is explained. Starch consists of 2 components amylose and amylopectin. Amylose is unbranched polygulcose chain while amylopectin is branched polysachharide.
What is the structural difference between glycogen and starch?
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ✍️ What is the structural difference between glycogen and starch?
Difference Between Cellulose, Starch and Glycogen (with Comparison Chart)
These three polysaccharides differ in their glycosidic linkages and their functions too. Starting from the cellulose which is the monomer of beta glucose and is found in plant cell wall only. While Starch and Glycogen act as the carbohydrate reserve in plants and animals respectively.
What are the similarities and differences between cellulose starch glycogen and chitin?
The human storage polysaccharide is called glycogen and the storage polysaccharide in plants is called starch. The structural polysaccharides provide the rigidity to the cells, hence cellulose is the structural polysaccharide found in plants, while chitin is found in some insects or crustaceans.
12 Difference Between Starch And Glycogen
What Is Starch? Starch is the most important source of carbohydrates in the human diet and accounts for more than 50% of our carbohydrate intake. It occurs in plants in the form of granules, and these are particularly abundant in seeds (especially the cereal grains) and tubers, where they serve as a storage form of …
What do the polysaccharides starch and glycogen have in common?
Three important polysaccharides, starch, glycogen, and cellulose, are composed of glucose. Starch and glycogen serve as short-term energy stores in plants and animals, respectively. The glucose monomers are linked by α glycosidic bonds. Glycogen and starch are highly branched, as the diagram at right shows.
14.7: Polysaccharides
Diabetes educators also work with hospital or nursing home staff to improve the care of diabetic patients.
What is the difference between cellulose and chitin?
The key difference between cellulose and chitin is that cellulose is the significant structural polymer in the primary cell walls of the plant cells while chitin is the main structural polymer found in the fungal cell wall.
What are chitin and cellulose?
Cellulose and chitin are two structural polymers found in nature. Cellulose is a polysaccharide made from linear chains of D-glucose monomers. Chitin is also an organic compound composed of modified glucose monomers which are derivatives of glucose known as N-acetylglucosamines. Cellulose is the most abundant organic polymer found on Earth. Chitin is second only to cellulose from its abundance on Earth. The key difference between cellulose and chitin is that cellulose is the significant structural polymer in the primary cell walls of the plant cells while chitin is the main structural polymer found in the fungal cell wall.
What are the most abundant organic polymers found on Earth?
Chitin and cellulose are most abundant structural organic polymers found on Earth. Cellulose is the primary compound of the cell walls of the plant cells. Chitin is the primary compound of the cell walls of the fungi and exoskeletons of arthropods. Cellulose is a polymer composed of D-glucose monomers. Chitin is a long polymer of N-acetylglucosamine. Both chitin and cellulose are important for the strength and protection of organisms. Both compounds are insoluble in water. This is the difference between chitin and cellulose.
What is the chemical formula for chitin?
Chitin is present on fungal cell walls, exoskeletons of arthropods and insects. The chemical formula of chitin is (C 8 H 13 O 5 N)n.
What is chitin used for?
And chitin is also used in dyes, adhesives, sizing and strengthening agents for papers.
What is the formula for chitin?
The chemical formula of chitin is (C 8 H 13 O 5 N)n. Albert Hofmann determined the structure of chitin in 1929. Chitin is an un-branched structural polysaccharide which contributes to strengthening and protecting organisms.
Which organic compound is the most abundant?
Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound on Earth. Amyl Group. Chitin has an amyl group as a substitution in the glucose molecule. Cellulose has a hydroxyl group in the glucose molecule. Nitrogen Molecules. Chitin has nitrogen molecules in its structure. Cellulose does not contain nitrogen in its structure.