What are the five steps of hemostasis?
- Vascular Spasms. blood vessels constrict to slow blood loss.
- Platelet plug formation. platelets stick together to plug break.
- Coagulation. Enzymatic process requiring clotting factors and Ca2+
- Clot retraction and repair.
- Fibrinolysis.
What are the 5 phases of hemostasis?
What is Hemostasis | Its Mechanism in 4 Stages
- Vasoconstriction
- Platelet plug formation
- Coagulation
- Fibrinolysis
What is the correct order of hemostasis?
What Are the Three Stages of Blood Clotting?
- The Vascular Phase
- The Platelet Phase
- The Coagulation Stage
What is the proper sequence of hemostasis?
The physiology of hemostasis involves the:
- Vasculature
- Liver
- Bone marrow
What are the 3 mechanisms of hemostasis?
- Vessel Spasm.
- Formation of Platelet Plug.
- Blood Coagulation.
- Clot Retraction.
- Clot Dissolution (Lysis)
What is the order of hemostasis?
Hemostasis includes three steps that occur in a rapid sequence: (1) vascular spasm, or vasoconstriction, a brief and intense contraction of blood vessels; (2) formation of a platelet plug; and (3) blood clotting or coagulation, which reinforces the platelet plug with fibrin mesh that acts as a glue to hold the clot ...Aug 13, 2020
What are the stages of homeostasis?
There are three stages of homeostasis. They are sensing, processing and responding. These stages are managed by the receptor, control center and effector respectively.
What is the last step of hemostasis?
Fibrin clot remodeling The last stage of hemostasis is when your body remodels the existing clot into a fibrin clot. Your body does that because blood clots are a temporary patch, not a permanent solution. That removal involves a process called fibrinolysis.Dec 8, 2021
What is the second step in hemostasis?
During hemostasis three steps occur in a rapid sequence. Vascular spasm is the first response as the blood vessels constrict to allow less blood to be lost. In the second step, platelet plug formation, platelets stick together to form a temporary seal to cover the break in the vessel wall.
What are the steps of platelet plug formation?
The three steps to platelet plug formation are platelet adherence, activation, and aggregation.Aug 13, 2020
Is fibrinolysis a phase of hemostasis?
Fibrinolysis describes the process of removing (lyzing) the clot formed by activation of hemostatic pathways, either in physiological response to vascular trauma or in pathological thrombosis.
What is mechanical hemostasis?
Techniques for hemostasis in trauma and orthopedic surgery Mechanical methods include direct pressure, ligating clips and staples, sutures, fabric pads and gauze while hemostatic scalpels and lasers also reduce bleeding during surgery [6, 7, 17].
How many systems are there in hemostasis?
Overview of the Coagulation System Hemostasis means stopping blood loss or bleeding. Hemostasis is an orchestrated, balanced and tightly regulated process. Hemostasis can be subdivided into three sequential processes: primary hemostasis, secondary hemostasis, and tertiary hemostasis.
What is hemostasis quizlet?
hemostasis. refers to the collection of events that STOPS the bleeding when a BLOOD VESSEL is damaged.
Which is the first step in hemostasis?
Hemostasis is the natural process that stops blood loss when an injury occurs.It involves three steps: (1) vascular spasm ( vasoconstriction ); (2) platelet plug formation; and (3) coagulation.
What is the first step in hemostasis quizlet?
The first step in hemostasis is: platelet plug formation.
What are fibrin strands?
Fibrin is a tough protein substance that is arranged in long fibrous chains; it is formed from fibrinogen, a soluble protein that is produced by the liver and found in blood plasma. When tissue damage results in bleeding, fibrinogen is converted at the wound into fibrin by the action of thrombin, a clotting enzyme.
What are the steps of hemostasis?
Hemostasis has three major steps: 1) vasoconstriction, 2) temporary blockage of a break by a platelet plug, and 3) blood coagulation, or formation of a fibrin clot. These processes seal the hole until tissues are repaired.
How does hemostasis occur?
Hemostasis occurs when blood is present outside of the body or blood vessels. It is the instinctive response for the body to stop bleeding and loss of blood. During hemostasis three steps occur in a rapid sequence. Vascular spasm is the first response as the blood vessels constrict to allow less blood to be lost. In the second step, platelet plug formation, platelets stick together to form a temporary seal to cover the break in the vessel wall. The third and last step is called coagulation or blood clotting. Coagulation reinforces the platelet plug with fibrin threads that act as a “molecular glue”. Platelets are a large factor in the hemostatic process. They allow for the creation of the “platelet plug” that forms almost directly after a blood vessel has been ruptured. Within seconds of a blood vessel’s epithelial wall being disrupted platelets begin to adhere to the sub-endotheliumsurface. It takes approximately sixty seconds until the first fibrin strands begin to intersperse among the wound. After several minutes the platelet plug is completely formed by fibrin. Hemostasis is maintained in the body via three mechanisms:
What are the proteins that travel along the blood plasma in an inactive state?
There are a dozen proteins that travel along the blood plasma in an inactive state and are known as clotting factors. Once the platelet plug has been formed by the platelets, the clotting factors begin creating the Blood Clot. When this occurs the clotting factors begin to form a collagen fiber called fibrin.
What is the role of coagulation in hemostatic hemostasis?
Coagulation reinforces the platelet plug with fibrin threads that act as a “molecular glue”. Platelets are a large factor in the hemostatic process. They allow for the creation of the “platelet plug” that forms almost directly after a blood vessel has been ruptured.
What is the first response to a vascular spasm?
Vascular spasm is the first response as the blood vessels constrict to allow less blood to be lost. In the second step, platelet plug formation, platelets stick together to form a temporary seal to cover the break in the vessel wall. The third and last step is called coagulation or blood clotting.
How do platelets help with hemostatic process?
This process is regulated through thromboregulation. Platelets play one of the biggest factors in the hemostatic process. Being the second step in the sequence they stick together (aggregation) to form a plug that temporarily seals the break in the vessel wall.
What is the second stage of hemostasis?
The second stage of hemostasis involves platelets that move throughout the blood. When the platelets find an exposed area or an injury, they begin to form what is called a platelet plug.
How long does it take for a hemostasis to take effect?
Steps in Hemostasis. There are broadly four steps in the process of hemostasis. The first step takes effect almost immediately after there has been a break in the blood vessel and may even occur with injury to the blood vessel without a tear. The tear is sealed anywhere within a few minutes to about 20 minutes.
What is the process of stopping blood loss?
Hemostasis Process – Mechanism to Stop Blood Loss. Blood is contained within the cardiovascular system – the heart and blood vessels – with additional amounts stored in the liver and spleen. The quantity of blood in the human body is approximately 5.5 liters. When bleeding, up to 20% of this total blood volume can be lost without a person being ...
What is the clotting phase?
Clotting Phase. The formation of a blood clot provides a more long lasting plug. The clotting process involves the laying down of fibrin which reinforces the platelet plug. Fibrin is a long protein strand which forms from fibrinogen by the action of thrombin.
What is the process of blood clotting?
Simply, hemostasis is the blood clotting process but a number of mechanisms exist before and after the formation of the actual blood clot. Without hemostasis, bleeding would continue unabated and eventually result in death. This process although efficient does have its limitations with severe hemorrhages.
What happens when blood vessels are compromised?
However, the moment the blood vessel wall is compromised, the platelets are strongly attracted to the site of injury. Once attached, the platelet swells and portions of it extend outwards to attached to neighboring platelets or other portions of the torn vessel wall. The platelets can also contract to form a tight and firm plug.
What is the body's series of processes developed to prevent blood loss when a vessel is compromised?
What is hemostasis ? Hemostasis is the body’s series of processes developed to prevent blood loss when a vessel is compromised.
How long does it take for a blood vessel to heal after a break?
The final process that permanently seals the blood vessel may only be completed about 1 to 2 weeks after ...
What are the steps of coagulation?
The coagulation process can be described in three major steps: Formation of factor X and prothrombinase. Prothrombinase (prothrombin activator) can form either intrinsically (inside the blood vessels) or extrinsically (outside the blood vessels).
What is the process of stopping bleeding?
Hemostasis. Hemostasis , the stoppage of bleeding, is accomplished through three steps: A vascular spasm, a constriction of the damaged blood vessel, occurs at the site of injury. Vasoconstriction is initiated by the smooth muscle of the blood vessel in response to the injury and by nerve signals from pain receptors.
What is the process of clotting?
The Clotting Process. Following its formation, a clot is further strengthened by a process called clot retraction . Platelets in the clot contract, pulling on the fibrin strands to which they are attached. The result is a more tightly sealed patch.
What is the breakdown of a clot as the damaged blood vessel is repaired?
The result is a more tightly sealed patch. Fibrinolysis is the breakdown of the clot as the damaged blood vessel is repaired. During the formation of a clot, the plasma protein plasminogen is incorporated into the clot.
What is the pathway that converts prothrombin to thrombin?
Prothrombin is converted to thrombin. In this common pathway that follows both the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways , prothrombinase (with Ca 2+) converts prothrombin to thrombin. Fibrinogen is converted to fibrin. The common pathway continues as thrombin (with Ca 2+) converts fibrinogen to fibrin.
How many factors are involved in coagulation?
Coagulation (blood clotting) is a complex series of reactions that transform liquid blood into a gel (clot), providing a secure patch to the injured blood vessel. Thirteen coagulation factors (numbered I through XIII in order of their discovery) are involved. Most of these factors are proteins released into the blood by the liver.
Which pathway activates factor X?
In the intrinsic pathway, the collagen of the damaged blood vessel initiates a cascade of reactions that activate factor X. In the extrinsic pathway, damaged tissues release thromboplastin (tissue factor, TF), which initiates a shorter and more rapid sequence of reactions to activate factor X.
What are the stages of hemostasis?
Hemostasis is a series of overlapping processes intended to stop the bleeding during an injury to the blood vessel. It occurs in 4 stages as. Vasoconstriction. Platelet plug formation. Coagulation. Fibrinolysis. The process begins within 15 seconds after the injury.
How is a blood clot broken down?
The clot is broken down by the enzyme plasmin which is an activated form of plasminogen. This plasmin converts insoluble fibrin to soluble form which is removed byphagocytosis. The healing process continues after the clot is removed until the restoration of blood vessel integrity.
Which pathway is faster, intrinsic or extrinsic?
The extrinsic pathway is faster and gets activated within seconds of tissue damage. The thromboplastin is released by damaged tissue which goes on to initiate coagulation. The intrinsic pathway is slower and acts in 3 to 6 minutes. This is initiated when the blood gets in contact with damaged blood vessel inner walls.
How long does it take for a thrombocyte to form a platelet plug?
Many thrombocytes arrive at the injured site due to a positive feedback system to form a platelet plug or seal. This plug formation occurs in 6 minutes and prevents further leakage of blood from the injured site.
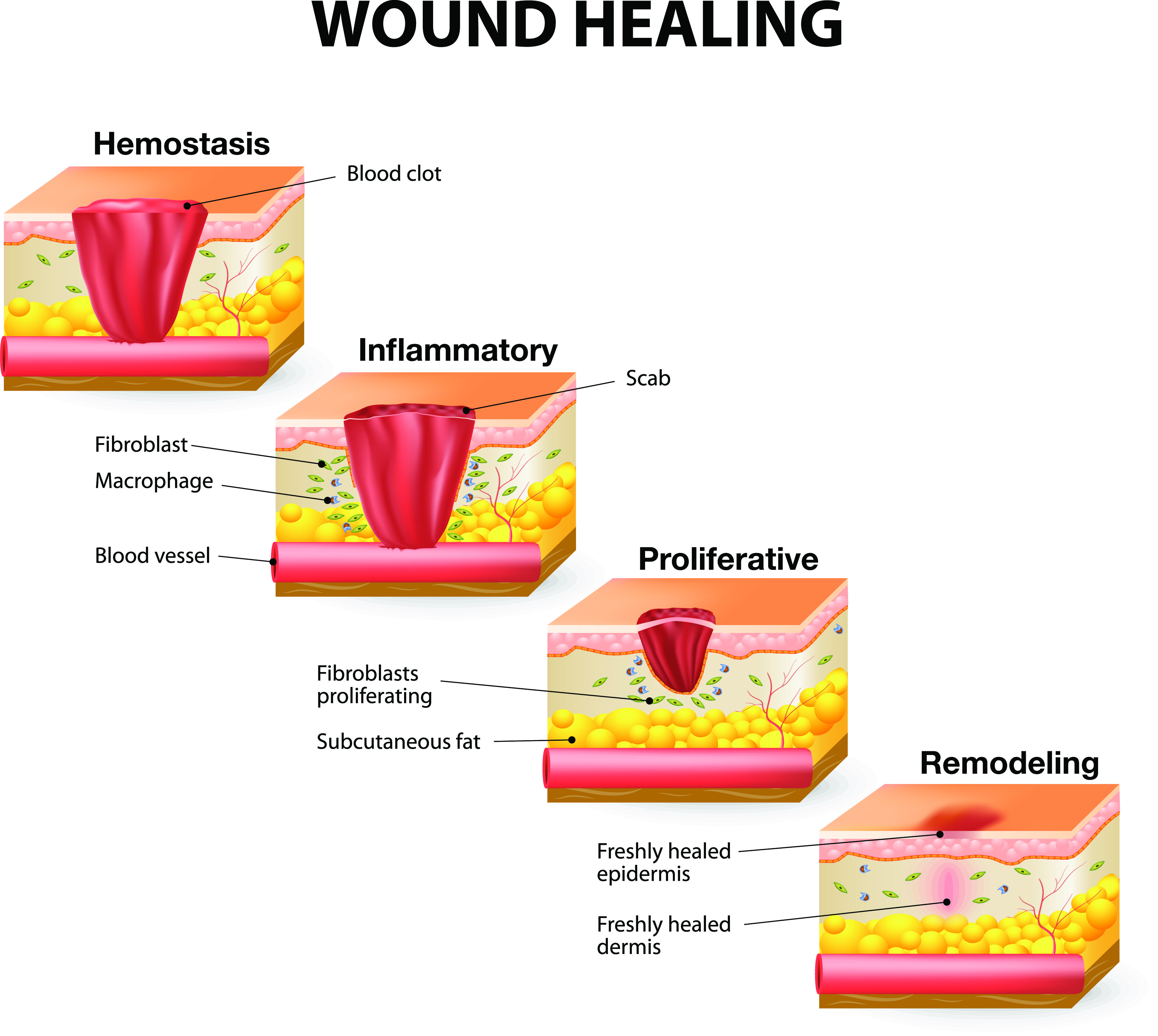
Introduction
Mechanism
- Hemostasis occurs when blood is present outside of the body or blood vessels. It is the instinctive response for the body to stop bleeding and loss of blood. During hemostasis three steps occur in a rapid sequence. Vascular spasm is the first response as the blood vessels constrict to allow less blood to be lost. In the second step, platelet plug f...
Function
- 2. Platelet plug formation Platelets adhere to damaged endothelium to form platelet plug (primary hemostasis) and then degranulate. This process is regulated through thromboregulation. Platelets play one of the biggest factors in the hemostatic process. Being the second step in the sequence they stick together (aggregation) to form a plug that temporarily seals the break in th…
Pathophysiology
- The second stage of hemostasis involves platelets that move throughout the blood. When the platelets find an exposed area or an injury, they begin to form what is called a platelet plug. The platelet plug formation is activated by a glycoprotein called the Von Willebrand factor (vWF), which are found in the bodys blood plasma. When the platelets in the blood are activated, they t…
Clinical significance
- DISORDERS The bodys hemostasis system requires careful regulation in order to work properly. If the blood does not clot sufficiently, it may be due to bleeding disorders such ashemophilia; this requires careful investigation. Over-active clotting can also cause problems; thrombosis, where blood clots form abnormally, can potentially causeembolisms, where blood clots break off and s…
Causes
- Hemostasis disorders can develop for many different reasons. They may be congenital, due to a deficiency or defect in an individuals platelets or clotting factors. A number of disorders can be acquired as well.