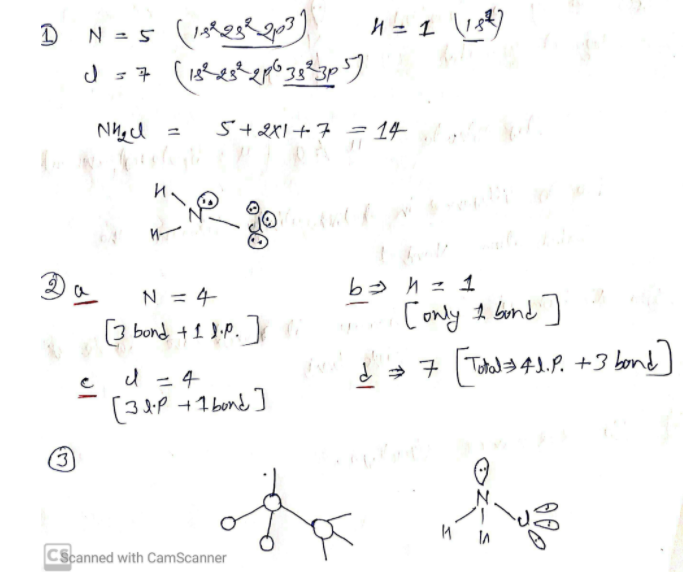What type of bond is nitrogen carbon and fluorine?
These elements are considered to be covalent. Other elements that can form covalent bonds include nitrogen, carbon and fluorine. Click to see full answer. Correspondingly, what type of bond is nitrogen and fluorine? Nitrogen tends to form three bonds and have on e lone pair. Oxygen tends to form two bonds and have two lone pairs.
Is nitrogen and fluorine ionic or covalent?
Is nitrogen and fluorine a covalent bond? These elements are considered to be covalent. Other elements that can form covalent bonds include nitrogen, carbon and fluorine. Click to see full answer.
Is fluorine a single or covalent bond?
Most frequently, covalent bonds involving fluorine atoms are single bonds, although at least two examples of a higher order bond exist. Fluoride may act as a bridging ligand between two metals in some complex molecules. What element would form a covalent bond with fluorine?
Is nitrogen a covalent bond?
These elements are considered to be covalent. Other elements that can form covalent bonds include nitrogen, carbon and fluorine. Click to see full answer. Considering this, what forms a covalent bond with nitrogen?
What type of bond is between nitrogen and fluorine?
The three fluorine atoms form covalent bonds with the nitrogen atom by sharing one electron of each other to get stabilized.
Is nitrogen and fluorine covalent or ionic?
0:011:15Is NF3 (Nitrogen trifluoride ) Ionic or Covalent/Molecular? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBetween nitrogen and fluorine and that means it'll be a covalent bond let's look at a scale to seeMoreBetween nitrogen and fluorine and that means it'll be a covalent bond let's look at a scale to see that. So 0.94 that's about right there that means that the bonds between the nitrogen.
What type of bond is NF?
tunable covalent bondThe investigation showed that the NF bond is a tunable covalent bond, with bond strength orders ranging from 2.5 (very strong) to 0.1 (very weak). NF bond strengthening is caused by a combination of different factors and can be achieved by e.g. ionization.
Is fluorine and fluorine a covalent bond?
The two fluorine atoms form a stable F 2 molecule by sharing two electrons; this linkage is called a covalent bond.
What does nitrogen and fluorine form?
Nitrogen trifluoride, NF. Nitrogen difluoride radical, ·NF.
Is nitrogen a covalent bond?
Nitrogen is a very stable molecule and relatively unreactive, being held together by a strong triple covalent bond. In this Lewis diagram, each oxygen atom is surrounded by seven electrons (not eight).
How do you identify a covalent bond?
A covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the number of electrons it needs to reach octet. Hydrogen is an exception to the octet rule. H forms only one bond because it needs only two electrons.
Which elements can form covalent bonds?
Covalent Elementshydrogen.carbon.nitrogen.phosphorus.oxygen.sulfur.selenium.
Which of the following contains covalent bond?
Expert-verified answer HCl contains covalent bonds in its formulation. A covalent bond is a chemical relationship that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms.
Why is nitrogen covalent bond?
Nitrogen atoms will form three covalent bonds (also called triple covalent) between two atoms of nitrogen because each nitrogen atom needs three electrons to fill its outermost shell. Another example of a nonpolar covalent bond is found in the methane (CH4) molecule.
Is fluorine covalent or ionic?
Fluorine and the other halogens in group 7A (17) have seven valence electrons and can obtain an octet by forming one covalent bond....How Many Covalent Bonds Are Formed?Atom (Group number)Number of BondsNumber of Lone PairsOxygen (Group 16 or 6A)22Fluorine (Group 17 or 7A)132 more rows•Jul 1, 2019
Does fluorine form ionic or covalent bond?
With other atoms, fluorine forms either polar covalent bonds or ionic bonds. Most frequently, covalent bonds involving fluorine atoms are single bonds, although at least two examples of a higher order bond exist.
How many valence electrons does nitrogen have?
Nitrogen has five valence electrons, so it needs three more valence electrons to complete its octet. A nitrogen atom can fill its octet by sharing three electrons with another nitrogen atom, forming three covalent bonds, a so-called triple bond. Also Know, which element will form covalent bonds with chlorine?
Why do atoms covalently bond?
Covalent bonding occurs when pairs of electrons are shared by atoms. Atoms will covalently bond with other atoms in order to gain more stability, which is gained by forming a full electron shell. By sharing their outer most (valence) electrons, atoms can fill up their outer electron shell and gain stability.
What are the elements that form covalent bonds?
These elements are considered to be covalent. Other elements that can form covalent bonds include nitrogen, carbon and fluorine. Click to see full answer. In this regard, what forms a covalent bond with nitrogen?
How many atoms are in nitrogen trifluoride?
Nitrogen trifluoride consists of 3 fluorine and 1 nitrogen atoms that differ in their electronegativity. The shape of this molecule is trigonal pyramidal due to the presence of lone pair on the nitrogen atom.
How do fluorine and nitrogen form covalent bonds?
The three fluorine atoms form covalent bonds with the nitrogen atom by sharing one electron of each other to get stabilized. One lone pair remains on the nitrogen atom that causes repulsion between lone pair and bond pairs resulting in the bent shape (trigonal pyramidal) of the NF3 molecule.
How many valence electrons does NF3 have?
The molecule of NF3 consists of a total of 8 valence electrons. Nitrogen atom contains 5 electrons in its outermost shell and requires 3 electrons to complete its octet. And, Fluorine has 7 valence electrons in its outermost shell and requires a single electron to complete its octet.
How is nitrogen trifluoride made?
Nitrogen trifluoride gas is considered as a strong greenhouse gas (causing global warming). The molecule of nitrogen trifluoride is made up of 1 nitrogen atom and 3 fluorine atoms. The nitrogen atom is a central atom surrounded ...
What is the electronegativity of nitrogen trifluoride?
The shape of the Nitrogen trifluoride is formed as trigonal pyramidal similar to the shape of the ammonia molecule (NH3). The electronegativity of Nitrogen is 3.04 and that of fluorine is 3.98. Due to this difference, the N-F bond ensures polarity in it.
Why do atoms have equal charge distribution?
The atoms within these molecules have equal charge distribution on them due to which no polarity occurs in them. The two atoms that are covalently bonded form a nonpolar bond if the electronegativity of both atoms is the same. Few examples of such molecules are PCl5, SO3, Cl2, etc.
What are the factors that affect the polarity of a molecule?
Factors affecting polarity of a molecule. Electronegativity: The electronegativity of an atom is the strength to attract the bonded electron pair towards its side. In a molecule, if there is a difference between the electronegativity of two atoms then there exists a polarity in that bond.
What is NF#N#3 used for?
Nitrogen trifluoride is primarily used to remove silicon and silicon-compounds during the manufacturing of semiconductor devices such as LCD displays, some thin-film solar cells, and other microelectronics. In these applications NF#N#3 is initially broken down within a plasma. The resulting fluorine radicals are the active agents that attack polysilicon, silicon nitride and silicon oxide. They can be used as well to remove tungsten silicide, tungsten, and certain other metals. In addition to serving as an etchant in device fabrication, NF#N#3 is also widely used to clean PECVD chambers.
What is nitrogen trifluoride?
It is a rare example of a binary fluoride that can be prepared directly from the elements only at very uncommon conditions, such as an electric discharge. After first attempting the synthesis in 1903, Otto Ruff prepared nitrogen trifluoride by the electrolysis of a molten mixture of ammonium fluoride and hydrogen fluoride. It proved to be far less reactive than the other nitrogen trihalides nitrogen trichloride, nitrogen tribromide and nitrogen triiodide, all of which are explosive. Alone among the nitrogen trihalides it has a negative enthalpy of formation. It is prepared in modern times both by direct reaction of ammonia and fluorine and by a variation of Ruff's method. It is supplied in pressurized cylinders.
What is fluorine radical?
3 is initially broken down within a plasma. The resulting fluorine radicals are the active agents that attack polysilicon, silicon nitride and silicon oxide. They can be used as well to remove tungsten silicide, tungsten, and certain other metals. In addition to serving as an etchant in device fabrication, NF.
Is nitrogen trifluoride a fluorine gas?
Nitrogen trifluoride is also used in hydrogen fluoride and deuterium fluoride lasers, which are types of chemical lasers. There it is also preferred to fluorine gas due to its more convenient handling properties.
Is ammonia polar or nonpolar?
It is nonbasic with a low dipole moment of 0.2340 D. By contrast, ammonia is basic and highly polar (1.47 D). This difference arises from the fluorine atoms acting as electron withdrawing groups, attracting essentially all of the lone pair electrons on the nitrogen atom. NF 3 is a potent yet sluggish oxidizer.
Is nitrogen tribromide explosive?
It proved to be far less reactive than the other nitrogen trihalides nitrogen trichloride, nitrogen tribromide and nitrogen triiodide, all of which are explosive. Alone among the nitrogen trihalides it has a negative enthalpy of formation.
Is NF3 flammable?
For other uses, see NF3. Nitrogen trifluoride ( NF. 3) is an inorganic, colorless, non- flammable, toxic gas with a slightly musty odor. It finds increasing use within the manufacturing of flat-panel displays, photovoltaics, LEDs and other microelectronics.
What are some examples of dinitrogen complexes?
The first example of a dinitrogen complex to be discovered was
How is nitrogen gas produced?
Nitrogen gas is an industrial gas produced by the fractional distillation of liquid air, or by mechanical means using gaseous air (pressurised reverse osmosis membrane or pressure swing adsorption ). Nitrogen gas generators using membranes or pressure swing adsorption (PSA) are typically more cost and energy efficient than bulk delivered nitrogen. Commercial nitrogen is often a byproduct of air-processing for industrial concentration of oxygen for steelmaking and other purposes. When supplied compressed in cylinders it is often called OFN (oxygen-free nitrogen). Commercial-grade nitrogen already contains at most 20 ppm oxygen, and specially purified grades containing at most 2 ppm oxygen and 10 ppm argon are also available.
What is the name of the mixture of nitric and hydrochloric acids?
The mixture of nitric and hydrochloric acids was known as aqua regia (royal water), celebrated for its ability to dissolve gold, the king of metals. The discovery of nitrogen is attributed to the Scottish physician Daniel Rutherford in 1772, who called it noxious air.
Why do we use nitrogen in aircraft fuel?
In some aircraft fuel systems to reduce fire hazard (see inerting system ). To inflate race car and aircraft tires, reducing the problems of inconsistent expansion and contraction caused by moisture and oxygen in natural air. Nitrogen is commonly used during sample preparation in chemical analysis.
How many electrons does a nitrogen atom have?
From left to right: 1s, 2s (cutaway to show internal structure), 2p x, 2p y, 2p z. A nitrogen atom has seven electrons. In the ground state, they are arranged in the electron configuration 1s 2. 2s 2. 2p 1.
What is the nitrogen cycle?
The nitrogen cycle describes movement of the element from the air, into the biosphere and organic compounds, then back into the atmosphere.
Why is gelatin added to hydrazine?
The reason for adding gelatin is that it removes metal ions such as Cu 2+ that catalyses the destruction of hydrazine by reaction with monochloramine (NH 2 Cl) to produce ammonium chloride and nitrogen. Hydrogen azide (HN 3) was first produced in 1890 by the oxidation of aqueous hydrazine by nitrous acid.