Hyperosmotic can refer to solutions that have increased osmotic pressure, or a greater difference between solutes and solutions between a membrane. In other instances, hyperosmotic refers to a solution that has more solutes, or components of a solution, than a similar solution. Similarly, you may ask, is Hyperosmotic the same as hypertonic?
Are hyperosmotic solutions always hypertonic?
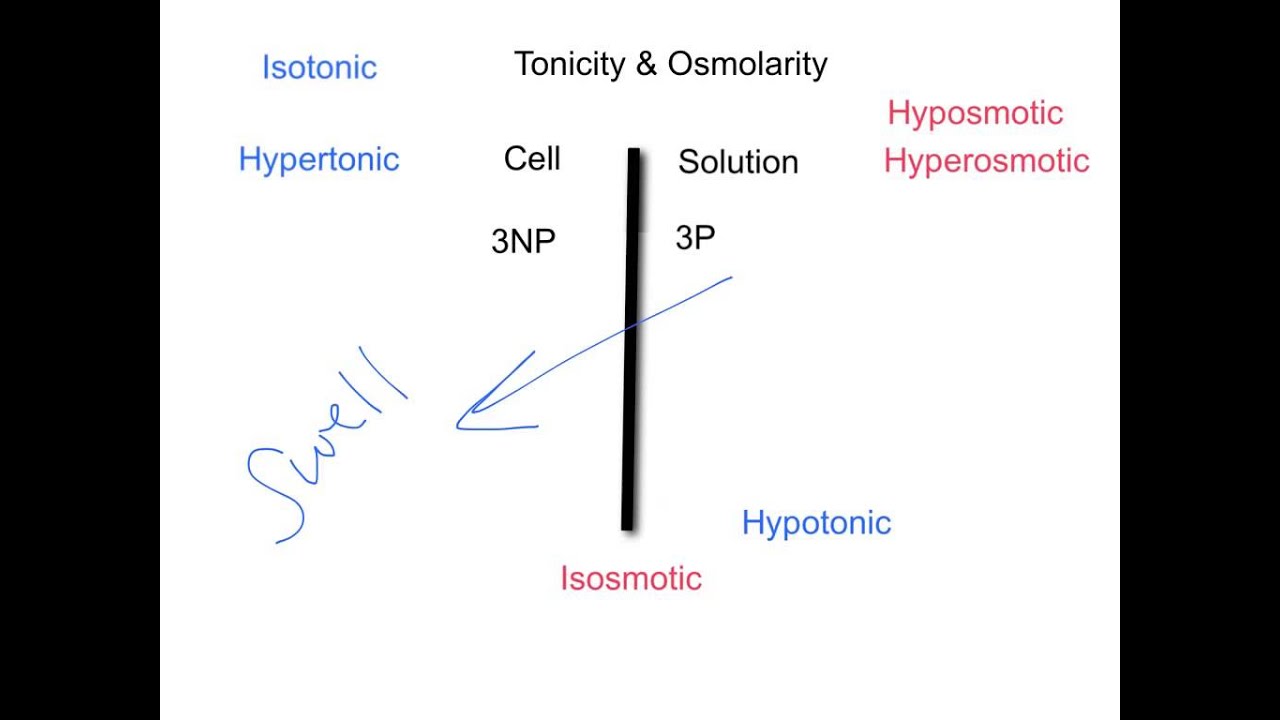
10/04/2020 · Hyperosmotic solutions are not always hypertonic. But hyposmotic solutions are always hypotonic. If the solution has a lower concen- tration of nonpenetrating solutes than the cell does, then there will be net movement of water into the cell at equilibrium and the solution is hypotonic.
What is the difference between hypotonic and hypertonic?
04/01/2022 · Hyperosmotic adjective. Relating to hyperosmolarity. Hypertonic adjective. (anatomy) having a very high muscular tension; spastic. Hyperosmotic adjective. Relating to hyperosmosis. Hypertonic noun. Having a higher osmotic pressure than a comparison solution; - of an aqueous solution.
What does hyperosmotic mean in chemistry?
31/01/1996 · Hypertonic refers to a greater concentration. In biology, a hypertonic solution is one with a higher concentration of solutes outside the cell than inside the cell. Hypotonic refers to a lesser concentration. In biology, a hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of solutes outside the cell than inside the cell.
What is hypotonic and hyposmotic solution?
As adjectives the difference between hypertonic and hyperosmotic is that hypertonic is (of a solution) having a greater osmotic pressure than another while hyperosmotic is hypertonic.
Is Hyperosmotic and hypertonic the same thing?
As adjectives the difference between hypertonic and hyperosmotic. is that hypertonic is (of a solution) having a greater osmotic pressure than another while hyperosmotic is hypertonic.
Are hypertonic solutions hyperosmolar?
Hyperosmotic solutions are not always hypertonic. But hyposmotic solutions are always hypotonic. The response to this rapid fire presentation of osmolarity and tonicity was overwhelmingly positive.18-Oct-2016
Can a solution be Hyperosmotic and hypotonic?
When a cell is placed in a hyperosmotic but hypotonic solution like 10% dextran, water movement will occur. Therefore, a solution can be hyperosmotic and hypotonic.
What is the difference between Hyperosmotic and Hypoosmotic?
The key difference between isosmotic hyperosmotic and hypoosmotic is that isosmotic refers to the property of having equal osmotic pressures, but hyperosmotic refers to the property of having a high osmotic pressure. Meanwhile, hypoosmotic refers to the property of having a low osmotic pressure.11-Mar-2020
What is hyperosmolar?
The loss of water also makes the blood more concentrated than normal. This is called hyperosmolarity. It is a condition in which the blood has a high concentration of salt (sodium), glucose, and other substances. This draws the water out of the body's other organs, including the brain.26-Jan-2020
What are hyperosmolar fluids?
Hyperosmolar: In biochemistry, pertaining to an osmolar concentration of the body fluids that is abnormally increased.29-Mar-2021
Can a solution be Hyperosmotic and isotonic?
Non-penetrating solutes cannot cross the cell membrane; therefore, the movement of water across the cell membrane (i.e., osmosis) must occur for the solutions to reach equilibrium. A solution can be both hyperosmotic and isotonic.
What's the difference between tonicity and osmolarity?
The key difference between tonicity and osmolarity is that the tonicity measures only the concentration of non-penetrating solutes through a semipermeable membrane while the osmolarity measures the total concentration of penetrating and non-penetrating solutes.23-Apr-2011
What happens to a cell in a Hypoosmotic solution?
In a hypotonic solution, the solute concentration is lower than inside the cell. Depending on the amount of water that enters, the cell may look enlarged or bloated. ... If the water continues to move into the cell, it can stretch the cell membrane to the point the cell bursts (lyses) and dies.06-May-2018
What are Hyperosmotic regulators?
Animals that are hyper-isosmotic regulators have mechanisms for hyperosmotic regulation but not hyposmotic regulation. Hyper-hyposmotic regulators have mechanisms for both types of regulation. Euryhaline fish, such as species that migrate between seawater and freshwater, are excellent hyper-hyposmotic regulators.
What does Hypoosmotic urine mean?
By definition, hyposmotic (dilute) urine has an osmolarity lower than blood osmolarity. Hyposmotic urine is produced when there are low circulating levels of ADH (e.g., water drinking, central diabetes insipidus) or when ADH is ineffective (e.g., nephrogenic diabetes insipidus).
Is a marine fish Hyperosmotic or Hypoosmotic?
Saltwater fish are hypoosmotic to the sea, their blood has a lower solute content and, therefore, a lower osmotic pressure (about 400 mOsmol) than sea water (about 1000 mOsmol).
What does tonicity mean in biology?
loltopsy. Tonicity refers to what the cell does in a certain environment. If the environment is hypertonic, the cell will shrink due to water leaving the cell. Hypotonic means water enters the cell and caused it to expand and possibly explode.
Is tonicity the same as osmolarity?
Tonicity and osmolarity generally will have the same prefix. However, there are some solutes that will act oddly and can create a situation where the system is hypertonic and isoosmotic. Just look at what the cell does and relative concentration of each solution, and you can figure it out. More options….
Why is my message considered spam?
Your message may be considered spam for the following reasons: Your new thread title is very short, and likely is unhelpful. Your reply is very short and likely does not add anything to the thread. Your reply is very long and likely does not add anything to the thread.
What is hypotonic osmolarity?
Hypotonic means water enters the cell and caused it to expand and possibly explode. Osmolarity refers to the relative concentration of two solutions. If the outer environment is hyperosmotic, the concentration of solutes outside the cell is greater than the concentration inside the cell.
What is a hypotonic solution?
A hypotonic solution is any solution that has a lower osmotic pressure than another solution. In the biological fields, this generally refers to a solution that has less solute and more water than another solution.
What is an example of a hypotonic solution?
A common example of a hypotonic solution is 0.45% normal saline (half normal saline). When a patient develops diabetic ketoacidosis, the intracellular space becomes dehydrated, so the administration of a hypotonic solution helps to rehydrate the cells.
What happens to a cell in a hypotonic solution?
Hypotonic Solution. In a hypotonic solution, the solute concentration is lower than inside the cell. Depending on the amount of water that enters, the cell may look enlarged or bloated. If the water continues to move into the cell, it can stretch the cell membrane to the point the cell bursts (lyses) and dies.
When would you use a hypotonic solution?
Hypotonic solutions are used when the cell is dehydrated and fluids need to be put back intracellularly. This happens when patients develop diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or hyperosmolar hyperglycemia.
What is hypertonic and hypotonic solution?
In your body, these solutes are ions like sodium and potassium. A hypotonic solution is one in which the concentration of solutes is greater inside the cell than outside of it, and a hypertonic solution is one where the concentration of solutes is greater outside the cell than inside it.
Is water hypertonic or hypotonic?
This more concentrated outside solution is termed hypertonic. In the last case, where the solution outside the cell has a lower solute concentration than the cell fluid, water will move into the cell towards the higher solute concentration. The less concentrated outside solution is termed hypotonic.
How do you remember hypertonic and hypotonic?
hypertonic= water will move out the cell, because the amount of "stuff" outside the cell is bigger. hypotonic=water will move into the cell, because the amount of "stuff" inside the cell is bigger. i always imagine it as a balloon: if you keep blowing up the balloon it will eventually pop.
What are some examples of misinformation?
Here are just a few recent examples of the misinformation found on the Web: 1 “Tonicity is the relative concentration of solutions that determine the direction and extent of diffusion” ( 5 ). 2 “Tonicity: . . . is related to the number of particles found in solution. Osmolarity is most often used when referring to blood, and tonicity is most often used when referring to iv fluid, but the terms may be used interchangeably” ( 1 ). 3 “Isotonic solution: a solution that has the same salt concentration as cells and blood” ( 2 ). 4 “When two environments are isotonic, the total molar concentration of dissolved solutes is the same in both of them” ( 3 ).
What is the difference between osmolarity and osmolarity?
Both terms describe solutions, but the similarity ends there. Osmolarity is concentration expressed in units of solute/volume. It can be measured on a machine called an osmometer, and it has units, usually osmoles or milliosmoles per liter (osmolality is expressed using kilograms of water instead of liters).
How to determine tonicity of a solution?
What determines the tonicity of a solution? The tonicity is determined by comparing the concentration of nonpenetrating solutes, those that cannot enter the cell, in the solution to the concentration of the cell.
Is 5% dextrose hypotonic?
A solution of 5% dextrose has zero nonpenetrating solutes, and therefore, it is hypotonic.
Is glucose hypotonic or tonic?
Tonicity depends only on the concentration of nonpenetrating solutes, so any solution of pure glucose will be hypotonic, no matter what its osmolarity, and tonicity describes only the change in cell volume at equilibrium. Water crosses cell membranes faster than solutes do, so a cell placed in a hyperosmotic but hypotonic solution ...
What is tonicity in biology?
Tonicity is a behavioral term. It describes what a solution would do to a cell's volume at equilibrium if the cell was placed in the solution. A cell placed in a hypotonic solution will gain volume and swell. A cell placed in a hypertonic solution will lose volume and shrink. Tonicity cannot be measured on an osmometer, and it has no units.
How does glucose enter the cell?
As glucose enters cells, the movement of solute from the extracellular fluid into the cells causes water to follow by osmosis. The cell gains volume, so the solution is hypotonic. But the story doesn't stop there. Glucose inside the cell is metabolized by aerobic respiration with the end products of CO 2 and water.