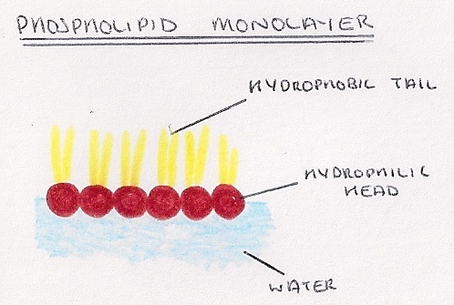
What are hydrophilic and hydrophobic molecules called?
Hydrophilic and hydrophobic molecules are also known as polar molecules and nonpolar molecules, respectively. Some hydrophilic substances do not dissolve. This type of mixture is called a colloid .
What is a hydroxyl group?
Updated April 28, 2017. A hydroxyl group is a functional group that attaches to some molecules containing an oxygen and hydrogen atom, bonded together. Also spelled hydroxy, this functional group provides important functions to both alcohols and carboxylic acids.
Is the carboxyl group hydrophilic?
Among the hydrophilic functional groups is the carboxyl group found in amino acids, some amino acid side chains, and the fatty acid heads that form triglycerides and phospholipids. Also Know, are hydroxyl groups polar or nonpolar?
Are hygroscopics hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
Hygroscopics are attracted to water, but are not dissolved by water. A hydrophilic molecule or portion of a molecule is one whose interactions with water and other polar substances are more thermodynamically favorable than their interactions with oil or other hydrophobic solvents. They are typically charge-polarized and capable of hydrogen bonding.
Which functional groups are hydrophobic?
Functional groups can be classified as hydrophobic or hydrophilic based on their charge and polarity characteristics. The only hydrophobic group below is the methyl (CH 3start subscript, 3, end subscript) group, which is nonpolar.
Which functional groups are hydrophilic and hydrophobic?
An example of a hydrophobic group is the non-polar methane molecule. Among the hydrophilic functional groups is the carboxyl group found in amino acids, some amino acid side chains, and the fatty acids that form triglycerides and phospholipids.
Is the hydroxyl group water soluble?
Hydroxyl groups are also able to form hydrogen bonds with water, a property that increases the hydrophilicity and solubility of molecules containing them. The carbohydrates are an example of a group of molecules that are extremely soluble due to hydroxyl functional groups.
Is the hydroxyl group polar or nonpolar?
polar covalent bondsHydroxyl R-OH The oxygen atom is much more electronegative than either the hydrogen or the carbon, which will cause the electrons in the covalent bonds to spend more time around the oxygen than around the C or H. Therefore, the O-H and O-C bonds in the hydroxyl group will be polar covalent bonds.
What is a hydroxyl functional group?
A hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula -OH and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy groups.
Is hydroxyl an acid or base?
H 3O + is called a hydronium ion, and it makes things acidic. OH - is called a hydroxyl ion and it makes things basic. However, in water, there is a balance between hydroniums and hydroxyls so they cancel each others' charges. Pure water is neither acidic or basic; it is neutral.
What are the characteristics of a hydroxyl group?
Hydroxyl groups are a functional group found in sugars and alcohols. A hydroxyl group consists of one hydrogen and one oxygen atom and can be written as either -OH or HO-. Hydroxyl groups are polar, and the oxygen side is always negative, while the hydrogen side is always positive.
What is a hydroxyl group quizlet?
hydroxyl group: structure. —OH : A hyrdrogen atom bonded to an oxygen atom, bonded to the carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
Does water have a hydroxyl group?
alcohols. …properties because water molecules contain hydroxyl groups that can form hydrogen bonds with other water molecules and with alcohol molecules, and likewise alcohol molecules can form hydrogen bonds with other alcohol molecules as well as with water.
Are carboxyl groups polar or nonpolar?
Classifying Functional GroupsTable 1. Important Functional Groups in BiologyFunctional GroupPropertiesMethylNonpolarCarbonylPolarCarboxylCharged, ionized to release H+. Since carboxyl groups can release H+ ions into a solution, they are considered acidic.4 more rows
Does polar equal hydrophilic?
If a molecule has areas where there is a partial positive or negative charge, it is called polar, or hydrophilic (Greek for "water-loving"). Polar molecules dissolve easily in water.
Which atoms does a hydroxyl functional group contain quizlet?
Hydroxyl- have one hydrogen paired with one oxygen atom (symbolized as -OH). This group is attached to a carbon skeleton.
What are surface hydroxyl groups?
Surface hydroxyl groups are responsible for the inherent self-adhesion property of cellulose nanomaterials. This characteristic provides strength to the nanomaterials, increases chemical reactivity, and makes them suitable for composite nanomaterials [31]. Surface hydroxyl groups can provide sites for making hydrogen bonds with the hydroxyl group of other hydrophilic polymer or induce wetting nature to the hydrophobic or nonpolar surfaces. For instance, the surface hydroxyl group of CNFs were used to form hydrogen bonding with 3-Methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane to promote linkage between hydrophilic cellulose and hydrophobic polylactic acid [32]. The surface hydroxyl groups of CNCs react with acetic anhydride, and form surface acetylated crystals that are used to reinforce polylactic acid [33]. Such type of reinforced polymeric composite is an excellent candidate to use in controlled release formulations. The surface hydroxyl group's exposure is the primary characteristic of cellulose nanomaterial that makes it an excellent candidate to fabricate biodegradable composites for drug delivery applications.
What is the role of hydroxyl group in chemical reactions?
This group can also participate in chemical reactions to link molecules together, forming chains of sugars or fatty acids. The addition of a hydroxyl group converts many organic compounds into alcohols, enhancing their solubility in water.
What is the molecule that overexpresses the sigma receptor?
pHBA is a small molecule with an affinity toward sigma receptors that overexpresses in brain tumor. Swami et al. conjugated pHBA on to G4 PAMAM dendrimers loaded with docetaxel for targeting to brain. The prepared conjugates were characterized and preceded for evaluation of in-vitro studies on U87MG brain tumor cells and in vivo studies on mice for determining pharmacokinetic and biodistribution in comparison to marketed formulation taxotere. Results demonstrated that pHBA conjugated dendrimers showed superior activity in terms of cytotoxicity and cellular uptake. In vivo studies for conjugated formulations showed two-fold increase in drug concentration in brain when compared to unconjugated dendrimers [80].
What is a hydroxyl functionalized cyclic phosphoester monomer?
Hydroxyl functionalized five-membered cyclic phosphoester monomers, namely 2- (2-hydroxyethoxy)ethoxy-2-oxo-1,3,2-dioxaphospholane (HEEP), have been prepared for the synthesis of a water-soluble hyperbranched polyphosphate (HPHEEP) (13 ). The polymer was synthesized through a so-called self-condensation ROP (SCROP) in bulk without the addition of any catalyst. 53,66 The terminal hydroxyl groups potentially provide a unique opportunity for further modification and functionalization in biomedical applications.67–70
What are the two lone pairs of a hydrogen atom?
Hydroxyl groups are simple structures consisting of an oxygen atom with two lone pairs bonded to a hydrogen atom. They readily participate in hydrogen bonding, generating either a net positively or negatively charged ion.
What is the HV of oil?
The hydroxyl value ( HV) of an oil is an indication of its hydroxyl group content. The hydroxyl groups can be part of fatty acid moieties such as ricinoleic acid (9Z ,12 R)-12-hydroxyoctadecenoic acid, but they can also be part of the glycerol moiety when this is not esterified as in partial glycerides. So, in oils without fatty acids ...
Is PHA a homopolymer?
PHA polymers have a semicrystalline structure with a rather high degree of crystallinity ranging from 40 to 80%. P (3HB) homopolymer is a stiff and brittle material. It has a melting temperature (Tm ∼ 180 °C) and mechanical properties (Young’s modulus and tensile strength) closed to those of PP. The elongation at break is, however, substantially lower than that of PP. The incorporation of hydroxyalkanoate comonomers into a P (3HB) chain can greatly improve the mechanical properties of the material.
What is hydroxyl group?
A hydroxyl group is a functional group that attaches to some molecules containing an oxygen and hydrogen atom, bonded together. Also spelled hydroxy, this functional group provides important functions to both alcohols and carboxylic acids. Alcohols are chains of carbon molecules with a functional hydroxyl group side chain. The electronegativity of the oxygen adds a slight polarity to alcohols, which is why they are able to interact with other polar molecules such as water and some solutes. Below is a general alcohol which contains a hydroxyl group. The oxygen is the red atom, while the hydrogen is represented by the grey atom. The R represent any generic carbon chain.
Which group is bonded to an oxygen and also bonded to a hydroxyl group?
Carboxyl group – A carbon doubled bonded to an oxygen and also bonded to a hydroxyl group. Carbonyl group – A carbon double bonded to an oxygen and any other molecules, including more carbons. Electronegativity – The attraction that an atom has for electrons, compared to the other types of atoms that it shares electrons with in covalent bonds.
What happens when the carboxyl group loses the hydroxyl group attached to it?
When the protein is formed, the carboxyl group loses the hydroxyl group attached to it, while the amino group loses a hydrogen. With the loss of these molecules, the amino group binds to the carbonyl group, forming a peptide bond. What else is produced during this reaction? A. Water.
What is the difference between oxygen and hydrogen?
The oxygen is the red atom, while the hydrogen is represented by the grey atom. The R represent any generic carbon chain. Carboxylic acids contain a hydroxyl group within their functional carboxyl group. A carboxyl group consists of a carbonyl group bonded to a hydroxyl group. A carbonyl group is simply a carbon double bonded to an oxygen.
Why does the hydroxyl group lose hydrogen?
As mentioned, a large part of the action caused by the hydroxyl group is due to the electronegativity of the oxygen. Because oxygen has a stronger attraction with the electrons bonding hydrogen to the molecule , the hydroxyl group can easily lose the hydro gen to an atom that will share electrons more equally. When this happens, the oxygen takes on ...
What is the side chain of alcohol?
Alcohols are chains of carbon molecules with a functional hydroxyl group side chain . The electronegativity of the oxygen adds a slight polarity to alcohols, which is why they are able to interact with other polar molecules such as water and some solutes. Below is a general alcohol which contains a hydroxyl group.
Is carboxylic acid a hydroxyl group?
Along with alcohols, carboxylic acids are commonly seen in nature. A generic carboxylic acid with its hydroxyl group can be seen below. Besides these two large classes of molecules that are functionally dependent on the hydroxyl group, many other molecules contain hydroxyl groups. As mentioned, a large part of the action caused by ...
What is hydrophilic molecule?
A hydrophilic molecule or portion of a molecule is one whose interactions with water and other polar substances are more thermodynamically favorable than their interactions with oil or other hydrophobic solvents.
What is a hydrophile?
Jump to navigation Jump to search. Molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolved by water. Play media.
What is the termite that uses hydrophilic surfaces?
Schedorhinotermes termites use hydrophilic surfaces on body and wings to attach themselves to plants they colonize. A hydrophile is a molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolved by water.
How much solubility does a molecule have in water?
An approximate rule of thumb for hydrophilicity of organic compounds is that solubility of a molecule in water is more than 1 mass % if there is at least one neutral hydrophile group per 5 carbons, or at least one electrically charged hydrophile group per 7 carbons. Hydrophilic substances (ex: salts) can seem to attract water out of the air.
What is hydrophilic membrane filtration?
Hydrophilic membrane filtration is used in several industries to filter various liquids. These hydrophilic filters are used in the medical, industrial, and biochemical fields to filter elements such as bacteria, viruses, proteins, particulates, drugs, and other contaminants. Common hydrophilic molecules include colloids, cotton, and cellulose (which cotton consists of).
Which alcohol has the shortest carbon chain?
Methanol has the shortest carbon chain of all alcohols (one carbon atom) followed by ethanol (two carbon atoms), and 1-propanol along with its isomer 2-propanol, all being miscible with water. Tert-Butyl alcohol, with four carbon atoms, is the only one among its isomers to be miscible with water.
Do hydrophilic membranes need prewetting?
Unlike other membranes, hydrophilic membranes do not require pre-wetting: they can filter liquids in their dry state. Although most are used in low-heat filtration processes, many new hydrophilic membrane fabrics are used to filter hot liquids and fluids.
What is the hydrophilic group?
The hydrophilic group acquires a negative charge (anion) when it is dissolved in water. Anionic hydrophilic groups include sulfates (ROSO3− ), sulfonates (RSO 3− ), carboxylates (RCOO − ), and phosphates ( RPO 4 − ). Soaps are sodium or potassium fatty acid carboxylates, which have been implemented by man for more than 2000 years [25]. One of the common anionic surfactants is sodium dodecyl sulfate ( C 12 H 25 SO 4 − Na + ), a synthetic material. The name is often abbreviated to sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) [24]. Sodium dodecanoate (C 11 H 23 COO − Na +), a material that can be synthesized is another one. There is also a large group of materials of this type formed from natural sources, e.g., the hydrolysis of triglycerides [22–24].
What is the antifouling material?
Here, we discuss two commonly used polysaccharide antifouling materials such as hyaluronic acid (HA), chitosan (CHI), and dextran. Hyaluronic acid is a kind of hydrophilic anionic polysaccharide, which possesses large numbers of amide (CO-NH) and carboxyl (COOH) groups.
Does lignin have hydrophilic groups?
As lignin surfactants contain hydrophilic groups, when it is dispersed in the discrete-phase coal particles, it can weaken the hydrophobic interaction of the surface on coal particles and form a layer of hydration film on the surface.