What is the knob on your elbow called?
The bony prominences, or bumps, at the bottom of the humerus are called the epicondyles. The bump on the outer side of the elbow is called the lateral epicondyle.
What is the part below elbow called?
ForearmForearm. The forearm is the area between the elbow joint and the wrist.
What are the 3 joints of the elbow?
The three joints of the elbow include:Ulnohumeral joint is where movement between the ulna and humerus occurs.Radio humeral joint is where movement between the radius and humerus occurs.Proximal radioulnar joint is where movement between the radius and ulna occurs.
What is the part of your arm that bends called?
The elbow is the joint that bends your arm. It helps you to lift and move objects. It is a modified hinge joint made up of three bones. These are the humerus (bone of the upper arm) and the forearm bones, known as the radius and ulna.
What are the 4 articulations of the elbow?
The elbow is a trochoginglymoid (combination hinge and pivot) joint 4, 5:the hinge component (allowing flexion-extension) is formed by the ulnohumeral articulation. forearm flexors at elbow: ... the pivot component (allowing pronation-supination) is formed by the radiohumeral articulation and the proximal radioulnar joint.
What is the anatomy of the elbow?
Anatomy of the Elbow. The elbow is a hinge joint made up of the humerus, ulna and radius. The unique positioning and interaction of the bones in the joint allows for a small amount of rotation as well as hinge action. This rotation is easily noticed during activities such as hand-to-mouth eating motions. The primary stability of the elbow is ...
What is the name of the pinched nerve in the elbow?
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome. Cubital tunnel syndrome is a pinched nerve at the elbow commonly known as the "funny bone". This might be caused by trauma or repetitive use of the elbow and may be caused by continuous use of the elbow in a flexed position. This causes the nerve to become stretched and irritated as opposed to when ...
What is the term for inflammation of the tendon attachment of the flexor pronator muscles in the fore
Golfer's Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis) Medial epicondylitis is inflammation of the tendon attachment of the flexor pronator muscles in the forearm. Usually this begins as microscopic tears in the tissue which leads to an inflammatory or hypervascular process.
What is the procedure to cut the medial epicondyle?
There are three types of procedures, one is to cut the medial epicondyle which is the bone pinching the nerve or the other two operations are to actually move the nerve out of the cubital tunnel either above or below the muscles of the forearm.
What is the ligament that provides stability to the elbow?
The primary stability of the elbow is provided by the ulnar collateral ligament, on the medial (inner) side of the elbow. However, one of the most common injuries to the elbow occurs on the lateral, or outer, side of the elbow -- it is called Lateral Epicondylitis, or Tennis Elbow.
Can micro tears cause pain in the elbow?
Many doctors feel that micro tears in the tendon lead to a hyper-vascular phenomenon resulting in pain. The pain is usually worse with strong gripping with the elbow in an extended position, as in a tennis back hand stroke, but this problem can occur in golf and other sports as well as with repetitive use of tools.
Which ligaments connect the bones of the elbow?
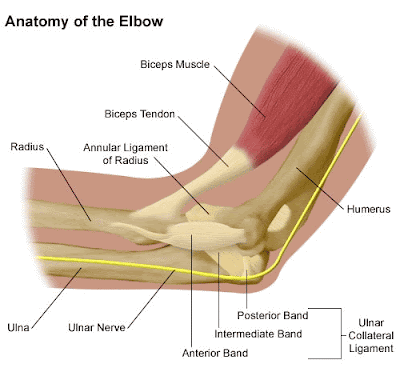
The major ligaments that connect the bones of the elbow include the ulnar collateral ligament, radial collateral ligament, and annular ligament. Several major muscles and tendons—fibrous bands that join muscles to bone or muscles to other muscles—meet at the elbow.
Why do people use their elbows?
The elbow is frequently used as a fulcrum for seated activities that involve the hands, such as writing or using a keyboard.
What holds joints together?
Joints are held together by a network of ligaments. Liga ments are made of tough, flexible connective tissue. In addition to their role holding joints together, ligaments can also connect bones and cartilages.
What is the resting angle of the elbow?
The resting angle of the elbow prevents the arms from hitting the sides of your body as you walk. This is also known as the “carrying angle.”. Women typically have smaller shoulders and wider hips than men. This results in variations between carrying angles in men versus women.
What is the largest joint in the body?
The elbow is one of the largest joints in the body. In conjunction with the shoulder joint and wrist, the elbow gives the arm much of its versatility, as well as structure and durability.
What is the elbow?
24901. Anatomical terminology. The elbow is the visible joint between the upper and lower parts of the arm. It includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the elbow pit, the lateral and medial epicondyles, and the elbow joint.
What is the medical term for the elbow?
Medical Subject Headings defines the elbow specifically for humans and other primates, though the term is frequently used for the anterior joints of other mammals, such as dogs. The name for the elbow in Latin is cubitus, and so the word cubital is used in some elbow-related terms, as in cubital nodes for example.
What is the joint between the elbow and the humerus?
Joint. The elbow joint has three different portions surrounded by a common joint capsule. These are joints between the three bones of the elbow, the humerus of the upper arm, and the radius and the ulna of the forearm. Is a simple hinge-joint, and allows for movements of flexion and extension only.
Why does my elbow hurt?
Elbow pain can occur for a multitude of reasons, including injury, disease, and other conditions. Common conditions include tennis elbow, golfer’s elbow, distal radioulnar joint rheumatoid arthritis, and cubital tunnel syndrome.
Which joint shares capsule with elbow joint?
While the superior radioulnar joint shares joint capsule with the elbow joint, it plays no functional role at the elbow. With the elbow extended, the long axis of the humerus and that of the ulna coincide.
How many bones are there in the elbow?
There are three bones at the elbow joint, and any combination of these bones may be involved in a fracture of the elbow. Patients who are able to fully extend their arm at the elbow are unlikely to have a fracture (98% certainty) and an X-ray is not required as long as an olecranon fracture is ruled out.
How long does it take for a dislocated elbow to heal?
A full dislocation of the elbow will require expert medical attention to re-align, and recovery can take approximately 8–14 weeks.
What are the two major structures of the elbow?
Other major structures of the elbow include: Ligaments. Tough bands of connective tissue called ligaments hold the bones of the elbow together. The two main ligaments connecting the humerus and ulna are: ulnar-collateral ligament, also called the medial collateral ligament, which runs along the inside of the elbow.
What are the tendons in the elbow?
Several tendons connect the muscles and bones of the elbow. The primary tendons are: 1 biceps tendon, which attaches the biceps on the front of the arm to the radius, enabling you to forcefully bend your bend your elbow 2 triceps tendon, which attaches the triceps to the ulna, enabling you to forcefully straighten your elbow .
What is the fluid that surrounds the elbow?
The ligaments form a capsule around the joint that is lined with a smooth membrane called the synovium. The synovium produces a viscous liquid, called synovial fluid, which lubricates the joint. Muscles. Several muscles surround the elbow, making it possible for you to move your arm.
Which joint is the joint where the radius and humerus meet?
humeroradial joint – the joint formed where the radius and humerus meet. The joint not only allows you to bend and straighten your arms, it also is involved in supination and pronation, the motion of turning the hand over so the palm faces up or down. proximal radioulnar joint – the joint where the radius and ulna meet.
Which joint allows you to bend your arms?
These protrusions fit into two corresponding depressions (the olecranon fossa and coronoid fossa) at the lower end of the humerus to form the hinge-like humeroulnar joint, which allows you to bend and straighten your arms. It is what we typically think of as the elbow joint.
What are the tendons that connect the muscles and bones of the elbow?
Tendons. Several tendons connect the muscles and bones of the elbow. The primary tendons are: biceps tendon , which attaches the biceps on the front of the arm to the radius, enabling you to forcefully bend your bend your elbow.
Which muscles attach to the inside of the elbow?
The main muscles of the elbow involved in wrist and finger movement are: flexors, which attach to the inside of the elbow and enable you to bend your wrists and fingers. extensors, which attach to the outside of the elbow and enable you to extend or straighten your wrists and fingers. Tendons.
What are the bones of the elbow?
Bones and Joints. The bones of the elbow are the humerus (the upper arm bone), the ulna (the larger bone of the forearm, on the opposite side of the thumb), and the radius (the smaller bone of the forearm on the same side as the thumb). The elbow itself is essentially a hinge joint, meaning it bends and straightens like a hinge.
What are the ligaments in the elbow?
There are several important ligaments in the elbow. Ligaments are soft tissue structures that connect bones to bones. The ligaments around a joint usually combine together to form a joint capsule. A joint capsule is a watertight sac that surrounds a joint and contains lubricating fluid called synovial fluid.
Why is the radius at the elbow shaped like a smooth knob?
The joint is even more complex because the radius has to slide against the ulna as it rotates the wrist as well. As a result, the end of the radius at the elbow is shaped like a smooth knob with a cup at the end to fit on the end of the humerus.
What is the end of the radius at the elbow shaped like?
As a result, the end of the radius at the elbow is shaped like a smooth knob with a cup at the end to fit on the end of the humerus. The edges are also smooth where it glides against the ulna. Articular cartilage is the material that covers the ends of the bones of any joint.
What is the bump above the elbow called?
The inside, or medial, bump just above the elbow is called the medial epicondyle.
Why is my elbow torn?
They can be torn when there is an injury or dislocation to the elbow. If they do not heal correctly the elbow can be too loose, or unstable. There is also an important ligament called the annular ligament that wraps around the radial head and holds it tight against the ulna.
Which artery travels across the front crease of the elbow?
Traveling along with the nerves are the large vessels that supply the arm with blood. The largest artery is the brachial artery that travels across the front crease of the elbow. If you place your hand in the bend of your elbow, you may be able to feel the pulsing of this large artery.
What are the bones of the elbow?
There are three bones that comprise the elbow joint: the humerus. the radius. the ulna. These bones give rise to two joints: Humeroulnar joint is the joint between the trochlea on the medial aspect of the distal end of the humerus and the trochlear notch on the proximal ulna.
Where is the elbow joint located?
The elbow joint is a synovial joint found in the upper limb between the arm and the forearm. It is the point of articulation of three bones: the humerus of the arm and the radius and the ulna of the forearm. The elbow joint is classified structurally as a synovial joint. It is also classified structurally as a compound joint, ...
What is the collateral ligament?
The ulnar collateral ligament extends from the medial epicondyle of the humerus to the coronoid process of the ulna. It is triangular in shape, and is composed of three parts: an anterior, a posterior and an inferior band . Ligaments of the elbow and forearm (overview)
What is the proximal radioulnar joint?
The proximal radioulnar joint is the articulation between the circumferential head of the radius and a fibro-osseous ring formed by the radial groove of the ulna and the annular ligament that hold the head of the radius in this groove.
What is the name of the joint that allows movement in only one plane?
A fibrous capsule encloses the joint, and is lined internally by a synovial membrane. Synovial joints can be further categorized based on function. The elbow joint is functionally a hinge joint, allowing movement in only one plane (uniaxial). Key facts about the elbow joint. Type.
Which joints give the elbow its characteristic hinge like properties?
The humeroulnar and the humeroradial joints are the joints that give the elbow its characteristic hinge like properties. The rounded surfaces of the trochlea and capitulum of the humerus rotate against the concave surfaces of the trochlear notch of the ulna and head of the radius.
Which ligaments connect the bones of the elbow joint?
There are a collection of ligaments that connect the bones forming the elbow joint to each other, contributing to the stability of the joint. The humeroulnar and the humeroradial joints each have a ligament connecting the two bones involved at the articulation: the ulnar collateral and the radial collateral ligaments.
What are the three major bones that make up the elbow?
Connected to the bones by tendons, muscles move those bones in several ways. The bones that create the elbow are: Humerus: This long bone extends from the shoulder socket and joins the radius and ulna to form the elbow.
What are the tendons that attach to the elbow?
Inside and outside the elbow joint, there are points where tendons attach. These tendons allow for wrist and hand movements. For example, they allow the hand to rotate. The elbow bones are held together primarily by fibrous tissue known as ligaments.
What is the most common short term injury to the elbow?
Bone fractures are among the most common short-term injuries of the elbow as it is a common point of contact during high-impact collisions such as automobile accidents, falls, and sport injuries. The radius and ulna —the bones of the forearm—are also commonly broken.
Which bone joins the radius and ulna to form the elbow?
Humerus: This long bone extends from the shoulder socket and joins the radius and ulna to form the elbow. Radius: This forearm bone runs from the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist. Ulna: This forearm bone runs from the elbow to the “pinkie” side of the wrist.
What is the hinge action of the hand?
The first is the large hinge action that is used in most movements of the arms, such as holding bags of groceries or doing bicep curls. The other movements are so small that the untrained eye rarely notices the changes in position, but they are important for motor function of the hand and wrist.
What is the opposite side of the elbow called?
The opposite side of the elbow is called the antecubital space, the cubital fossa or the chelidon. Some people call it the "elbow pit," which is intended to echo the word "armpit.". Click to see full answer. Subsequently, one may also ask, what do you call the crease in your arm?
What is the slang word for the excess or loose skin at the joint of one's elbow?
Weenus (or weenis or wenis) is a slang word for the excess or loose skin at the joint of one's elbow, which is technically referred to as olecranal skin.
Where is the pain on the inside of the elbow?
The pain is located on the outside (lateral side) of the elbow, but may radiate down the back of your forearm. You'll likely feel the pain when you straighten or fully extend your arm. Keeping this in view, is the inside of your elbow called a Wagina? The skin that covers the tip of the elbow.
What does cubital fossa mean?
A fossa is a shallow depression from the Latin word for “ditch” so that cubital fossa literally means “elbow crease.”. why does the opposite side of my elbow hurt?
Overview
The elbow is the region between the arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa (also called the chelidon, or the elbow pit), and the lateral and the medial epicondyles of the humerus. The elbow joint is a hinge joint between the arm and the forearm; more specifically between the humerus in the upper arm and the radius and ulna in the forearm which allows the forearm and hand to be moved towards a…
Structure
The elbow joint has three different portions surrounded by a common joint capsule. These are joints between the three bones of the elbow, the humerus of the upper arm, and the radius and the ulna of the forearm.
When in anatomical position there are four main bony landmarks of the elbow. At the lower part of the humerus are the medial and lateral epicondyles, on the sid…
Function
The function of the elbow joint is to extend and flex the arm grasp and reach for objects. The range of movement in the elbow is from 0 degrees of elbow extension to 150 degrees of elbow flexion. Muscles contributing to function are all flexion (biceps brachii, brachialis, and brachioradialis) and extension muscles (triceps and anconeus).
Pathology
The types of disease most commonly seen at the elbow are due to injury.
Two of the most common injuries at the elbow are overuse injuries: tennis elbow and golfer's elbow. Golfer's elbow involves the tendon of the common flexor origin which originates at the medial epicondyle of the humerus (the "inside" of the elbow). Tennis elbow is the equivalent injury, but at the common extensor …
Clinical significance
Elbow pain can occur for a multitude of reasons, including injury, disease, and other conditions. Common conditions include tennis elbow, golfer's elbow, distal radioulnar joint rheumatoid arthritis, and cubital tunnel syndrome.
Tennis elbow is a very common type of overuse injury. It can occur both from chronic repetitive motions of the hand and forearm, and from trauma to the same areas. These repetitions can inj…
Society and culture
The now obsolete length unit ell relates closely to the elbow. This becomes especially visible when considering the Germanic origins of both words, Elle (ell, defined as the length of a male forearm from elbow to fingertips) and Ellbogen (elbow). It is unknown when or why the second "l" was dropped from English usage of the word. The ell as in the English measure could also be taken to come from the letter L, being bent at right angles, as an elbow. The ell as a measure was taken a…
Other primates
Though the elbow is similarly adapted for stability through a wide range of pronation-supination and flexion-extension in all apes, there are some minor difference. In arboreal apes such as orangutans, the large forearm muscles originating on the epicondyles of the humerus generate significant transverse forces on the elbow joint. The structure to resist these forces is a pronounced keel on the trochlear notch on the ulna, which is more flattened in, for example, hum…
Notes
1. ^ "MeSH Browser". meshb.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 8 January 2022.
2. ^ "MeSH Browser". meshb.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 8 January 2022.
3. ^ Kapandji 1982, pp. 74–7
4. ^ Palastanga & Soames 2012, p. 138