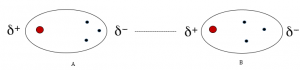How to Identify Dipole-Dipole Forces. Polar molecules contain polar bonds that contain form dipoles. To determine whether a bond is polar, you look at the electronegativity difference between the atoms. If the electronegativity difference is between 0.4 and 1.7, then it is considered to be a polar bond.
What are examples of dipole forces?
- Writer’s samples
- Part-by-part delivery
- Overnight delivery
- Copies of used sources
- Expert Proofreading
How do you identify an ion dipole force?
These include:
- Charge/non-polar interactions
- Dipole-dipole interactions
- Dipole-induced dipole interactions
- Dipole (rotating)/non-polar interactions
- Hydrogen bonds
- Ion-dipole interactions
- Ion-induced dipole interactions
- Ion-ion interactions
- Interactions between two neutral non-polar atoms
What is the difference between dipole and induced dipole?
CONTENTS
- Overview and Key Difference
- What is Induced Dipole
- What is Permanent Dipole
- Side by Side Comparison – Induced Dipole vs Permanent Dipole in Tabular Form
- Summary
What are any practical examples of an electric dipole?
What is the charge of a dipole?
- Thanks.
- Pls up vote.
- Regards. What is the difference between electric dipole moment and magnetic dipole moment? The strength of polarity of bonds can be measured in terms of dipole moment.
How do you know if a molecule is dipole-dipole?
Key PointsA dipole exists when a molecule has areas of asymmetrical positive and negative charge.A molecule's polarity (its dipole) can be experimentally determined by measuring the dielectric constant.Molecular geometry is crucial when working with dipoles.
What molecules have dipole-dipole forces?
Dipole-Dipole Attractions An electric monopole is a single charge, while a dipole is two opposite charges closely spaced to each other. Molecules that contain dipoles are called polar molecules and are very abundant in nature. For example, a water molecule (H2O) has a large permanent electric dipole moment.
What makes something dipole-dipole?
Dipole-dipole forces are attractive forces between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another polar molecule. ... Polar molecules have a partial negative end and a partial positive end. The partially positive end of a polar molecule is attracted to the partially negative end of another.
How do you determine a dipole force?
0:325:36How to Identify the Intermolecular Force a Compound Has - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIf a compound is nonpolar. Then it will have london dispersion forces. Only if a compound is polarMoreIf a compound is nonpolar. Then it will have london dispersion forces. Only if a compound is polar it will have lung dispersion. And dipole dipole.
Which molecules have dipole-dipole forces quizlet?
Dipole-dipole forces occur between polar molecules (i.e., molecules with a permanent dipole).
Which molecule has only dispersion forces with like molecules?
Br2By the way, trick question here: which molecule has the highest boiling point? And since only Br2 is nonpolar, it is the only one with only dispersion forces. H2S is polar, and has dipole-dipole interactions as its dominant intermolecular force.10-Sept-2017
What is molecule dipole?
Dipolar or polar molecules are the molecules that posses an electric dipole. The dipoles of some molecules depend on their environment and can change substantially when they are transferred from one medium to another, especially when molecules become ionized in a solvent.
Do all molecules have dispersion forces?
Dispersion forces are present between all molecules, whether they are polar or nonpolar. Larger and heavier atoms and molecules exhibit stronger dispersion forces than smaller and lighter ones. ... The ease with which the electron distribution around an atom or molecule can be distorted is called the polarizability.
What force holds atoms and molecules together?
covalent bondsThe bonds that hold atoms together to form molecules are called covalent bonds. They are pretty tough and not easily made or broken apart. It takes energy to make the bonds and energy is released when the bonds are broken.15-Oct-2013
How can you tell the difference between dipole-dipole and dispersion?
The main difference between dipole-dipole and London dispersion forces is that dipole-dipole forces occur among molecules with dipole moment whereas London dispersions occur due to instantaneous dipoles that form in atoms or nonpolar molecules.26-Jan-2017
What is a dipole in biology?
Introduction: A molecular dipole is the sum of all the individual polarized bonds. If a molecule has a strong dipole moment, then it will form strong attractive interactions with other molecules with a dipole moment such as itself.
What is the arrow in a molecular dipole?
This property is important for predicting many molecular properties such as boiling point, melting point, and solubilities. Molecular dipoles are represented by an arrow with a bar. The direction of the arrow represents the orientation of the molecular dipole. The length of the arrow represents the magnitude of the molecular dipole.
Why are carbon-hydrogen and carbon-carbon (C-C) bonds ignored?
HINTS: • The carbon-hydrogen (C-H) and carbon-carbon (C-C) bonds can be generally ignored because they have little or no polarization. This is very helpful for organic molecules where these two bonds make up the highest percentage of bonds. • For a molecule with a central tetrahedral atom, the only way symmetrically arrange polarized bonds is ...
Can polarized bonds be symmetrically arranged?
The polarized bonds cannot be symmetrically arranged so that the dipoles of the individual polarized bonds cancel out. For example, all the molecules above have polarized bonds. However, the bonds are arranged symmetrically in two of the examples so that there is no net dipole.
How do dipole-dipole interactions work?
To understand the nature of dipole-dipole interactions, remember that when two atoms with different electronegativities are connected, we have a polar covalent bond, and the shared electron pair of the covalent bond is not in the middle of the two atoms. There is a higher density towards the more electronegative element and as a result, both elements have partial charges. Mainly, the more electronegative atom bears a partial negative, and the other atom has a partial positive charge which are indicated by the delta plus (δ+) and delta minus (δ-) symbols:
How to find the direction of polarity in a bond?
The direction and magnitude of polarity in a bond are given by the dipole moment which is indicated by an arrow. The arrow starts from the less electronegative element and points toward the more electronegative element as shown above.
What happens when hydrogen atoms are connected to the more electronegative oxygen atoms?
What happens is that the hydrogen atom connected to the more electronegative oxygen atom bears a partial positive charge (δ+) because of the oxygen pulling the electron density through induction. This δ+ then interacts with a lone pair of the more electronegative oxygen atom of another molecule of ethanol.
What type of interaction occurs when hydrogen bonds to an electronegative atom?
Hydrogen bonding is another type of intermolecular electrostatic interaction that occurs between a hydrogen atom bonded to an electronegative atom such as O, N, or F, is attracted to a lone pair of electrons on an atom in another molecule.
What color is the electron density of a polar covalent bond?
The electron density of a polar covalent bond can also be shown with electrostatic maps. These are simply color-coded clouds where the blue usually corresponds to the most electron-deficient, and the red, to the most electron-rich region.
What are the main types of intermolecular interactions responsible for the physical properties of compounds?
Dipole-dipole, London dispersion (also known as Van der Waals) interactions, hydrogen bonding, and ionic bonds are the main types of intermolecular interactions responsible for the physical properties of compounds. All of them are electrostatic interactions meaning that they all occur as a result of the attraction between opposite charges ...
What is the weakest intramolecular interaction?
These are the weakest intramolecular interactions and occur as an electrostatic interaction of temporary dipole moments formed in the molecule right at the time when they get in a close enough distance.