Is fluorenone soluble in water?
An important thing to realize however, is that fluorenone is NOT soluble in water. This is actually the case for a lot of organic compounds. The reason will become more apparent when we talk about its polarity in the next section.
Is 9 fluorenone soluble in hexane?
Dispersion interactions are strong for such aromatic rings, and the point can be made that this factor will drive the solvation of 9-fluorenone in hexane. This is confirmed by the fact that 9-fluorenone is insoluble in water. Also know, is 9 Fluorenone more polar than ferrocene?
What is the standard state of fluorenone?
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). ?) Fluorenone is an aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C 13 H 8 O. It is used to make antimalaria drugs.
What is the chemical name of fluorenone?
?) Fluorenone is an aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C 13 H 8 O. It is used to make antimalaria drugs. It can be synthesised from fluorene with the addition of glacial acetic acid and sodium hypochlorite solution, undergoing an oxidation reaction.
Why is 9-Fluorenone not soluble in water?
9-fluorenone has one polar C=O. bond, but it also has two aromatic rings. Dispersion interactions are strong for such aromatic rings, and the point can be made that this factor will drive the solvation of 9-fluorenone in hexane. This is confirmed by the fact that 9-fluorenone is insoluble in water.
Can fluorenone dissolve in water?
9-Fluorenone is a fluorene derivative. Solubility : Soluble in water (25.3 mg/l at 25 °C), alcohol, acetone, ether, and benzene .
Why is fluorenone insoluble in water?
So why is fluorenone insoluble in water? Because even though fluorenone is polar (like water), the non-polar aspects of the molecule repel water molecules, making it unavailable for forming a solution with water.
Is 9 Fluorenol soluble in water?
9-Fluorenol is used in Organic Synthesis, Pharmaceuticals, Agrochemicals and Dyestuffs. Insoluble in water.
Why is 9-fluorenone soluble in diethyl ether?
Since diethyl ether is nonpolar, 9-fluorenone, which is also nonpolar will dissolve better in diethyl ether than in the aqueous (polar) phase.
Is 9-fluorenone a solid?
It is bright fluorescent yellow in color and is a solid at room temperature.
Is 9-fluorenone more polar than benzoic acid?
Different solvents would be used because you must consider their relative polarity. benzoic acid is more polar than 9-fluorenone.
Is 9-fluorenone an organic base?
Fluorenone is an aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C13H8O.
Which compound is more polar fluorene or 9-fluorenone?
Fluorenone is more polar than fluorene because of its C=O. bond. Fluorenone's spot will be lower than fluorene because of its "stickness."
Is 9 Fluorenol polar or nonpolar?
a) Fluorene is essentially non-polar. Briefly explain, with respect to atoms that are present and absent in fluorene, and their relative electronegativities, why fluorene is non-polar.
Is 9 Fluorenol an alcohol?
This entity has been manually annotated by the ChEBI Team. Fluorenol is an alcohol derivative of fluorene. In the most significant isomer, fluoren-9-ol or 9-hydroxyfluorene, the hydroxy group is located on the bridging carbon between the two benzene rings.
What functional groups are in 9 Fluorenol?
Fluoren-9-ol is a member of the class of hydroxyfluorenes that is 9H-fluorene substituted by a hydroxy group at position 9 (the non-aromatic carbon). It has a role as an animal metabolite. It is a member of hydroxyfluorenes and a secondary alcohol.
Where is fluorenone found?
Fluorenone is also found in fly ash from municipal incinerators, and in wood smoke and fossil fuel combustion products. If released to the atmosphere, fluorenone will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the ambient atmosphere based on an estimated vapor pressure of 5.7X10-5 mm Hg at 25 °C.
What is the Henry's law constant for fluorenone?
The Henry's Law constant for fluorenone is estimated as 6.8X10-7 atm-cu m/mole (SRC) using a fragment constant estimation method (1). This value indicates that fluorenone will volatilize from water surfaces (2,SRC). Based on this Henry's Law constant, the volatilization half-life from a model river (1 m deep, flowing 1 m/sec, wind velocity of 3 m/sec) is estimated as approximately 73 hours (2,SRC). The volatilization half-life from a model lake (1 m deep, flowing 0.05 m/sec, wind velocity of 0.5 m/sec) is estimated as approximately 530 days (2,SRC). Fluorenone's estimated values for vapor pressure, 5.7X10-5 mm Hg (3,SRC), and Henry's Law constant (1,SRC) indicate that volatilization from dry and moist soil will not be a major fate process for this compound (SRC).
How does fluorenone release to the atmosphere?
Fluorenone's production and use as an intermediate or reagent may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams. Fluorenone is also found in fly ash from municipal incinerators, and in wood smoke and fossil fuel combustion products. If released to the atmosphere, fluorenone will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the ambient atmosphere based on an estimated vapor pressure of 5.7X10-5 mm Hg at 25 °C. Vapor-phase fluorenone is degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically produced hydroxyl radicals with an estimated half-life of about 3 days. An estimated Koc of 2300 suggests that fluorenone will have only slight mobility in soil. Volatilization from dry and moist soil surfaces should not be a major fate process for this compound. Based on limited data, this compound may biodegrade in both soil and water. Groundwater, taken from a gasoline contaminated aquifer, was used to inoculate samples containing fluorenone as the sole carbon source; complete degradation was observed by day 11-15. In water, fluorenone is expected to adsorb to sediment and suspended matter based on its Koc value. Fluorenone may volatilize slowly from water surfaces given an estimated Henry's Law constant of 6.8X10-7 atm-cu m/mole. Estimated half-lives for a model river and model lake are 73 and 530 days, respectively. Bioconcentration in aquatic organisms may occur based on an estimated BCF value of 310; fluorenone has been detected in samples of catfish and snails. The general population may be exposed to this compound by ingestion of contaminated drinking water and inhalation of aerosols containing fluorenone. (SRC)
What is the koc of fluorenone?
The Koc of fluorenone is estimated as approximately 2300 (SRC), using a measured log Kow of 3.58 (1) and a regression-derived equation (2,SRC). According to a recommended classification scheme (3), this estimated Koc value suggests that fluorenone has only slight mobility in soil (SRC).
How is fluorenone produced?
Fluorenone can be produced by catalytic oxidation of fluorene, or of fluorene fractions in the presence of a quarternary ammonium salt, or by catalytic oxidative cracking (oxicracking) of a suitable aromatic.
What is phenalen-1-one?
UV spectra were reported along with retention data for gas and liquid chromatography. Mutagenic activity was determined in Salmonella typhimurium, using resistance to the purine analogue 8-azaguanine as a genetic marker. Phenalen-1-one was a potent mutagen, while benzo (c)cinnoline was 6-fold less active. Fluoren-9-one was completely inactive as a bacterial mutagen.
Is fluorene polar or nonpolar?
Because carbon and hydrogen have electronegativity values that are not significantly different from one another, it is a non-polar molecule.
Is 9 fluorenone soluble in water?
This is confirmed by the fact that 9-fluorenone is insoluble in water.
Is 9 fluorenone acidic?
9-fluorenone is not acidic or basic in water, and in insoluble in aqueous solutions. The benzoic acid was recovered on acidifying the basic extract. The ethyl 4- aminobenzoate was recovered by adding base to the acid extract. The 9-fluorenone was recovered from the ether solution. Similar Asks.
Why is fluorenone insoluble in water?
So why is fluorenone insoluble in water? Because even though fluorenone is polar (like water), the non-polar aspects of the molecule repel water molecules, making it unavailable for forming a solution with water. And that, class, concludes our lecture for the day on fluorenone!
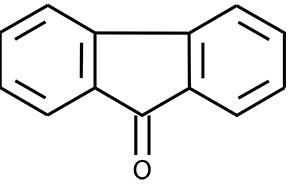
What is the structure of fluorenone?
Fluorenone is an aromatic compound that contains a five-membered ring with a carbonyl group attached and two benzene rings fused on either side. Let's break that down a bit.
What is the functional group of fluorenone?
Since the carbonyl group is bonded to two other carbon atoms, the particular functional group is known as a ketone .
Is fluorenone soluble or insoluble?
If it does, we say that the compound is soluble. If it doesn't, it is insoluble.
Is fluorenone a polar compound?
Since there is an unequal sharing of the electrons between carbon and oxygen, we would say that there is a polar bond between the two, thus making fluorenone overall a polar compound. Even though the molecule is overall polar, it still has some non polar aspects as well, namely the carbon-carbon bonds and carbon-hydrogen bonds. This 'dual nature' is why it is soluble in a wide range of organic solvents.
What is the chemical formula for fluorenone?
Chemical compound. Fluorenone is an aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C 13 H 8 O . It is used to make antimalaria drugs. It can be synthesised from fluorene with the addition of glacial acetic acid and sodium hypochlorite solution, undergoing an oxidation reaction.
What is the CAS number for fluorenone thiosemicarbazone?
According to UBC, the derivative compound fluorenone thiosemicarbazone (CAS number 68279-50-5) can be used to counterbalance androgens. It is used as a fragrance or odor agent in candles .
How to make azafluorenone?
Azafluorenones by one step oxidation and cyclization of the corresponding alcohol which, in turn, can be prepared by Grignard reaction upon 2-bromopyridine-3-carboxaldehyde. Here, Grignard reagents were first prepared from suitably substituted halides in anhydrous diethyl ether. These freshly prepared Grignard reagents were then added to an anhydrous ethereal solution of 2-bromopyridine-3carboxaldehyde at 0 °C which yielded Heck precursors quantitatively. Alcohol was then subjected to cyclization under Heck reaction conditions in good yield.
When was the first azafluorenone synthesized?
In 1949 , Petrow and co-workers reported the first synthesis of an azafluorenone.
How many aromatic rings does 9 fluorenone have?
I would argue differently from Mike. 9-fluorenone has one polar C = O bond, but it also has two aromatic rings. Dispersion interactions are strong for such aromatic rings, and the point can be made that this factor will drive the solvation of 9-fluorenone in hexane.
Is a molecule with more than 6 carbons polar?
This is a very general rule and doesn't work in all circumstances. Thus, this molecule is not as polar.
Is 9 fluorenone soluble in water?
This is confirmed by the fact that 9-fluorenone is insoluble in water.