What are mature bone cells found within lacunae of compact bone called?
Besides, what are mature bone cells found within lacunae of compact bone called? Mature bone cells found in lacunae are called. osteoclasts. giant multinucleated cells involved in the process of osteolysis are. the basic functional unit is the osteon.
How are lacunae formed in bone?
These cells are formed from the embedding of osteoblasts in the bone matrix. As a consequence, lacunae or small cavities are incorporated into the bone structure.
What are bone lining cells?
The flattened cells found along the bone surfaces, where remodeling of the bone does not occur, are known as the bone lining cells. The cells that line the internal surfaces of a bone are called endosteal cells. However, the cells that are found on external surfaces are termed periosteal cells.
What are lacunae in the human body?
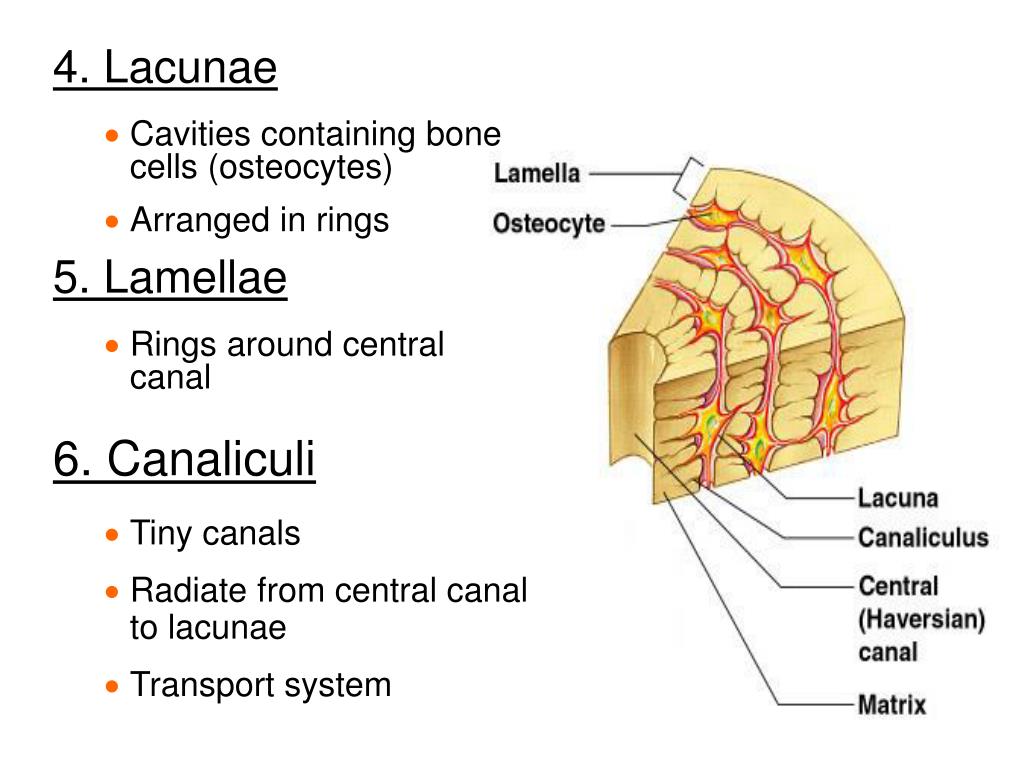
The lacunae are situated between the lamellae, and consist of a number of oblong spaces. Each lacuna is occupied during life by a branched cell, termed an osteocyte, bone-cell or bone-corpuscle. Lacunae are connected to one another by small canals called canaliculi.
What are mature bone cells in lacunae called quizlet?
Osteocytes= re mature bone cells that occupy spaces (lacunae) that conform to their shape. All of these except for the osteoclasts originate from embryonic connective tissue cells. 1.
What are the cells called in the lacuna of the bone?
Each lacuna is occupied during life by a branched cell, termed an osteocyte, bone-cell or bone-corpuscle. Lacunae are connected to one another by small canals called canaliculi.
What are mature bones cells called?
Osteoblasts when transformed into osteocytes become mature bone cells. Osteoblasts synthesize and secrete a collagen matrix and calcium salts. When the area surrounding an osteoblast calcifies, the osteoblast becomes trapped and transforms into an osteocyte, which is the most common and mature type of bone cell.
Is an osteocyte a mature bone cell?
Osteocytes are the most mature and abundant cells in bone tissue and are formed when some osteoblasts become embedded in their secreted osteoid and begin to extend cytoplasmic cell processes to interconnect with each other (Figure 4(b)).
What are osteoblasts and osteocytes?
Cells that are involved in growing bone: Osteoblasts, lining the surface of bone, secrete collagen and the organic matrix of bone (osteoid), which becomes calcified soon after it has been deposited. As they become trapped in the organic matrix, they become osteocytes. Osteocytes maintain bone tissue.
Are osteoclasts mature?
Bone homeostasis is regulated by communication between bone-forming mature osteoblasts (mOBs) and bone-resorptive mature osteoclasts (mOCs).
What is an osteocyte?
Osteocytes are the longest living bone cell, making up 90–95% of cells in bone tissue in contrast to osteoclasts and osteoblasts making up ~5% (40). Osteocytes form when osteoblasts become buried in the mineral matrix of bone and develop distinct features.
What are osteoclasts?
Osteoclasts are the cells that degrade bone to initiate normal bone remodeling and mediate bone loss in pathologic conditions by increasing their resorptive activity. They are derived from precursors in the myeloid/ monocyte lineage that circulate in the blood after their formation in the bone marrow.
Bone Cells
What are bone cells? These cells are the ones in the body that contribute to the growth, structure, maintenance, and function of the bone tissue. These cells collectively comprise less than 2 percent of the bone mass. However, they are very important to the function of bones.
Osteogenic Cells
Before we dive into the four types of bone cells, we need to first learn what osteogenic cells are. These cells, sometimes called osteoprogenitor cells, are the immature cells found in deep layers of the periosteum and the bone marrow. These mono-nucleated cells appear squamous or flattened in structure and have high mitotic activity.
What are the Four Types of Bone Cells?
Bones consist of four basic types of cells: osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts, and bone lining cells. Each bone cell type has a specific structure and performs unique functions. In this section, you'll learn what these bone cells do.
What are the components of the skeletal system?
cartilage, bone, tendons, and ligaments are all components of the. Skeletal system. The layer of hyaline cartilage found covering the ends of bones within a synovial joint is also called_______ cartilage. articular. Hyaline, elastic and fibro are all forms of.
What is the articular cartilage of synovial joints?
articular cartilage of synovial joints consists of. hyaline cartilage. describe the overall composition of bone tissue. Bone consists of bone cells and matrix. the bone cells create the matrix, which is constantly being maintained and replaced.
What cells are trapped in lacunae?
The parallel Haversian canals are connected to one another by the perpendicular Volkmann’s canals. The lamellae of the Haversian systems are created by osteoblasts. As these cells secrete matrix, they become trapped in spaces called lacunae and become known as osteocytes.
When bone cells found within lacunae are surrounded by bone matrix they are called?
Osteocytes are mature osteoblasts that cannot divide by mitosis (Figure 4). Figure 4. Osteocytes are mature osteoblasts that reside in a lacuna. They are surrounded by bony matrix.
What are mature bone cells in lacunae called?
In mature bones, osteocytes and their processes reside inside spaces called lacunae (Latin for a pit) and canaliculi, respectively. Osteocytes are simply osteoblasts trapped in the matrix that they secrete.
What is the process of dissolving bone?
Bone resorption is resorption of bone tissue, that is, the process by which osteoclasts break down the tissue in bones and release the minerals, resulting in a transfer of calcium from bone tissue to the blood. The osteoclasts are multi-nucleated cells that contain numerous mitochondria and lysosomes.
Where is lacunae found in the body?
In the bone, the lacunae are located between the lamellae. When viewed under an ordinary microscope, they appear as spots in the bone tissue. They are opaque and have a fusiform shape. They are occupied by an osteocyte and are connected to each other by canaliculi (small canals or ducts).
Why do cells in cartilage have to live in lacunae?
They lie in spaces called lacunae with up to eight chondrocytes located in each. Chondrocytes rely on diffusion to obtain nutrients as, unlike bone, cartilage is avascular, meaning there are no vessels to carry blood to cartilage tissue. This lack of blood supply causes cartilage to heal very slowly compared with bone.
What are the 4 types of bone cells?
Bone is a mineralized connective tissue that exhibits four types of cells: osteoblasts, bone lining cells, osteocytes, and osteoclasts [1, 2]. Bone exerts important functions in the body, such as locomotion, support and protection of soft tissues, calcium and phosphate storage, and harboring of bone marrow [3, 4].