What are the five steps of glycolysis?
The Energy-Requiring Phase of Glycolysis
- In the first step of glycolysis, a phosphate group is transferred from ATP to glucose, creating glucose-6-phosphate.
- During step two of glycolysis, glucose-6-phosphate is converted into fructose-6-phosphate by the enzyme phosphoglucomutase.
- A second ATP molecule is used to phosphorylate fructose-6-phosphate, producing fructose-1,6-bisphosphate.
What is the net ATP production in glycolysis?
Glycolysis, the first process in cell respiration, produces four ATP, but it uses two of the ATP molecules, therefore producing a net two ATP molecules. The process also yields two molecules of NADH. Glycolysis begins with glucose and breaks it down into two molecules of phosphoglyceraldehyde. This process utilizes two molecules of ATP for energy. Next, the phosphoglyceraldehyde molecules are converted into two molecules of pyruvate, which also produces four ATP molecules.
What does NADH transport?
- NAD refers to both NAD+ and NADH
- NAD is important in energy production and powers your longevity genes
- NAD levels naturally decrease as you age—but there are resources to help!
What does insulin do to glycolysis?
- World's first diabetes app will be able to check glucose levels without drawing a drop of blood and will be able to reveal what a can of coke REALLY does ...
- Olive oil in the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies and intervention trials
- Exercise and Blood Glucose Levels
How many NADH and FADH2 are produced in glycolysis?
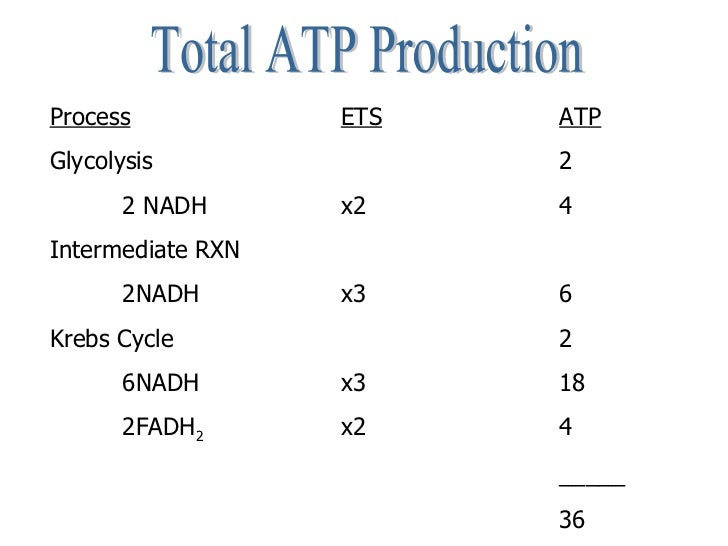
GlycolysisCitric Acid CycleReactantsGlucose 2 ATP 2 NAD+2 acetyl-CoA 6 NAD+ 2 FADProducts2 pyruvate 4 ATP 2 NADH4 CO2 6 NADH 2 FADH2 2 ATPATP required2NoneATP produced422 more rows
How many NADH are produced by glucose?
two moleculesGlycolysis: Glucose is split into two molecules called pyruvate and 2 ATP molecules are generate per molecule of glucose as well as 2 molecules of NADH.
How many NADH are produced during glycolysis quizlet?
How many NADH are produced by glycolysis? Two NADH molecules are produced by glycolysis.
How many ATP and NADH are produced during glycolysis?
During glycolysis, glucose ultimately breaks down into pyruvate and energy; a total of 2 ATP is derived in the process (Glucose + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 Pi --> 2 Pyruvate + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2 ATP + 2 H2O).
Does glycolysis produce NADH?
1: Glycolysis produces 2 ATP, 2 NADH, and 2 pyruvate molecules: Glycolysis, or the aerobic catabolic breakdown of glucose, produces energy in the form of ATP, NADH, and pyruvate, which itself enters the citric acid cycle to produce more energy.
How many NADH are produced in each step of cellular respiration?
Each turn of the cycle forms three NADH molecules and one FADH2 molecule. These carriers will connect with the last portion of aerobic respiration to produce ATP molecules. One GTP or ATP is also made in each cycle.
How many ATP and NADH are produced during glycolysis quizlet?
During glycolysis, one glucose molecule is split into two pyruvate molecules, using 2 ATP while producing 4 ATP and 2 NADH molecules.
How many NADH are produced by TCA?
3 moleculesIn one turn of the Krebs cycle, 3 molecules of NADH are produced.
How many FADH2 are in glycolysis?
FADH2Summary: the three stages of Aerobic RespirationGlycolysisCitric acid cycleElectron transport chainCytoplasmMitochondriaMitochondriaBreaks down Glucose to PyruvateTurns Pyruvate into CO2Converts NADH and FADH2 into ATP2 ATP 2 NADH2 ATP 6 NADH 2 FADH232 ATP
How does glycolysis produce 2 NADH?
As a result, there is a net gain of two ATP molecules during glycolysis. During this stage, high-energy electrons are also transferred to molecules of NAD+ to produce two molecules of NADH, another energy-carrying molecule. NADH is used in stage III of cellular respiration to make more ATP.
How does 1 NADH produce 3 ATP?
The oxidation of one molecule of NADH thus leads to the synthesis of three molecules of ATP, whereas the oxidation of FADH2, which enters the electron transport chain at complex II, yields only two ATP molecules.
Does glycolysis produce 2 or 4 ATP?
During glycolysis, one glucose molecule is split into two pyruvate molecules, using 2 ATP while producing 4 ATP and 2 NADH molecules.
What are the steps of glycolysis?
The energy‐yielding steps of glycolysis involve reactions of 3‐carbon compounds to yield ATP and reducing equivalents as NADH. The first substrate for energy production is glyceraldehyde‐3‐phosphate, which reacts with ADP, inorganic phosphate, and NAD in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme glyceraldehyde‐3‐phosphate dehydrogenase:
How does NAD regenerating occur?
The simplest way of regenerating NAD is simply to transfer the electrons to the keto group of pyruvate, yielding lactate, in the reaction catalyzed by lactate dehydrogenase. This reaction takes place in animal cells, especially muscle cells, and is carried out by lactic acid bacteria in the fermentation ...
What happens when alcohol dehydrogenase is produced?
Then alcohol dehydrogenase transfers a pair of electrons from NADH to the acetaldehyde, resulting in ethanol. . When ethanol is produced, the reaction of glycolysis becomes: The preceding equation explains some traditional winemaking practices. Grapes with the highest sugar content generally make the best wine.
Why can't phoenol pyruvate tautomerize?
Phosphoenol pyruvate, the product of enolase, is unable to tautomerize to the keto form because of the phosphate group. (Recall from organic chemistry that tautomers are compounds that react as if they were made up of two components, differing only in the placement of a substituent, like a hydrogen atom.)
Why is glycolysis a positive energy balance?
This reaction, which is highly favored thermodynamically, brings glycolysis into positive energy balance because two ATP bonds are made—one from each of the 3‐carbon units from glucose. The overall reaction of glycolysis is therefore: This still leaves one bit of unfinished business.
Where does the glycolytic breakdown of glucose take place?
This reaction takes place in animal cells, especially muscle cells, and is carried out by lactic acid bacteria in the fermentation of milk to yogurt. The formation of lactate oxidizes the two NADH molecules into NAD; therefore, the glycolytic breakdown of one molecule of glucose becomes:
Does liver alcohol dehydrogenase cause alcohol toxicity?
The acetaldehyde produced by liver alcohol dehydrogenase may contribute to short ‐ and long‐term alcohol toxicity. Conversely, different levels of intestinal alcohol dehydrogenase may help explain why some individuals show more profound effects after only one or two drinks than others.