What happens when you mix cyanoacrylate and cotton?
Cyanoacrylate and cotton react because cotton is made up primarily of cellulose. As you can see from the structure on the right, cellulose has many hydroxyl (OH-) groups which initiate the polymerisation reaction. Only a trace amount is needed for the reaction to occur.
How do acids affect cyanoacrylates?
The type of acid also affects cyanoacrylates; weak acids inhibit and slow down polymerisation whereas strong acids stop polymerisation completely.
What happens if you put cyanoacrylate on wool?
Heat and occasionally even smoke and fire can be produced when cyanoacrylate adhesives come into contact with natural fibers, particularly cotton and wool. It's recommended not to use cotton or wool gloves when handling the glue, as this can result in severe skin burns.
Can cyanoacrylate glue burn cotton?
Heat and occasionally even smoke and fire can be produced when cyanoacrylate adhesives come into contact with natural fibers, particularly cotton and wool. It's recommended not to use cotton or wool gloves when handling the glue, as this can result in severe skin burns. Leather can also have an exothermic reaction.
Does cyanoacrylate react with cotton?
Super Glue Chemically Reacts with Cotton or Wool to Generate Enough Heat to Start a Fire. Applying Super Glue (cyanoacrylate) to cotton or wool results in a rapid chemical reaction that releases enough heat to cause minor burns, so typically this should be avoided.
Can you use super glue on cotton?
Super glue tends to react with cotton fibers and can easily generate a fire. Unless you want to impress everyone by how quickly you can create a flame in a survival situation, using super glue on cotton should be avoided.
What does cyanoacrylate react with?
Super glue reacts with the traces of amino acids, fatty acids, and proteins in the latent fingerprint and the moisture in the air to produce a visible, sticky white material that forms along the ridges of the fingerprint.
What materials does cyanoacrylate not bond well with?
Such as oily and dirty surfaces, liquids and gases, the following plastics do not adhere to the cyanoacrylate adhesive.Delrin Plastics. Delrin plastics are acetal plastics that go by the brand name Delrin. ... Polypropylene Plastic. ... Teflon Plastic. ... High-Density Polyethylene Plastic. ... Wrapping it up.
Is cyanoacrylate super glue?
Cyanoacrylates—also known as CA glue, ethyl cyanoacrylates, super glues, instant adhesives, or Krazy Glues—are adhesives made from cyanoacrylate esters (most commonly ethyl). These adhesives are primarily characterized by their fast cure time when moisture is present.
What is the best super glue for fabric?
The best option for fabric is Aleene's Original Super Fabric Adhesive. This permanent glue dries quickly and offers a clear, flexible bond on cotton, denim, nylon, linen, elastic, and other cloth types. It can be used to attach various embellishments, too, like beads, sequins, and lace.
Why is the cyanoacrylate monomer so reactive?
Cyanoacrylate and cotton react because cotton is made up primarily of cellulose. As you can see from the structure on the right, cellulose has many hydroxyl (OH-) groups which initiate the polymerisation reaction. Only a trace amount is needed for the reaction to occur.
What causes cyanoacrylate to polymerize?
Cyanoacrylates rapidly polymerize in the presence of water, to be more specific in the presence of (trace amounts) of hydroxide ions. For this reason, super glues typically contain acidic stabilizers to prevent premature polymerization.
Does super glue react with anything?
The molecules of this acrylic resin react on contact with the hydroxyl ions found in water. Because some trace of water can be found on the surface of almost anything, super glue can bond immediately and tightly to almost any object.
What are three advantages and three disadvantages to cyanoacrylate adhesives?
Most cyanoacrylates are one-part systems that cure rapidly at room temperature and provide excellent shear and tensile strength. Disadvantages include joint brittleness, limited gap curing, poor peel strength, poor solvent and temperature resistance, and rapid bonding to skin.
Can you drink from a cup fixed with superglue?
Unfortunately, these chemicals are often not “food-safe,” meaning they should not be used on dishes, cups, or other items used for food and drinks. Most super glues contain cyanoacrylate. The chemical can cause skin irritation and minor stomach upset if ingested.
Why does super glue turn white?
It refers to when excess cyanoacrylate monomers vaporize or become airborne, reacting with moisture in the air. The monomers then cure into small particles that fall onto the area around the bond line. This is the white residue you often see on darker parts bonded with a cyanoacrylate.
Can Gorilla super glue be used on fabric?
You can use Gorilla Glue on fabrics. It is considered a high-strength variant to most glues on the market today for several reasons—one such reason being its durability. Since Gorilla Glue is waterproof, the bond does not wash away after a cycle in your washing machine.
What can I use instead of fabric glue?
The Best Alternatives to Fabric Glue are: Fusible Hem Tape & Fusible Web (Quickly creates a strong and flexible bond)...Contents show Fusible Hem Tape & Web. Fusible Tape Vs Fabric Glue. ... Fabric Glue Stick. Hot Glue Gun. ... Velcro. ... Staples. DIY Fabric Glue.
Does super glue come out in the wash?
Super glue is very easy to spread when it's wet, making the stained area much larger. Don't try and rush the drying process. The high heat of a tumble dryer can set the stain into the fabric if it isn't completely removed in the washing machine.
Which glue is used to stick clothes?
Use on Everyday ItemsBrandFevicrylModel NameFabric Glue (80 Ml) : Pack Of 10Quantity10 mlSuitable ForFabric, cloth, garments, canvasAdhesive TypeLiquid6 more rows
When was cyanoacrylate invented?
Development. Harry Wesley Coover Jr. shortly before being awarded the National Medal of Technology and Innovation in 2010. The original patent for cyanoacrylate was filed in 1942 by the B.F. Goodrich Company as an outgrowth of a search for materials suitable for clear plastic gun sights for the war effort.
What is cyanoacrylate glue?
When added to baking soda ( sodium bicarbonate ), cyanoacrylate glue forms a hard, lightweight adhesive filler. This works well with porous materials that do not work well with the adhesive alone. This method is sometimes used by aircraft modelers to assemble or repair polystyrene parts. It is also used to repair small nicks in the leading edge of wood propeller blades on light aircraft, although this technique is limited to use on aircraft registered in the "experimental" category (composite propellers can be repaired in a similar way using two-part epoxies ). This technique can also be used to fill in the slots in the nut of a guitar so that new ones can be cut. The reaction between cyanoacrylate and baking soda is very exothermic (heat-producing) and also produces noxious vapors.
What glue is used to glue arrows?
Cyanoacrylate is used in archery to glue fletching to arrow shafts. Some special fletching glues are primarily cyanoacrylate repackaged in special fletching glue kits. Such tubes often have a long, thin metal nozzle for improved precision in applying the glue to the base of the fletching and to ensure secure bonding to the arrow shaft.
How long does it take for cyanoacrylate glue to separate?
Without force, however, the glue will spontaneously separate from the skin in time (up to four days). Separation can be accelerated by applying vegetable oil near, on, and around the glue.
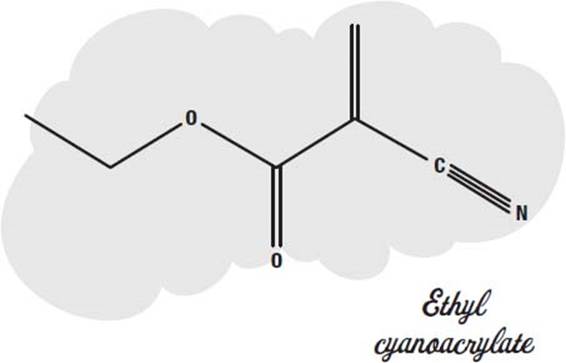
What is the chemical structure of ethyl cyanoacrylate?
Chemical structure of ethyl cyanoacrylate, the precursor to many commercial adhesives. Cyanoacrylates are a family of strong fast-acting adhesives with industrial, medical, and household uses. They are derived from ethyl cyanoacrylate and related esters. The cyanoacrylate group in the monomer rapidly polymerize in the presence ...
How long does cyanoacrylate last?
When kept unopened in a cool, dry location such as a refrigerator at a temperature of about 55 °F (13 °C), the shelf life of cyanoacrylate will be extended from about one year from manufacture to at least 15 months. If the adhesive is to be used within six months, it is not necessary to refrigerate it.
How is cyanoacrylate used in forensics?
Cyanoacrylate is used as a forensic tool to capture latent fingerprints on non-porous surfaces like glass, plastic, etc. Cyanoacrylate is warmed to produce fumes that react with the invisible fingerprint residues and atmospheric moisture to form a white polymer (polycyanoacrylate) on the fingerprint ridges. The ridges can then be recorded. The developed fingerprints are, on most surfaces (except on white plastic or similar), visible to the naked eye. Invisible or poorly visible prints can be further enhanced by applying a luminescent or non-luminescent stain.
Does super glue cause burns?
Super Glue Chemically Reacts with Cotton or Wool to Generate Enough Heat to Start a Fire. Applying Super Glue (cyanoacrylate) to cotton or wool results in a rapid chemical reaction that releases enough heat to cause minor burns, so typically this should be avoided.
Can cyanoacrylate be used in first aid?
However, if enough cyanoacrylate is added to the cotton or wool, the fabric will catch on fire, making this a great trick to keep in mind in survival situations. Generally, cotton and wool are readily available and cyanoacrylate is always a good thing to have on hand in first aid kits, due to its wound sealing ability.
What is the blooming property of cyanoacrylate?
As a fun fact, the blooming property of cyanoacrylate is used in crime labs successfully as latent fingerprint detectors for non-porous surfaces. The white residue created from the reaction of airborne particles of cyanoacrylate and moisture, adhere to latent fingerprints, exposing them under lab conditions.
What causes low bloom cyanoacrylate?
Blooming occurs when un-reacted cyanoacrylate particles (monomers) evaporate, then once airborne, react with surrounding moisture and fall back down in areas surrounding the joint.
Why does super glue bond to glass?
Super glue also bonds badly on glass due to the curing process. A surface insensitive cyanoacrylate is specially formulated to react quicker and in more extreme situations, on active and inactive surfaces, and in very dry climates, with paper, glass or leather substrates.
How to stop blooming glue?
Aside from using a low blooming adhesive, other ways to reduce blooming are by increasing airflow (carrying residue away from the joint), reduce glue areas exposed to air outside the joint (overflows), ensure temperatures and humidity are controlled to midranges and speed up curing times.
What is cyanoacrylate used for?
Medical grade cyanoacrylate topical skin adhesive is used effectively for closing wounds, terme d liquid bandaging. It is also widely used in orthopedic and dental applications.
How long does it take for cyanoacrylate to cure?
What is the average cure time of cyanoacrylate? From 5 up to 90 seconds for a fixture, and from 8 to 24 hours for full curing. The cure time will depend on the surfaces engaged and primarily their moisture absorption qualities, as well as the type of cyanoacrylate used.
What are the different types of cyanoacrylate?
What types of cyanoacrylate are there? The main types of cyanoacrylate are methyl 2-cyanoacrylate, ethyl-2-cyanoacrylate, referred to by the generic term superglue, and n-butyl cyanoacrylate and 2-octyl cyanoacrylate, which are both used in medical applications.
What is the reaction that makes cyanoacrylate?
The synthesis of cyanoacrylate is based on the Knovenagel Reaction [2]. This is the condensation of formaldehyde (methanal) and an alkyl cyanoacetate. In the first step, an enolate is formed from the alkyl cyanide. The resulting enolate anion acts as a nucelophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon on the formaldehyde.
Why are cyanoacrylates not used as herbicides?
This is a new use for cyanoacrylates and as a result, they are currently not used as herbicides on a commercial scale because large doses are required to have the desired herbicidal effect [21]. To wrap up ... Cyanoacrylate is incredibly useful and is found in many areas of the chemical industry.
Why does monomer polymerise?
When made on an industrial scale [3], the monomer polymerises after the condensation reaction because the monomer is extremely reactive in the presence of base. This means that the polymer needs to be cracked and forms a crude mixture of the monomer and bits of the broken-up polymer.
When was cyanoacrylate first used?
Molecule of the Month - July 2009. History of Cyanoacrylate. Cyanoacrylate was first invented in 1949 by Dr Harry Coover [1]. At the time Coover was working for Kodak Laboratories where he was trying to synthesise optically clear plastics for precision gunsights during WWII. He was working with cyanoacrylates that seemed to be promising ...
What happens if the reaction is not terminated?
If the reaction is not terminated the anion exists as a 'living' polymer - this means that should another monomer be introduced into the reaction, the living polymer could propagate further, attack the monomer and lengthen the carbon chain.
What is the reaction that is terminated by the presence of water, air and acidic protons?
The reaction is terminated by the presence of water, air and acidic protons because they react with the nucleophile, effectively quenching the reaction [6]. The type of acid also affects cyanoacrylates; weak acids inhibit and slow down polymerisation whereas strong acids stop polymerisation completely.
Does cottonwool catch fire?
Only a trace amount is needed for the reaction to occur. The reaction is extremely exothermic and more often than not, you'll find that the cotton-wool will catch fire!
What happens when you are exposed to cyanoacrylates?
When exposed to cyanoacrylates, organic or natural materials, such as cotton and wool, experience a rapid exothermic reaction that generates heat and, potentially, smoke that can cause serious burns or smoke inhalation injuries.
How to reduce the risk of cyanoacrylates?
Any associated health risks of using cyanoacrylates can be further reduced by: Performing applications in a well-ventilated or filtered area. Using respiratory and other protective equipment, such as masks, gloves, and goggles. Introducing and maintaining more moisture in the work environment.
What are some examples of tissue bonding?
Here are several examples: Tissue bonding. Cyanoacrylates are able to replace traditional sutures used to close cuts and incisions in emergencies and surgeries. Bonding live coral fragments. Instant adhesives are safe to use in sensitive marine and aquascaping environments to bond coral to walls, rocks, and more, even in sandy environments.
What is cyanoacrylate used for?
Cyanoacrylates—also known as instant adhesives, superglues, and Krazy Glue—are fast curing adhesives used to form adhesive bonds between surfaces, compatible with a wide range of environmental and operating conditions. They are applied with versatility across industries due to their advantageous properties, which include: High adhesive strength.
What are the properties of cyanoacrylates?
They are applied with versatility across industries due to their advantageous properties, which include: High adhesive strength . Cyanoacrylates are able to create a strong adhesive bond even between dissimilar or hard-to-bond materials, including ceramics, engineering plastics, metal, rubber and elastomers, and wood.
Do cyanoacrylates need solvents?
Cyanoacrylates don’t need solvents or multiple bonding components, making them a streamlined option. Despite these and other benefits, some industry professionals have reservations about using cyanoacrylates.
Is cyanoacrylate a toxic substance?
Cyanoacrylates are highly versatile adhesives employed across a wide range of industries. In contrast to common assumptions, they are largely non-toxic and safe to use given the proper precautions and protective equipment are implemented.
Why does a cotton bud get hot?
Since the reaction gives out heat, the cotton bud therefore gets hot (and as it becomes hotter so the reaction goes faster etc), and it may get hot enough to catch fire. Though the monomers in cyanoacrylate glues contain an ester, their polymerization doesn't rely on that ester group directly.
What is cotton wool made of?
In cotton wool, which is made of cellulose, a polymer of sugar molecules, there are lots and lots of hydroxy (-OH or alcohol groups), which can start the reaction in the same way as the water does, only because there are lots of them they can start many more reactions at once.
Does cyanoacrylate polymerize?
The Wikipedia article for cyanoacrylates shows the polymerization more clearly than I can easily explain in words. The many hydroxyl groups in cellulose do start polymerization effectively, and the large surface area of cotton wool provides a large number of sites for the glue to cure.
CarbonCopy
Super glue seems to react with cotton or wool to give smoke and fire. But, why does this happen.
Knumbnuts
I would guess that this is probably the case as the WIKI says it polymerises in the presence of nucleophiles for example, water.
overtone
It doesn't light fire to my cotton T-shirts, canvas jeans, wool gloves, wool hat, kitchen towels, etc.
Phi for All
I really don't like how tightly the camera is pulled in as the cotton catches fire. It suggests to me that an open flame somewhere nearby was applied to provide combustion. I think this video is faked.
CarbonCopy
I really don't like how tightly the camera is pulled in as the cotton catches fire. It suggests to me that an open flame somewhere nearby was applied to provide combustion. I think this video is faked.
Phi for All
There's definitely an exothermic reaction taking place. I'm just skeptical that the first video didn't use something besides glue and cotton to initiate the combustion.
CarbonCopy
There's definitely an exothermic reaction taking place. I'm just skeptical that the first video didn't use something besides glue and cotton to initiate the combustion.
Overview
Uses
Cyanoacrylates are mainly used as adhesives. Thin layers bond effectively, thick layers much less so. They bond many substances, including human skin and tissues, natural fibres, cotton, wool, and leather.
Cyanoacrylate glue has a low shearing strength, which has led to its use as a temporary adhesive in cases where the piece needs to be sheared off later. Co…
Development
The original patent for cyanoacrylate was filed in 1947 by the B.F. Goodrich Company as an outgrowth of a search for materials suitable for clear plastic gun sights for the war effort. In 1942, a team of scientists headed by Harry Coover Jr. stumbled upon a formulation that stuck to everything with which it came in contact. The team quickly rejected the substance for the wartime application, but in 1951, while working as researchers for Eastman Kodak, Coover and a colleagu…
Monomers
In its liquid form, cyanoacrylate consists of monomers of cyanoacrylate ester molecules. Methyl 2-cyanoacrylate (CH2=C(C≡N)COOCH3) has a molecular weight of 111.1 g/mol, a flashpoint of 79 °C (174 °F; 352 K), and a density of 1.1 g/mL. Ethyl 2-cyanoacrylate ((CH2=C(C≡N)COOCH2CH3)) has a molecular weight of 125 g/mol and a flashpoint of more than 75 °C (167 °F; 348 K). To fa…
Safety issues
Cyanoacrylate adhesives may adhere to body parts, and injuries may occur when parts of the skin are torn off. Without force, however, the glue will spontaneously separate from the skin in time (up to four days). Separation can be accelerated by applying vegetable oil near, on, and around the glue. In the case of glued eyelids, a doctor should be consulted.
The fumes from cyanoacrylate are a vaporized form of the cyanoacrylate monomer that irritate t…
Solvents and debonders
Acetone, commonly found as a fraction of nail polish remover (or at hardware stores in pure form), is a widely available solvent capable of softening cured cyanoacrylate. Other solvents include nitromethane, dimethylformamide, dimethyl sulfoxide, and methylene chloride. gamma-butyrolactone may also be used to remove cured cyanoacrylate. Commercial debonders are also available, many based on propylene carbonate.
Shelf life
Cyanoacrylate adhesives have a short shelf life. Date-stamped containers help to ensure that the adhesive is still viable. One manufacturer supplies the following information and advice:
When kept unopened in a cool, dry location such as a refrigerator at a temperature of about 55 °F (13 °C), the shelf life of cyanoacrylate will be extended from about one year from manufacture to at least 15 months. If the adhesive is to be used within six months, it is not necessary to refriger…
Further reading
• derma+flex QS 510k Letter: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf10/K101276.pdf
• LiquiBand 510k Letter: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf8/K083531.pdf
• Fernandez, Tania & Bliskovsky, Val (2 January 2003). "Cyanoacrylate Technology: Stay Glued". test.pharmabiz.com. Retrieved 4 May 2022.