Aggregate supply
In economics, aggregate supply (AS) or domestic final supply (DFS) is the total supply of goods and services that firms in a national economy plan on selling during a specific time period. It is the total amount of goods and services that firms are willing and able to sell at a given price level in an …
What is the formula for aggregate supply?
Mar 12, 2020 · The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical because in the long run, changes in the price level do not affect potential GDP, as potential GDP depends on the size of the labor force, capital stock, and technology.
What shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve?
Dec 26, 2021 · The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical because in the long run wages are flexible. The level of output that the economy would produce if all prices, including nominal wages, were fully flexible is called: -potential GDP.
What shifts aggregate demand and supply?
Oct 15, 2021 · The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical because, the economy that produces the potential output, is not related to the price level of the products. The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical at the full-employment output level as this amount is produced as and when the prices are fully adjustable.
What is a long term aggregate supply curve?
Dec 21, 2021 · The long-run aggregate supply curve is perfectly vertical, which reflects economists’ belief that the changes in aggregate demand only cause a temporary change in an economy’s total output. For the short-run aggregate supply, the quantity supplied increases as …
What are the reasons that the aggregate supply curve is vertical in the long run but not in the short run?
The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical because, in the long run, resource prices adjust to changes at the price level, which leaves no incentive for firms to change their output. In the long run, prices and wages have no effect on the aggregate supply curve.May 21, 2021
Why is the long run aggregate supply curve vertical quizlet?
The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical because in the long run wages are flexible. The level of output that the economy would produce if all prices, including nominal wages, were fully flexible is called: -potential GDP.
Why is long run supply curve horizontal?
All firms have identical cost conditions. Hence, in the case of a constant cost industry, the long-run supply curve LSC is a horizontal straight line (i.e., perfectly elastic) at the price OP, which is equal to the minimum average cost. This means that whatever the output supplied, the price would remain the same.
What does a long run vertical as curve imply?
The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical which reflects economists' beliefs that changes in the aggregate demand only temporarily change the economy's total output. In the long-run, only capital, labor, and technology affect aggregate supply because everything in the economy is assumed to be used optimally.
Why is the LRAS curve vertical quizlet?
The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical because in the long run wages are flexible. The level of output that the economy would produce if all prices, including nominal wages, were fully flexible is called: -potential GDP.
Why is the LRAS curve vertical Course Hero?
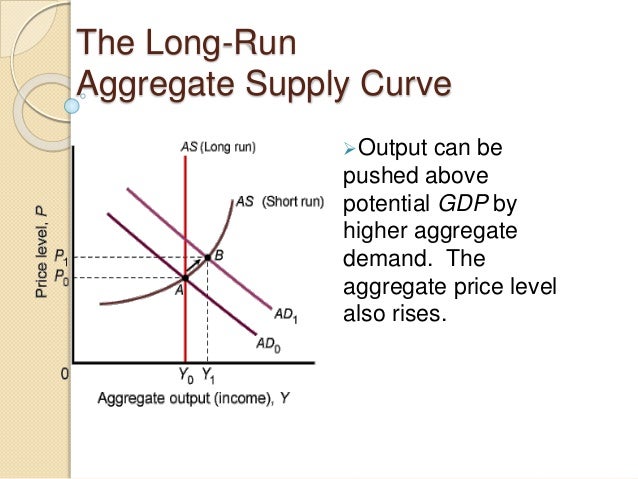
The long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve is a vertical line on a graph of output versus price level, indicating that in the long run, there is a potential level of output from an economy that is independent of price.
When the aggregate supply curve is vertical?
The long-run aggregate supply curve is perfectly vertical, which reflects economists’ belief that the changes in aggregate demand only cause a temporary change in an economy’s total output. In the long-run, there is exactly one quantity that will be supplied.
Why is the LRAS curve perfectly inelastic?
It is actually perfectly inelastic at the full employment level when there is no spare capacity remaining. The change in the elasticity of the AS curve means that the impact of AD shifts will result in differential outcomes for price level and real output.
What causes the LRAS curve to shift left?
The aggregate supply curve shifts to the left as the price of key inputs rises, making a combination of lower output, higher unemployment, and higher inflation possible. When an economy experiences stagnant growth and high inflation at the same time it is referred to as stagflation.
Can LRAS shift left?
The aggregate supply curve can also shift due to shocks to input goods or labor. … In this case, SRAS and LRAS would both shift to the left because there would be fewer workers available to produce goods at any given price.
What LRAS shows?
a curve that shows the relationship between price level and real GDP that would be supplied if all prices, including nominal wages, were fully flexible; price can change along the LRAS, but output cannot because that output reflects the full employment output.
Why is the aggregate supply curve horizontal in the short-run?
In the short run, a firm can only increase labor, but not capital. … Also, as wages are assumed to be static in the short run, increases in labor only result in increased quantity, but not price. This is why the SRAS curve is almost horizontal at this stage.
Why aggregate supply curve is vertical in long run?
Why is the LRAS vertical? The LRAS is vertical because, in the long-run, the potential output an economy can produce isn’t related to the price level. … The LRAS curve is also vertical at the full-employment level of output because this is the amount that would be produced once prices are fully able to adjust.
Why the short-run supply curve is not vertical but the long run aggregate supply curve is vertical?
The short-run aggregate supply curve is an upward slope. The short-run is when all production occurs in real time. The long-run curve is perfectly vertical, which reflects economists’ belief that changes in aggregate demand only temporarily change an economy’s total output.
Can the short-run aggregate supply curve be vertical?
If firms adjusted prices quickly and if sticky prices were the only possible cause for the upward slope of the short-run aggregate-supply curve, then the short-run aggregate-supply curve would be vertical, not horizontal.
What is the short-run aggregate supply curve?
The short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS) lets us capture how all of the firms in an economy respond to price stickiness. … For one, it represents a short-run relationship between price level and output supplied. Aggregate supply slopes up in the short-run because at least one price is inflexible.
What happens when the aggregate supply curve is horizontal?
Aggregate supply curve. … The Keynesian aggregate supply curve shows that the AS curve is significantly horizontal implying that the firm will supply whatever amount of goods is demanded at a particular price level during an economic depression.
What are the factors that can shift the aggregate supply curve?
A shift in aggregate supply can be attributed to many variables, including changes in the size and quality of labor, technological innovations, an increase in wages, an increase in production costs, changes in producer taxes, and subsidies and changes in inflation.