Significance of Turgidity
- It assists in the faction of nutrient solutions from cell to cell. ...
- Turgidity is needed for plant cells to make them keep their position standing. Plant cells that lose a lot of water have less turgor pressure and tend to become flaccid.
- It is fundamental for the development of dissimilar organs.
Why do plant cells become turgid when placed in water?
When the take up water by osmosis they start to swell, but the cell wall prevents them from bursting. Plant cells become "turgid" when they are put in dilute solutions. Turgidity is very important to plants because this is what make the green parts of the plant "stand up" into the sunlight. Click to see full answer.
Are plant cells subject to changes in turgor?
Certainly plant cells are subject to changes in turgor. In life, these turgor changes in a vascular plant can allow the affected cells to perform certain functions for the whole organism. In death (of the whole plant), the amount of remaining turgor is how you can tell how fresh produce is.
What happens to plant cells when they are put in dilute solutions?
Plant cells become "turgid" when they are put in dilute solutions. Turgid means swollen and hard. The pressure inside the cell rises, eventually the internal pressure of the cell is so high that no more water can enter the cell.
How do plants stay upright in hypotonic solution?
A plant cell is turgid when it is placed in a hypotonic solution, which allows it to take in water and swell. The cell wall prevents the cell from bursting, and that is what keeps plants upright. This goon is clearly just uploading their homework this is break of contract with whatever school you go to.
What Is Turgidity?
In biology, turgid refers to cells or tissues that are swollen from water uptake. Turgidity is the phase of being swollen or turgid, exclusively due to high fluid content. Turgidity is a cellular phase in which a plant cell, having absorbed water, is in a phase of tension.
Significance of Turgidity
It assists in the faction of nutrient solutions from cell to cell. This is because of the dissimilarity in the absorption of the cell sap between one cell and the other
Plant turgidity
The cell wall is one of the major elements of a plant cell and it accounts for plant turgidity. The plant cell wall is another layer besieging the cell aside from the plasma membrane. It may be comprised of one or two layers.
Turgid cell
A plasmolyzed plant cell has gaps between the cell wall and the cell membrane. This appears when a plant cell is placed in a hypotonic solution. Water molecules move out of the cell coming from the loss of turgor pressure. A flaccid plant cell is not swollen and the cell membrane does not pressurize against the cell wall tightly.
Flaccid cell
An isotonic solution refers to a solution wherein the solute concentration is comparably the same as the solute concentration inside the cell. This indicates that there would be no net movement of water molecules between the two. A plant cell that is placed in an isotonic solution would become flaccid. This condition is called flaccidity.
Plasmolysed cell
A hypotonic solution is a solution wherein the solute concentration is higher than the solute concentration inside the cell. A plant cell in a hypotonic solution loses its turgor pressure as the water molecules tend to move out of the cell. The cell that has lost its turgor pressure is defined as plasmolyzed.
Importance Of Turgidity
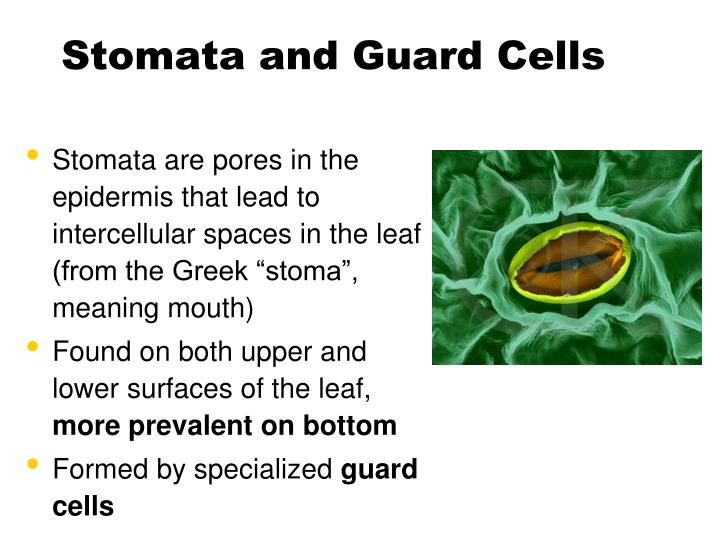
The closing and opening of Stomata are regulated by the turgidity of defender cells. Turgidity is very important for plants and bacteria. It also results in the bursting of a cell. It saves the plants from flaccid.
Why do plants have turgid cells?
Turgid means swollen and hard. The pressure inside the cell rises, eventually the internal pressure of the cell is so high that no more water can enter the cell. This liquid or hydrostatic pressure works against osmosis.
Why is turgidity important to plants?
This liquid or hydrostatic pressure works against osmosis. Turgidity is very important to plants because this is what make the green parts of the plant "stand up" into the sunlight. Turgidity is a characteristic associated with plants. In this condition vacuole of a plant cell intakes water.
What is turgor pressure?
In this condition vacuole of a plant cell intakes water. By doing so the volume of the vacuole increases which ultimately exerts pressure on the walls of the plant cell. This pressure on the plant cell wall exerted by storing water in vacuole is called turgor pressure.
What is turgidity in plants?
Turgidity is a characteristic associated with plants. In this condition vacuole of a plant cell intakes water. By doing so the volume of the vacuole increases which ultimately exerts pressure on the walls of the plant cell.
How does a cell become turgid?
A cell become turgid when osmotic flow of water occour from an area of low solute or high water concentration to an area of high solute or low water concentration. Then a turger pressure is build up against the cell wall, which pushes the plasma membrane against cell wall.
Why does water rush into the cell?
As water tends to enter regions of high concentration of solutes, the water would rush into the cell and the vacuole, a storage compound, would store the water. As the osmotic flow of water is increasing, the vacuole is also increasing in size. The cell becomes turgid when the vacuole cannot hold any more water.
What is the pressure on plant cells that results from the uptake of water called?
The pressure on plant cells that results from the uptake of water is called turgor pressure. As water flows into a plant cell and the cell becomes increasingly firm, or turgid, the increase in turgor pressure may slow the movement of water even if the water concentration hasn’t yet reached equilibrium. 2.5K views.